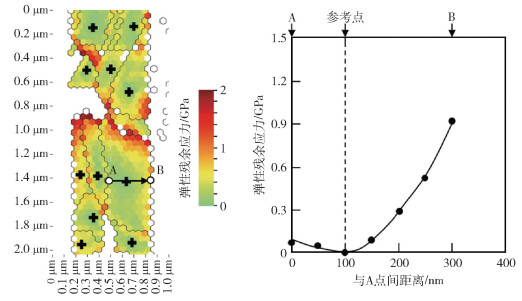
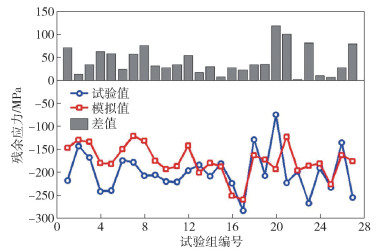
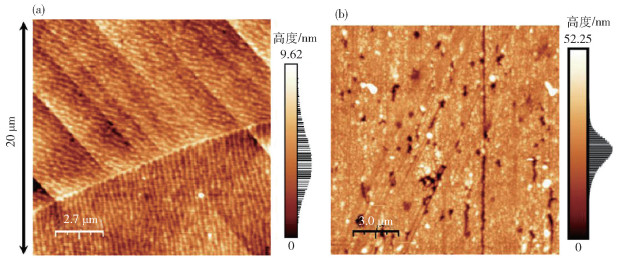
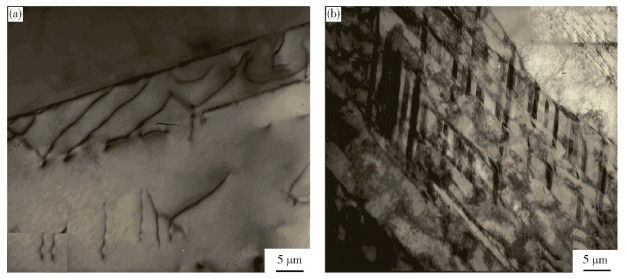
-
摘要: 基于殘余應力測試新方法與先進電化學測試技術的進展, 圍繞殘余應力類型和大小對金屬材料點蝕以及應力腐蝕行為的作用機理進行了總結和歸納. 研究發現, 盡管殘余壓應力對腐蝕行為的抑制作用得到了大量實驗的證實, 但是在不同條件下其作用方式以及機理不盡相同, 并且與材料的結構特點以及腐蝕產物等密切相關. 同時, 殘余拉應力的作用尚不明確, 受到材料類型和其他因素耦合的嚴重影響. 另外, 在某些環境下, 影響腐蝕行為的關鍵是殘余應力梯度或殘余應力的某個臨界值. 但是對有色金屬的研究表明殘余拉應力和壓應力均會導致基體中位錯和微應變等結構缺陷增加, 進而促進點蝕敏感性, 降低材料服役性能. 最后, 對目前研究存在的局限進行了討論和展望.Abstract: It has been generally recognized that the synergistic action of aggressive media and residual stress that arises during metals fabrication, processing, and service can affect the behavior of corrosion electrochemistry. However, due to the limitation of testing techniques, studies on the influence of residual stress and its synergistic effects with other factors on corrosion initiation and propagation are relatively rare and confined to macro levels. With the developments of residual stress measurements and local electrochemical methods, especially the application of localized electrochemical probe techniques, the effect of residual stress on corrosion electrochemical behavior in the micro-domain has been studied by many researchers in recent years. Based on new testing methods of residual stress and advanced electrochemical measurements, this paper mainly summarized the contents and progress of recent research on metallic materials pitting and stress corrosion behavior under different types and levels of residual stresses. For iron and steel materials, the inhibition of compressive residual stress on corrosion has been supported by many experiments, but it shows different roles and mechanisms in different conditions, closely correlating with material structure and corrosion product. In addition, research has demonstrated that tensile residual stress has different impacts on corrosion resistance in alkaline and acidic conditions and that the influence of tensile residual stress on corrosion, strongly influenced by material types and other coupling factors, is still uncertain. Moreover, some experimental results have also shown that residual stress gradient or its critical value is a significant contributor to corrosion behavior, and only when they are greater than a certain value can pitting or micro-cracks be significantly initiated. However, studies on nonferrous metals suggest that both tensile and compressive residual stresses reduce corrosion resistance because they can increase dislocation density and microstrain, and these structural defects increase the occurrence of active sites for pitting corrosion, thereby degrading performance. Finally, the limitations and prospect of current research were also presented in this paper.
-
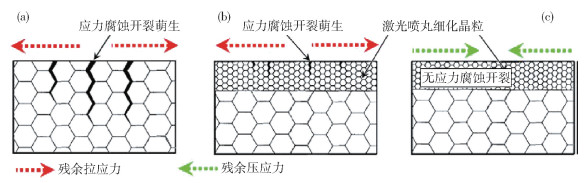
圖 6 晶粒尺寸和殘余應力對應力腐蝕開裂綜合作用示意圖. (a)拉伸應力作用;(b)晶粒細化與拉伸應力綜合作用;(c)晶粒細化和殘余壓應力綜合作用[58]
Figure 6. Schematic illustrations of the combined effect of grain size and residual stress on SCC initiation (RS-residual stress): (a) the negative effect of tensile residual stress; (b) the combined effect of grain refinement and tensile residual stress; (c) the duplicate beneficial effect of grain refinement and compressive residual stress[58]
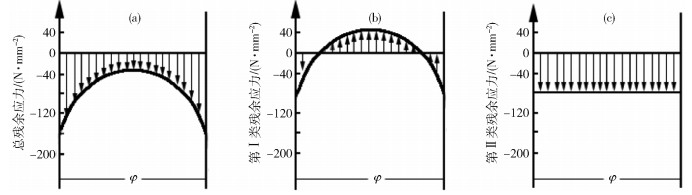
殘余應力類型 作用尺度/μm 典型缺陷 第Ⅰ類殘余應力 >10 宏觀形變 第Ⅱ類殘余應力 0.1~100 析出相 第Ⅲ類殘余應力 < 0.1 空位和間隙 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Gong M. Metallic Corrosion Theory and Corrosion Control. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009龔敏. 金屬腐蝕理論及腐蝕控制. 北京: 化學工業出版社, 2009 [2] Li X G. An Introduction to Corrosion and Protection of Materials. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2017李曉剛. 材料腐蝕與防護概論. 2版. 北京: 機械工業出版社, 2017 [3] Gutman. Mechanical Chemistry and Corrosion Protection of Metals. Beijing: Science Press, 1989古特曼. 金屬力學化學與腐蝕防護. 北京: 科學出版社, 1989 [4] Rao S X, Zhu L Q, Li D, et al. Effects of mechanochemistry to the pitting behaviour of LY12CZ aluminum alloy. J Chin Soc Corros Prot, 2007, 27(4): 228 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4537.2007.04.009饒思賢, 朱立群, 李荻, 等. 力學化學效應對LY12CZ鋁合金點蝕行為的影響. 中國腐蝕與防護學報, 2007, 27(4): 228 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4537.2007.04.009 [5] Gutman E M, Solovioff G, Eliezer D. The mechanochemical behaviour of type 316L stainless steel. Corros Sci, 1996, 38(7): 1141 doi: 10.1016/0010-938X(96)00008-X [6] Xiao J M, Cao C N. Principle of Material Corrosion. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002肖紀美, 曹楚南. 材料腐蝕學原理. 北京: 化學工業出版社, 2002 [7] Meng F J, Wang J Q, Han E, et al. The role of TiN inclusions in stress corrosion crack initiation for Alloy 690TT in high-temperature and high-pressure water. Corros Sci, 2010, 52(3): 928 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010938X09005691 [8] Xue H B, Cheng Y F. Characterization of inclusions of X80 pipeline steel and its correlation with hydrogen-induced cracking. Corros Sci, 2011, 53(4): 1201 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.12.011 [9] Yan Y J, Yan Y, He Y, et al. Hydrogen-induced cracking mechanism of precipitation strengthened austenitic stainless steel weldment. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(5): 2404 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.12.020 [10] Zhang Z B, Obasi G, Morana R, et al. In-situ observation of hydrogen induced crack initiation in a nickel-based superalloy. Scripta Mater, 2017, 140: 40 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.07.006 [11] Shen Z, Arioka K, Lozano-Pereza S. A mechanistic study of SCC in Alloy 600 through high-resolution characterization. Corros Sci, 2018, 132: 244 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018.01.004 [12] Zhou N, Pettersson R, Peng R L, et al. Effect of surface grinding on chloride induced SCC of 304L. Mater Sci Eng A, 2016, 658: 50 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.01.078 [13] Alvarez M G, Lapitz P, Ruzzante J. Analysis of acoustic emission signals generated from SCC propagation. Corros Sci, 2012, 55: 5 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2011.08.014 [14] Masuda H. SKFM observation of SCC on SUS304 stainless steel. Corros Sci, 2007, 49(1): 120 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.05.014 [15] Vignal V, Mary N, Oltra R, et al. A mechanical-electrochemical approach for the determination of precursor sites for pitting corrosion at the microscale. J Electrochem Soc, 2006, 153(9): B352 doi: 10.1149/1.2218762 [16] Oltra R, Vignal V. Recent advances in local probe techniques in corrosion research——Analysis of the role of stress on pitting sensitivity. Corros Sci, 2007, 49(1): 158 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.05.032 [17] Long F Y, Yang Y, Wang S L, et al. Microscale electrochemical measurement technology and its application in corrosion. Corros Sci Prot Technol, 2015, 27(2): 194 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSFJ201502015.htm龍鳳儀, 楊燕, 王樹立, 等. 微區電化學測量技術及其在腐蝕中的應用. 腐蝕科學與防護技術, 2015, 27(2): 194 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSFJ201502015.htm [18] Vieira L, Lucas F L C, Fisssmer S F, et al. Scratch testing for micro-and nanoscale evaluation of tribocharging in DLC films containing silver nanoparticles using AFM and KPFM techniques. Surf Coat Technol, 2014, 260: 205 doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.06.065 [19] Marques A G, Izquierdo J, Souto R M, et al. SECM imaging of the cut edge corrosion of galvanized steel as a function of pH. Electrochim Acta, 2015, 153: 238 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.192 [20] Mouanga M, Puiggali M, Devos O. EIS and LEIS investigation of aging low carbon steel with Zn-Ni coating. Electrochim Acta, 2013, 106: 82 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.05.021 [21] Sim?es A M, Bastos A C, Ferreira M G, et al. Use of SVET and SECM to study the galvanic corrosion of an iron-zinc cell. Corros Sci, 2007, 49(2): 726 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.04.021 [22] Wang F Y, Mao K M, Li B. Prediction of residual stress fields from surface stress measurements. Int J Mech Sci, 2018, 140: 68 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.02.043 [23] Rae W, Lomas Z, Jackson M, et al. Measurements of residual stress and microstructural evolution in electron beam welded Ti-6Al-4V using multiple techniques. Mater Charact, 2017, 132: 10 doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.07.042 [24] Kartal M E, Kiwanuka R, Dunne F P E. Determination of sub-surface stresses at inclusions in single crystal superalloy using HR-EBSD, crystal plasticity and inverse eigenstrain analysis. Int J Solids Struct, 2015, 67-68: 27 doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.02.023 [25] Salvati E, Korsunsky A M. An analysis of macro-and micro-scale residual stresses of Type Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ using FIB-DIC micro-ring-core milling and crystal plasticity FE modelling. Int J Plast, 2017, 98: 123 doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2017.07.004 [26] Withers P J. Residual stress and its role in failure. Rep Prog Phys, 2007, 70(12): 2211 doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/70/12/R04 [27] Song J K, Huang X B, Gao Y K. Test and analysis technology of residual stress. Surf Technol, 2016, 45(4): 75 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJIG199403000.htm宋俊凱, 黃小波, 高玉魁. 殘余應力測試技術分析. 表面技術, 2016, 45(4): 75 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJIG199403000.htm [28] James M N. Residual stress influences on structural reliability. Eng Fail Anal, 2011, 18(8): 1909 doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2011.06.005 [29] Withers P J, Bhadeshia H K D H. Residual stress Part 1-measurement techniques. Mater Sci Technol, 2001, 17(4): 355 doi: 10.1179/026708301101509980 [30] Pan L. Research on the Mechanisms and Related Experiments of Controlling Residual Stress in Carbon Steel based on Pulse Current Method[Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016潘龍. 脈沖電流法調控碳鋼殘余應力的機理及相關實驗研究[學位論文]. 杭州: 浙江大學, 2016 [31] Groth B P, Langan S M, Haber R A, et al. Relating residual stresses to machining and finishing in silicon carbide. Ceram Int, 2016, 42(1): 799 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.179 [32] Niku-Lari A. Residual Stresses. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1987 [33] Huang X F, Liu Z W, Xie H M. Recent progress in residual stress measurement techniques. Acta Mech Solida Sin, 2013, 26(6): 570 doi: 10.1016/S0894-9166(14)60002-1 [34] Wang N, Luo L, Liu Y, et al. Research progress on stress measurement technology for metal components. Chin J Sci Instrum, 2017, 38(10): 2508 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.10.020王楠, 羅嵐, 劉勇, 等. 金屬構件殘余應力測量技術進展. 儀器儀表學報, 2017, 38(10): 2508 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.10.020 [35] Bemporad E, Brisotto M, Depero L E, et al. A critical comparison between XRD and FIB residual stress measurement techniques in thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 572: 224 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2014.09.053 [36] Wang Q M, Sun Y. Research development on the test methods of residual stress. J Mech Electr Eng Mag, 2011, 28(1): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2011.01.003王慶明, 孫淵. 殘余應力測試技術的進展與動向. 機電工程, 2011, 28(1): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2011.01.003 [37] Sun G A, Chen B. The technology and application of residual stress analysis by neutron diffraction. Nucl Tech, 2007, 30(4): 286 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3219.2007.04.012孫光愛, 陳波. 中子衍射殘余應力分析技術及其應用. 核技術, 2007, 30(4): 286 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3219.2007.04.012 [38] Wilkinson A J, Meaden G, Dingley D J. High-resolution elastic strain measurement from electron backscatter diffraction patterns: new levels of sensitivity. Ultramicroscopy, 2006, 106(4-5): 307 doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2005.10.001 [39] Huang Y M, Pan C X. Micro-stress-strain analysis in materials based upon EBSD technique: a review. J Chin Electron Microsc Soc, 2010, 29(1): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2010.01.001黃亞敏, 潘春旭. 基于電子背散射衍射(EBSD)技術的材料微區應力應變狀態研究綜述. 電子顯微學報, 2010, 29(1): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2010.01.001 [40] Sato H, Shishido N, Kamiya S, et al. Local distribution of residual stress of Cu in LSI interconnect. Mater Lett, 2014, 136: 362 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.08.088 [41] Wen S, Dong A P, Lu Y L, et al. Finite element simulation of the temperature field and residual stress in GH536 superalloy treated by selective laser melting. Acta Metall Sin, 2018, 54(3): 393 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB201803005.htm文舒, 董安平, 陸燕玲, 等. GH536高溫合金選區激光熔化溫度場和殘余應力的有限元模擬. 金屬學報, 2018, 54(3): 393 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB201803005.htm [42] Bertali G, Scenini F, Burke M G. The effect of residual stress on the preferential intergranular oxidation of Alloy 600. Corros Sci, 2016, 111: 494 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.05.022 [43] Wu Q, Xie D J, Si Y, et al. Simulation analysis and experimental study of milling surface residual stress of Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al. J Manuf Processes, 2018, 32: 530 doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.03.015 [44] Kayser W, Bezold A, Broeckmann C. EBSD-based FEM simulation of residual stresses in a WC6wt. -%Co hardmetal. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2018, 73: 139 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.12.035 [45] Soltis J. Passivity breakdown, pit initiation and propagation of pits in metallic materials-review. Corros Sci, 2015, 90: 5 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.10.006 [46] Wang Y J, Han X P, Liu Y, et al. Effect of residual stress on corrosion sensitivity of carbon steel studied by SECM. Chem Res Chin Univ, 2014, 30(6): 1022 doi: 10.1007/s40242-014-4099-6 [47] Li M C, Cheng Y F. Corrosion of the stressed pipe steel in carbonate-bicarbonate solution studied by scanning localized electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta, 2008, 53(6): 2831 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2007.10.077 [48] Xiong Q R, Liu D X, Zhang G J, et al. Influence of residual tensile stress on stress corrosion behavior of the base metal of X80 pipe//Proceedings of the ASME 2014 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference. Anaheim, 2014: V001T01A073 [49] Xiong Q R, Li W W, Fu A Q, et al. Effect of residual stress on electrochemistry corrosion resistance of X80 UOE pipe. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2012, 41(Suppl 2): 749 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE2012S2180.htm熊慶人, 李為衛, 付安慶, 等. 殘余應力對X80 UOE鋼管耐電化學腐蝕性能的影響. 稀有金屬材料工程, 2012, 41(增刊2): 749 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE2012S2180.htm [50] Trethewey K R, Wenman M, Chard-Tuckey P, et al. Correlation of meso-and micro-scale hardness measurements with the pitting of plastically-deformed Type 304L stainless steel. Corros Sci, 2008, 50(4): 1132 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.11.026 [51] Martin F A, Bataillon C, Cousty J. In situ AFM detection of pit onset location on a 304L stainless steel. Corros Sci, 2008, 50(1): 84 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.06.023 [52] Lai W Y, Xu X, Bai Z Q, et al. Effect of residual tensile stresses on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 304 stainless steel. Mater Mech Eng, 2016, 40(2): 84 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201602024.htm來維亞, 徐欣, 白真權, 等. 殘余拉應力對304不銹鋼電化學腐蝕行為的影響. 機械工程材料, 2016, 40(2): 84 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201602024.htm [53] Vignal V, Mary N, Oltra R, et al. A mechanical-electrochemical approach for the determination of precursor sites for pitting corrosion at the microscale. J Electrochem Soc, 2006, 153(9): B352 doi: 10.1149/1.2218762 [54] Nguyen T T, Bolivar J, Shi Y, et al. A phase field method for modeling anodic dissolution induced stress corrosion crack propagation. Corros Sci, 2018, 132: 146 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.12.027 [55] Nam J Y, Seo D H, Lee S Y, et al. The effect of residual stress on the SCC using ANSYS. Procedia Eng, 2011, 10: 2609 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.04.435 [56] Bai L Y, Jiang K B, Gao L, et al. Influence mechanism of residual stress on stress corrosion behavior of welded structure. Hot Work Technol, 2017, 46(21): 168 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201721049.htm白林越, 江克斌, 高磊, 等. 殘余應力對焊接結構應力腐蝕行為影響機理研究. 熱加工工藝, 2017, 46(21): 168 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201721049.htm [57] Toribio J. Role of crack-tip residual stresses in stress corrosion behavior of prestressing steel. Constr Build Mater, 1998, 12(5): 283 doi: 10.1016/S0950-0618(98)00010-5 [58] Lu J Z, Luo K Y, Yang D K, et al. Effects of laser peening on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of ANSI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Corros Sci, 2012, 60: 145 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2012.03.044 [59] Wei X L, Zhang C, Ling X. Effects of laser shock processing on corrosion resistance of AISI 304 stainless steel in acid chloride solution. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 723: 237 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.283 [60] Ghosh S, Rana V P S, Kain V, et al. Role of residual stresses induced by industrial fabrication on stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of austenitic stainless steel. Mater Des, 2011, 32(7): 3823 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.03.012 [61] Zhang W Q, Fang K W, Hu Y J, et al. Effect of machining-induced surface residual stress on initiation of stress corrosion cracking in 316 austenitic stainless steel. Corros Sci, 2016, 108: 173 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.03.008 [62] Van Boven G, Chen W, Rogge R. The role of residual stress in neutral pH stress corrosion cracking of pipeline steels. Part Ⅰ: pitting and cracking occurrence. Acta Mater, 2007, 55(1): 29 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2006.08.037 [63] Gravier J, Vignal V, Bissey-Breton S. Influence of residual stress, surface roughness and crystallographic texture induced by machining on the corrosion behaviour of copper in salt-fog atmosphere. Corros Sci, 2012, 61: 162 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2012.04.032 [64] Pandey V, Singh J K, Chattopadhyay K, et al. Influence of ultrasonic shot peening on corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 723: 826 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.310 [65] Chen T, John H, Xu J, et al. Influence of surface modifications on pitting corrosion behavior of nickel-base alloy 718. Part 1: effect of machine hammer peening. Corros Sci, 2013, 77: 230 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.08.007 [66] Zheng Y, Li Y, Chen J H, et al. Effects of tensile and compressive deformation on corrosion behavior of a Mg-Zn alloy. Corros Sci, 2015, 90: 445 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.10.043 [67] Bertali G, Scenini F, Burke M G. The effect of residual stress on the preferential intergranular oxidation of Alloy 600. Corros Sci, 2016, 111: 494 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.05.022 -




 下載:
下載: