-
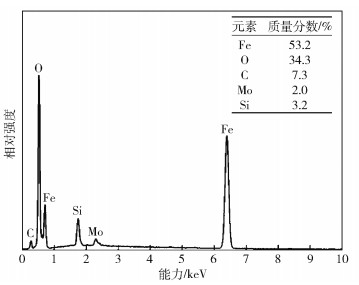
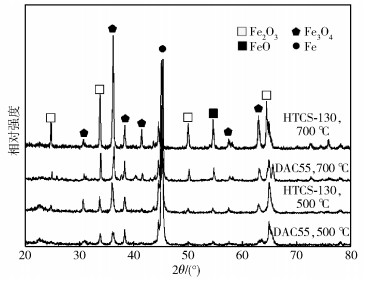
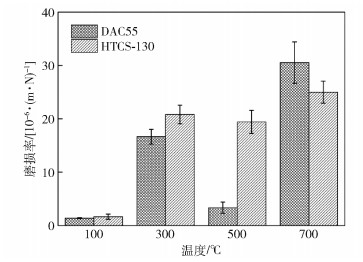
摘要: 采用高溫摩擦磨損試驗機研究了HTCS-130和DAC55兩種熱作模具鋼在100~700℃范圍內的耐磨性差異及磨損機制, 并結合X射線衍射儀(XRD)、掃描電子顯微鏡(SEM)、光學輪廓儀等手段對表面相組成、磨損表面、截面形貌等進行分析. 結果表明: 兩種鋼的磨損率均在100~700℃范圍內呈現先增后減的趨勢; 其磨損機制表現為在100℃和300℃分別發生黏著磨損和黏著-輕微氧化磨損; 500℃時磨損機制轉變為單一氧化磨損, 磨損表面氧化層由FeO、Fe2O3和Fe3O4組成, 亞表面發生輕微軟化并出現塑性變形層; 700℃時磨損進入嚴重氧化磨損階段, 氧化物數量急劇增多, 同時由于馬氏體基體回復導致材料出現嚴重軟化, 磨損表面形成連續的氧化層. HTCS-130鋼優異的熱穩定性能使得基體具有較高硬度和更窄的摩擦軟化區, 能夠更好地支撐氧化層, 從而在700℃下比DAC55鋼更耐磨.Abstract: Owing to work at high temperature and high loadings, hot work die steels wear easily, and are especially susceptible to high temperature oxidative wear. Under severe oxidative wear conditions, the wear rate is high, which may lead to premature wear failure of the dies. Therefore, severe oxidative wear should be limited or avoided during the service life of hot work die steels. For service materials, wear resistance is affected by temperature, load, time on the oxide type, plastic deformation, and debris morphology of the surface and sub-surface. Pioneering researchers tended to focus on the influences of temperature, load, and time on wear resistance, and little is known about the wear mechanism of different materials. In this work, the wear mechanism and resistance differences between two hot work die steels, HTCS-130 and DAC55, were studied at temperatures of 100-700℃, using a high temperature friction and wear tester. Surface phase composition, worn surface and cross-section morphology were analyzed by white-light interferometer, scanning electron microscope (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results show that the wear rates of the two steels both increase at first and then decrease at temperatures of 100-700℃. The wear mechanisms of both steels appeared as adhesive wear at 100℃ and adhesive-oxidative wear at 300℃. Then, the wear mechanism changed into oxidative wear at 500℃ and an oxide layer comprising FeO, Fe2O3, and Fe3O4 was observed on the worn surface. Meanwhile, the subsurface started to soften slightly and a plastically deformed layer appeared. Subsequently, severe oxidative wear occurred at 700℃ and the number of oxides had sharply increased. The materials were severely softened owing to the recovery of the martensite matrix. Meanwhile, a continuous oxide layer formed on the worn surface. Due to the excellent thermal stability of HTCS-130 steel, the high hardness and narrow softened zone of matrix could better support the oxide layer. Therefore, HTCS-130 steel shows better wear resistance than DAC55 steel at 700℃.
-
Key words:
- hot work die steel /
- high temperature wear /
- wear mechanism /
- oxide layer /
- thermal stability
-
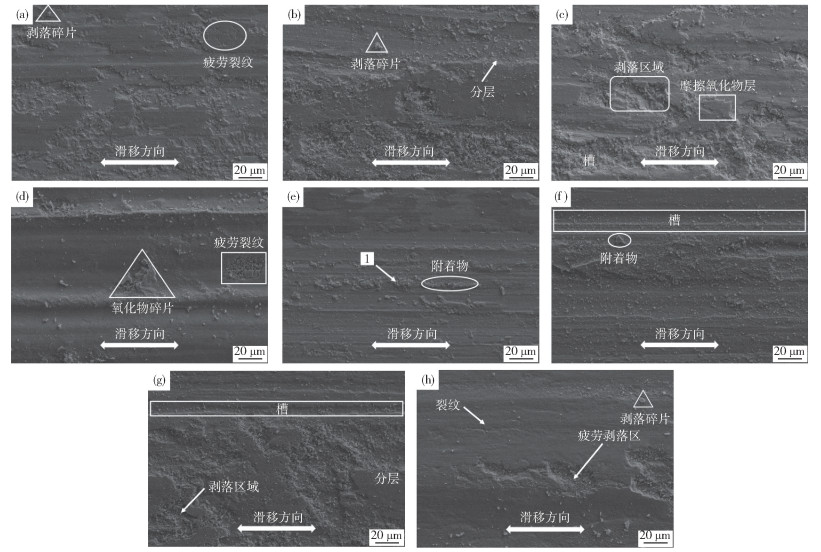
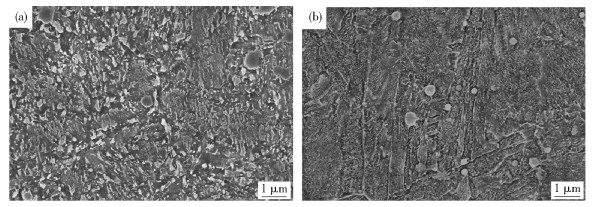
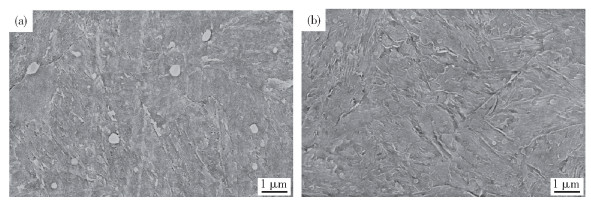
圖 2 DAC55鋼和HTCS-130鋼磨損后表面形貌. (a)100 ℃,DAC55;(b)300 ℃,DAC55;(c)500 ℃,DAC55;(d)700 ℃,DAC55;(e)100 ℃,HTCS-130;(f)300 ℃,HTCS-130;(g)500 ℃,HTCS-130;(h)700 ℃,HTCS-130
Figure 2. Surface morphology of DAC55 steel and HTCS-130 steel after wear: (a) 100 ℃, DAC55; (b) 300 ℃, DAC55; (c) 500 ℃, DAC55; (d) 700 ℃, DAC55;(e) 100 ℃, HTCS-130; (f) 300 ℃, HTCS-130; (g) 500 ℃, HTCS-130; (h) 700 ℃, HTCS-130
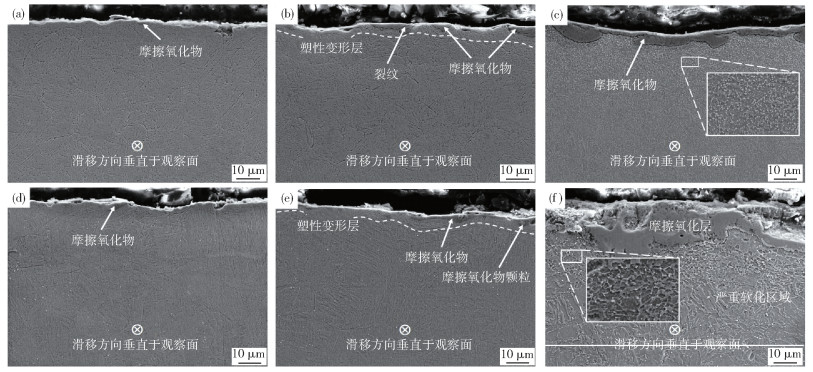
圖 5 DAC55鋼和HTCS-130鋼磨損后截面形貌. (a)300 ℃,DAC55;(b)500 ℃,DAC55;(c)700 ℃,DAC55;(d)300 ℃,HTCS-130;(e)500 ℃,HTCS-130;(f)700 ℃,HTCS-130
Figure 5. Cross-section morphology of DAC55 steel and HTCS-130 steel after wear: (a)300 ℃, DAC55;(b)500 ℃, DAC55;(c)700 ℃, DAC55;(d)300 ℃, HTCS-130;(e)500 ℃, HTCS-130;(f)700 ℃, HTCS-130
表 1 HTCS-130鋼和DAC55鋼的化學成分(質量分數)
Table 1. Table 1Chemical composition of HTCS-130 steel and DAC55 steel?
% 鋼號 C Si Mn Cr Mo Ni V W Co Fe HTCS-130 0.31 0.04 0.05 — 3.70 — — 1.88 — 余量 DAC55 0.35 0.21 0.53 5.06 2.41 0.61 0.77 — 0.65 余量 表 2 HTCS-130鋼和DAC55鋼碳化物類型及含量(質量分數)
Table 2. Types and contents of carbides in HTCS-130 steel and DAC55 steel?
% 鋼種 MC M2C M6C M23C6 總計 HTCS-130 0.82 3.96 1.53 — 6.31 DAC55 — 0.26 — 6.27 6.53 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Guan H, Luo A H. Development and application of a new hot-work die steel for hot stamping. Baosteel Tech Res, 2017, 11(2): 11 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BSTR201702003.htm [2] Chen S H, Li S, Wu X C. High temperature friction and wear property of hot stamping tool steel SDCM. Tribology, 2016, 36(5): 538 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MCXX201605002.htm陳士浩, 李爽, 吳曉春. 熱沖壓模具鋼SDCM高溫摩擦磨損性能. 摩擦學學報, 2016, 36(5): 538 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MCXX201605002.htm [3] Zhou Q C, Wu X C, Shi N N, et al. Microstructure evolution and kinetic analysis of DM hot-work die steels during tempering. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(18): 5696 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.04.024 [4] Karbasian H, Tekkaya A E. A review on hot stamping. J Mater Process Technol, 2010, 210(15): 2103 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.07.019 [5] Stott F H, Glascott J, Wood G C. Models for the generation of oxides during sliding wear. Proc R Soc London Ser A, 1985, 402(1822): 167 doi: 10.1098/rspa.1985.0113 [6] Li S, Chen S H, He X J, et al. A comparison of wear resistance of two types hot-work die steels at high temperature. Tribology, 2017, 37(1): 59 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MCXX201701008.htm李爽, 陳士浩, 何西娟, 等. 兩種熱作模具鋼高溫耐磨性對比研究. 摩擦學學報, 2017, 37(1): 59 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MCXX201701008.htm [7] Wang S Q, Wang L, Zhao Y T, et al. Mild-to-severe wear transition and transition region of oxidative wear in steels. Wear, 2013, 306(1-2): 311 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.08.017 [8] Hardell J, Hernandez S, Mozgovoy S, et al. Effect of oxide layers and near surface transformations on friction and wear during tool steel and boron steel interaction at high temperatures. Wear, 2015, 330-331: 223 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2015.02.040 [9] Anio?ek K, Kupka M, Barylski A. Sliding wear resistance of oxide layers formed on a titanium surface during thermal oxidation. Wear, 2016, 356-357: 23 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2016.03.007 [10] Varga M, Rojacz H, Winkelmann H, et al. Wear reducing effects and temperature dependence of tribolayer formation in harsh environment. Tribol Int, 2013, 65: 190 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2013.03.003 [11] Stott F H. High-temperature sliding wear of metals. Tribol Int, 2002, 35(8): 489 doi: 10.1016/S0301-679X(02)00041-5 [12] Ghiotti A, Sgarabotto F, Bruschi S. A novel approach to wear testing in hot stamping of high strength boron steel sheets. Wear, 2013, 302(1-2): 1319 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.12.051 [13] Wu S, Fu H T, Lian Y, et al. Investigation on high temperature wear behavior of a newly developed hot-work tool steel. Tribology, 2016, 36(1): 104 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MCXX201601018.htm吳帥, 付航濤, 連勇, 等. 一種新型熱作模具鋼的高溫磨損性能研究. 摩擦學學報, 2016, 36(1): 104 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MCXX201601018.htm [14] Yuan X Y, Zhao Y, Chen L Q. Effect of Cr content on high-temperature oxidation behavior of high-manganese austenitic TWIP steel. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 2016, 37(2): 184 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.02.008袁曉云, 趙陽, 陳禮清. Cr含量對高錳奧氏體TWIP鋼高溫氧化行為的影響. 東北大學學報(自然科學版), 2016, 37(2): 184 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.02.008 [15] Quinn T F J. The effect of "hot-spot" temperatures on the unlubricated wear of steel. A S L E Trans, 1967, 10(2): 158 doi: 10.1080/05698196708972175 [16] Cui X H, Wang S Q, Jiang Q C, et al. High-temperature wear mechanism of cast hot-forging die steel 4Cr3Mo2NiV. Acta Metall Sin, 2005, 41(10): 1116 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2005.10.022崔向紅, 王樹奇, 姜啟川, 等. 4Cr3Mo2NiV鑄造熱鍛模具鋼的高溫磨損機理. 金屬學報, 2005, 41(10): 1116 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2005.10.022 [17] Chen K M, Wang S Q, Yang Z R, et al. High temperature wear and oxide film of steels. Tribology, 2008, 28(5): 475 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0595.2008.05.017陳康敏, 王樹奇, 楊子潤, 等. 鋼的高溫氧化磨損及氧化物膜的研究. 摩擦學學報, 2008, 28(5): 475 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0595.2008.05.017 [18] Han Y B, Xue X Y, Zhang T B, et al. Effects of hot compression on carbide precipitation behavior of Ni-20Cr-18W-1Mo superalloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2016, 26(11): 2883 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64417-5 [19] Wei M X, Wang F, Wang S Q, et al. Comparative research on the elevated-temperature wear resistance of a cast hot-working die steel. Mater Des, 2009, 30(9): 3608 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.02.023 [20] Zhang Y B, Luo H, Wang G F. The effect of the microstructure on the wear-resistance in the welding deposited metal. Key Eng Mater, 2007, 353-358: 766 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.353-358.766 [21] Oh H, Lee S, Jung J, et al. Correlation of microstructure with the wear resistance and fracture toughness of duocast materials composed of high-chromium white cast iron and low-chromium steel. Metall Mater Trans A, 2001, 32(3): 515 doi: 10.1007/s11661-001-0068-z [22] Li S, Wu X C, Li X X, et al. High temperature performance of a Mo-W type hot work die steel of high thermal conductivity. Chin J Mater Res, 2017, 31(1): 32 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJB201701005.htm李爽, 吳曉春, 黎欣欣, 等. 鉬鎢系高導熱率熱作模具鋼高溫性能. 材料研究學報, 2017, 31(1): 32 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJB201701005.htm -




 下載:
下載: