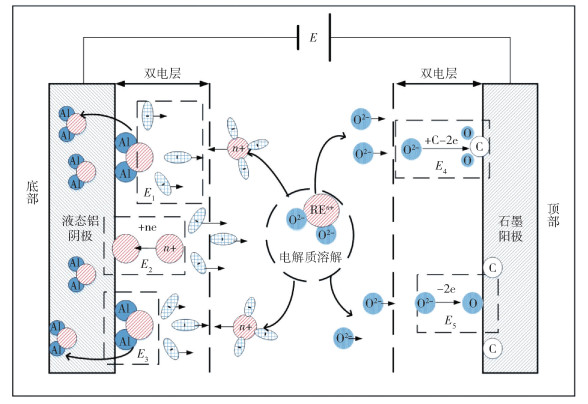
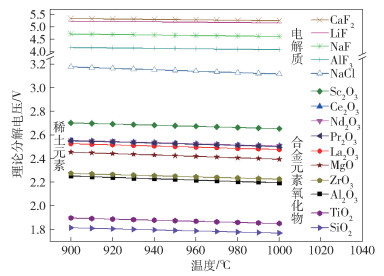
Production of aluminum alloys in electrolysis cells based on Hall-Héroult process: a review
-
摘要: 現代霍爾-埃魯特(H-H)法鋁電解槽規模大、工藝成熟, 利用該法電解制備鋁基合金具有明顯技術和經濟優勢. 目前國內外研究主要是在現有氟化物熔鹽體系中添加多種合金元素氧化物, 合理調節電解質成分和工藝參數, 借助共電沉積和欠電位機制, 成功制備出多種鋁基合金, 工業化試驗亦有初步成果. 本文綜合分析了上述進展及發展前景, 并指出在實現合金組成精準調控、合金產品成分均勻化、電解槽高電流效率運行等方面存在的問題, 旨在為相關研究提供參考.Abstract: Modern large-scale Hall-Héroult (H-H) aluminum electrolysis cells have super high amperage and a well-developed process technology; thus, they present great technical and economic advantages for the production of Al-based alloys. Compared with the traditional alloy production methods, H-H-based processes have a great potential in improving product quality, simplifying production process, and reducing energy consumption. In this review, the major achievements in the production of various common aluminum alloys, such as Al-RE (rare earth metals), Al-Mg, and Al-Si/Ti alloys using H-H-based processes, were summarized from the domestic and international literature. The main properties of cryolite-based electrolyte systems that determine whether the alloy production can proceed smoothly by H-H process were first discussed based on previous research results. Studies on the electrolyte structure, melting point, and conductivity of the cryolite-based electrolytes with varying compositions were described in details. For producing Al-based alloys, the conventional fluorides electrolytes can be modified by adding various oxides of alloying metals. The electrolysis mechanisms of cathode co-deposition and underpotential deposition are usually utilized with the addition of multiple metals oxides, and the electrolyte composition and processing parameters are appropriately adjusted in H-H-based processes. Moreover, the potential distribution in the interfacial reaction processes during electrolysis for the alloying process in electrolyte is proposed based on the existing electrochemical data. In addition, some industrial trials showed promising results for the future development. At present, these trials, especially for Al-Si and Al-Ti alloys, indicate that the contents of alloying elements can be stabilized within a certain range by adjusting electrolyte compositions, current density, feeding cycle, and other parameters. There are, however, problems associated with the accurate control of alloy compositions, the homogenous quality in bulk alloy products, and the electrolysis cell operation with high current efficiency. Further research is needed to address these problems.
-
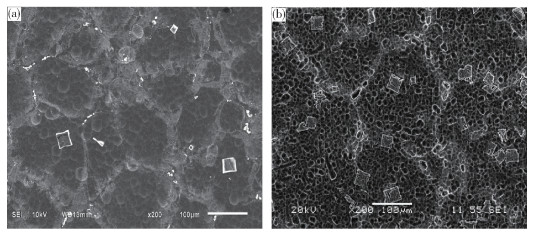
圖 4 Al-Sc合金掃描電鏡圖.(a)Sc質量分數為0.75%;(b)Sc質量分數為0.94%[18]
Figure 4. SEM micrographs of Al-Sc alloys: (a) 0.75% Sc; (b) 0.94% Sc
表 1 部分合金元素金屬氧化物在冰晶石基熔鹽體系中的溶解度
Table 1. Solubility of selected oxides of alloying metals in cryolitic melts
合金元素氧化物 冰晶石基電解質組成(質量分數/%) 溫度/℃ 溶解度/% 參考文獻 MgO 90NaF-NaCl 850 1.2 [22] NaCl-80Na3AlF6 850 1.9 [22] 17.5NaCl-NaF-40Na3AlF6 850 2.1 [22] Nd2O3 LiF-NdF3-BaF2 800~900 7~10 [23] Sc2O3 7LiF-3Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.2) 900~980 3~5 [24] (3~9)ScF3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.1) 950~990 4.01~5.68 [25] (CR=2.4~2.8)Na3AlF6-3MgF2-3CaF2-(1.5~4.5)Al2O3 960~980 1.95~4.75 [26] CeO2 5Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.7) 1040 1.65 [27] Ce2O3 6Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.7) 1000 13.6 [27] La2O3 5Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.7) 1000 14.3 [27] TiO2 3.5Al2O3-Na3AlF6 1020 5.2 [28] SiO2 Na3AlF6 1010 5 [29] CuO (1~9)Al2O3-Na3AlF6 1020 0.13~0.75 [30] Cu2O (0.4~10)Al2O3-Na3AlF6 1020 0.2~0.28 [30] 表 2 Al-RE金屬間化合物標準吉布斯自由能、偏摩爾吉布斯自由能以及欠沉積電位實驗值
Table 2. Experimental values of standard Gibbs free energies, partial molar Gibbs free energies of RE, and underpotential of Al-RE IMC
金屬間化合物 T/K ΔGf?/ (kJ·mol-1) $ \Delta {{\tilde G}_{{\rm{RE}}}}/\left( {{\rm{kJ}} \cdot {\rm{mo}}{{\rm{l}}^{ - 1}}} \right) $ ΔEUPD/V 參考文獻 Al3Sc 723 -150.7 -150.7 0.521 [40] 773 -145.1 -145.5 0.501 Al2Sc 723 -133.3.5 -98.4 0.340 [40] 773 -127.5 -92.4 0.319 AlSc 723 -93.2 -52.9 0.183 [40] 773 -84.1 -40.7 0.141 AlSc2 723 -108.4 -15.3 0.053 [40] 773 -105.0 -21.6 0.075 PrAl11/3 693 -180.65 -180.65 0.624 [49] 723 -179.92 -179.92 0.622 773 -177.66 -177.66 0.614 823 -174.86 -174.86 0.604 Al3Ho 673 -157.6 -157.6 0.544 [50] 723 -155.4 -155.4 0.537 773 -152.8 -152.8 0.528 表 3 H-H法制備鋁基合金工業化實驗數據
Table 3. Industrial experimental data of Al-based alloys prepared by Hall-Héroult based process
合金體系 電解質組成/% 溫度/℃ 電流強度/kA 槽電壓/V 合金元素質量分數/% 電流效率/% 參考文獻 Al-Ce (1~3)Ce2CO3-Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR= 2.35~2.45) 940~950 150 4.25~4.28 5.0~5.5 — [56] Al-Mn Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.9)-MnO2 958 24 5.1 1.0~1.8 82.9 [79] Al2O3-Na3AlF6(CR=2.8~2.9)-MnO2 950 30 4.5~4.6 2.5~2.7 85 [80] Al-Ti Al2O3-Na3AlF6-(0.2~0.5)TiO2 945~955 42 4.48~4.63 0.17~0.52 72~88 [74] Al2O3-Na3AlF6-(0.23~0.25)TiO2 959~963 — 4.13 0.22~0.27 92~93 [10] Al-Si (2~2.5)Al2O3-Na3AlF6-(0.1~0.5)SiO2 960 200 4.03~4.08 <4.38 — [77] Al-Si-Ti Al2O3-Na3AlF6-CaF2-MgF2-(0.87~ 1.47)SiO2-(0.075~0.15)TiO2 — 60 4.5 (4~10)Si- (0.39~0.91)Ti 73.86 [81] 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Grjotheim K. Aluminium Electrolysis: Fundamentals of the Hall-Héroult Process. 3rd Ed. Dusseldorf: Aluminum-Verlag, 2002 [2] Qiu Z X. Prebaked Aluminium. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006邱竹賢. 預焙槽煉鋁. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2006 [3] Liu Y X, Li J. Morden Alumuniun Electrolysis. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2008劉業翔, 李劼. 現代鋁電解. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2008 [4] Tang D X, Liu Y J, Zhang H J. The Rare Earth Metal Materials. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2011唐定驤, 劉余九, 張洪杰. 稀土金屬材料. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2011 [5] Wang X Y, Qiu S T, Zou Z S, et al. Study on steel deoxidation with Al-Ca compound alloy. Chin J Eng, 2017, 39(5): 702 doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2017.05.008王曉英, 仇圣桃, 鄒宗樹, 等. Al-Ca復合合金鋼水脫氧機理的研究. 工程科學學報, 2017, 39(5): 702 doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2017.05.008 [6] Kojima Y. Project of platform science and technology for advanced magnesium alloys. Mater Trans, 2001, 42(7): 1154 doi: 10.2320/matertrans.42.1154 [7] Park G H, Kim J T, Park H J, et al. Development of lightweight Mg-Li-Al alloys with high specific strength. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 680: 116 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.109 [8] Abu-Dheir N, Khraisheh M, Saito K, et al. Silicon morphology modification in the eutectic Al-Si alloy using mechanical mold vibration. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 393(1-2): 109 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.09.038 [9] Xiu Z Y, Chen G Q, Wang X F, et al. Microstructure and performance of Al-Si alloy with high Si content by high temperature diffusion treatment. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2010, 20(11): 2134 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60430-1 [10] Gao X Z, Liu T H, Li J K, et al. Study and practice of making aluminum and titanium alloy by aluminum electrolysis. Light Met, 2006(5): 48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2006.05.012高希柱, 劉同湖, 李景坤, 等. 電解生產鋁鈦合金研究與實踐. 輕金屬, 2006(5): 48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2006.05.012 [11] Yang S, Yang G Q. Production of Aluminum Alloys by Electrolysis. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2010楊昇, 楊冠群. 電解法生產鋁合金. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2010 [12] Chen Y X. Research progress of preparation of rare earth metals by electrolysis in fluoride salt system. Chin Rare Earths, 2014, 35(2): 99 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201402024.htm陳宇昕. 氟化物體系電解稀土氧化物制備稀土金屬研究. 稀土, 2014, 35(2): 99 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201402024.htm [13] Feng N X. Aluminium Electrolysis. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008馮乃祥. 鋁電解. 北京: 化學工業出版社, 2008 [14] Kan H M, Ban Y G, Qiu Z X, et al. Liquidus temperature, density and electrical conductivity of electrolyte for aluminum electrolysis. Chin J Process Eng, 2007, 7(3): 604 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2007.03.034闞洪敏, 班允剛, 邱竹賢, 等. 鋁電解質體系初晶溫度、密度和電導率. 過程工程學報, 2007, 7(3): 604 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2007.03.034 [15] Liu D R, Yang Z H, Li W X, et al. Research on potassium cryolite for low temperature aluminium electrolysis. Light Met, 2009(10): 18 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200910005.htm劉東任, 楊占紅, 李旺興, 等. 鉀冰晶石低溫電解質研究現狀. 輕金屬, 2009(10): 18 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200910005.htm [16] Apisarov A, Dedyukhin A, Redkin A, et al. Physical-chemical properties of the KF-NaF-AlF3 molten system with low cryolite ratio//TMS 2009 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. San Francisco, 2009: 401 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289830397_Physical-chemical_properties_of_the_KF-NAF-ALF3_molten_system_with_low_cryolite_ratio [17] Yang J, Graczyk D G, Wunsch C, et al. Alumina solubility in KF-AlF3-based low-temperature electrolyte system//TMS 2007 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. Orlando, 2007: 537 http://www.osti.gov/energycitations/product.biblio.jsp?osti_id=915006 [18] Liu Q C. Preparation of Al-Sc Alloys by Electrolysis in KF-AlF3-Sc2O3 Melts System[Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2012劉翹楚. KF-AlF3-Sc2O3體系直接電解制備鋁鈧合金基礎研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2012 [19] Liu Q S, Xue J L, Zhu J, et al. Effects of additives on the sodium penetration and expansion of carbon-based cathodes during aluminum electrolysis. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2008, 30(4): 403 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2008.04.015劉慶生, 薛濟來, 朱駿, 等. 添加劑對鋁電解炭基陰極鈉滲透膨脹過程的影響. 北京科技大學學報, 2008, 30(4): 403 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2008.04.015 [20] Tian Z L, Lai Y Q, Yin G, et al. Progress on low temperature aluminium electrolysis. Nonferrous Met (Extract Metall), 2004(5): 26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2004.05.009田忠良, 賴延清, 銀瑰, 等. 低溫鋁電解研究進展. 有色金屬(冶煉部分), 2004(5): 26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2004.05.009 [21] Chen J S, Li D X. Molten salts properties and electrolyte compositions with same solubility of alumina at 20 ℃ above liquidus of aluminium electrolyte for Na3AlF6-AlF3-LiF-MgF2-CaF2 system. Light Met, 2009(1): 22 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200901007.htm陳建設, 李德祥. 鋁電解質Na3AlF6-AlF3-LiF-MgF2-CaF2系初晶溫度上20 ℃的熔鹽性質和等溶成分. 輕金屬, 2009(1): 22 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS200901007.htm [22] Xu H, Liu W P, Dong R, et al. Study on solubility of MgO in melt salt. Nonferrous Met (Extract Metall), 2011(1): 20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2011.01.006徐徽, 劉衛平, 董瑞, 等. 氧化鎂在熔鹽中溶解度的研究. 有色金屬(冶煉部分), 2011(1): 20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2011.01.006 [23] Wu W Y, Sun J Z, Hai L, et al. Solubility of Nd2O3 in fluoride molten salt. Chin Rare Earths, 1991, 12(3): 34 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ199103007.htm吳文遠, 孫金治, 海力, 等. 氧化釹在氟鹽體系中的溶解度. 稀土, 1991, 12(3): 34 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ199103007.htm [24] Guo R, Zhai X J, Zhang T A. Dissolution of Sc2O3 in nNaF·AlF3-LiF molten salt. J Mater Metall, 2008, 7(4): 264 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2008.04.006郭瑞, 翟秀靜, 張廷安. 氧化鈧在冰晶石-氟化鋰體系中的溶解性能. 材料與冶金學報, 2008, 7(4): 264 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2008.04.006 [25] Lu G M, Liu X S. Dissolution of Sc2O3 in fluoride molten salt. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 1999, 9(3): 624 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.1999.03.035路貴民, 劉學山. 氧化鈧在nNaF·AlF3-ScF3熔鹽體系中的溶解. 中國有色金屬學報, 1999, 9(3): 624 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.1999.03.035 [26] Yang S, Li Q, Gu S Q. Solubility of Sc2O3 in nNaF·AlF3-Al2O3 melts. Chin J Rare Met, 2003, 27(3): 418 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2003.03.026楊昇, 李強, 顧松青. 氧化鈧在冰晶石-氧化鋁體系中的溶解性能研究. 稀有金屬, 2003, 27(3): 418 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2003.03.026 [27] Shen X Q, Shen S Y. The influence of valence and properties of rare earth metalls on its solubility in the cryolite-alumina molten salt. Chin Rare Earths, 1990(1): 59 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ199001015.htm沈祥清, 沈時英. 稀土原料的價態與性質對它在冰晶石-氧化鋁系熔體中溶解度的影響. 稀土, 1990(1): 59 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ199001015.htm [28] Jentoftsen T E, Lorentsen O A, Dewing E W, et al. Solubility of some transition metal oxides in cryolite-alumina melts: Part Ⅱ. Solubility of TiO2. Metall Mater Trans B, 2002, 33(6): 909 doi: 10.1007/s11663-002-0074-6 [29] Weill D F. Stability relations in the Al2O3-SiO2 system calculated from solubilities in the Al2O3-Na3AlF6 system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1966, 30(2): 223 doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(66)90109-8 [30] Lorentsen O A, Jentoftsen T E, Dewing E W, et al. The solubility of some transition metal oxides in cryolite-alumina melts: Part Ⅲ. Solubility of CuO and Cu2O. Metall Mater Trans B, 2007, 38(5): 833 doi: 10.1007/s11663-007-9043-4 [31] Lemaire G, Hebant P, Picard G S. DFT analysis of interfacial processes occurring in the first steps of electrodeposition of nickel from chloride melt. J Mol Struct, 1997, 419(1-3): 1 doi: 10.1016/S0166-1280(97)00250-9 [32] Zhou Z Y, Wu B, Dou S S, et al. Thermodynamic properties of elements and compounds in Al-Sc binary system from Ab initio calculations based on density functional theory. Metall Mater Trans A, 2014, 45(4): 1720 doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-2117-9 [33] Ar?kan N, Charifi Z, Baaziz H, et al. Electronic structure, phase stability, and vibrational properties of Ir-based intermetallic compound IrX (X=Al, Sc, and Ga). J Phys Chem Solids, 2015, 77: 126 doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2014.10.007 [34] Baehr H D. Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances. Forsch Ingenieurwes, 1992, 58(4): 103 doi: 10.1007/BF02561491 [35] Knacke O, Kubaschewski O, Hesselmann K. Thermochemical Properties of Inorganic Substances. Forschung im Ingenieurwesen, 1992, 58(4): 103 doi: 10.1007/BF02561491 [36] Barin I, Platzki G. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances. 3rd Ed. Weinheim: VCH Verlag, 1995 [37] Adzic R, Yeager E, Cahan B D. Optical and electrochemical studies of underpotential deposition of lead on gold evaporated and single-crystal electrodes. J Electrochem Soc, 1974, 121(4): 474 doi: 10.1149/1.2401841 [38] Kolb D M, Przasnyski M, Gerischer H. Underpotential deposition of metals and work function differences. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem, 1974, 54(1): 25 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0728(74)80377-3 [39] Castrillejo Y, Bermejo R, Martínez A M, et al. Application of electrochemical techniques in pyrochemical processes-Electrochemical behaviour of rare earths at W, Cd, Bi and Al electrodes. J Nucl Mater, 2007, 360(1): 32 doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2006.08.011 [40] Castrillejo Y, Vega A, Vega M, et al. Electrochemical formation of Sc-Al intermetallic compounds in the eutectic LiCl-KCl. Determination of thermodynamic properties. Electrochim Acta, 2014, 118: 58 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.163 [41] Castrillejo Y, Fernández P, Bermejo M R, et al. Electrochemistry of thulium on inert electrodes and electrochemical formation of a Tm-Al alloy from molten chlorides. Electrochim Acta, 2009, 54(26): 6212 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2009.05.095 [42] Castrillejo Y, Fernández P, Medina J, et al. Electrochemical extraction of samarium from molten chlorides in pyrochemical processes. Electrochim Acta, 2011, 56(24): 8638 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2011.07.059 [43] Bermejo M R, Barrado E, Martinez A M, et al. Electrodeposition of Lu on W and Al electrodes: Electrochemical formation of Lu-Al alloys and oxoacidity reactions of Lu(Ⅲ) in the eutectic LiCl-KCl. J Electroanal Chem, 2008, 617(1): 85 doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2008.01.017 [44] Bermejo M R, Gomez J, Medina J, et al. The electrochemistry of gadolinium in the eutectic LiCl-KCl on W and Al electrodes. J Electroanal Chem, 2006, 588(2): 253 doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2005.12.031 [45] Kononov A, Polyakov E. High-temperature electrochemical synthesis and properties of intermetallic compounds of the Ni-Sc system. Part 1. Electrochemical behaviour of Sc(Ⅲ) in chloride-fluoride melts. J Alloys Compd, 1996, 239(2): 103 doi: 10.1016/0925-8388(96)02209-8 [46] Liu Q C, Xue J L, Zhu J, et al. Preparing aluminium-scandium inter-alloys during reduction process in KF-AlF3-SC2O3 melts//TMS 2012 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. Orlando, 2012: 685 [47] Nohira T, Kambara H, Amezawa K, et al. Electrochemical formation and phase control of Pr-Ni alloys in a molten LiCl-KCl-PrCl3 system. J Electrochem Soc, 2005, 152(4): C183 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10026708479 [48] Ji D B, Yan Y D, Zhang M L, et al. Study on electrochemical behavior of La(Ⅲ) and preparation of Al-La intermetallic compound whiskers in chloride melt. J Electrochem Soc, 2016, 163(2): D1 doi: 10.1149/2.0101602jes [49] Castrillejo Y, Bermejo M R, Arocas P D, et al. The electrochemical behaviour of the Pr(Ⅲ)/Pr redox system at Bi and Cd liquid electrodes in molten eutectic LiCl-KCl. J Electroanal Chem, 2005, 579(2): 343 doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2005.03.001 [50] Castrillejo Y, Bermejo M R, Barrado E, et al. Electrodeposition of Ho and electrochemical formation of Ho-Al alloys from the eutectic LiCl-KCl. J Electrochem Soc, 2006, 153(10): C713 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/239262095_Electrodeposition_of_Ho_and_Electrochemical_Formation_of_Ho-Al_Alloys_from_the_Eutectic_LiCl-KCl [51] Zhang Y X. Study on Preparation and Mechanism of Al-Sc and Mg-Li Based Alloys by Electrolysis in Molten Salt[Dissertation]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2011張艷霞. 鋁鈧與鎂鋰基合金的熔鹽電解制備及機理研究[學位論文]. 哈爾濱: 哈爾濱工程大學, 2011 [52] Chen H H, Chen B X, Lin L J. Preparing Al-Ti-B-RE medium alloys by electrolysis. Jiangxi Nonferrous Met, 2001, 15(4): 15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9669.2001.04.005陳輝煌, 陳本孝, 林立杰. 電解法制取鋁鈦硼中間合金. 江西有色金屬, 2001, 15(4): 15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9669.2001.04.005 [53] Gibilaro M, Massot L, Chamelot P, et al. Study of neodymium extraction in molten fluorides by electrochemical co-reduction with aluminium. J Nucl Mater, 2008, 382(1): 39 doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.09.004 [54] Yu X G, Qiu Z X. Preparation of Al-RE alloy by molten salt electrolysis. Chin Rare Earths, 2006, 27(6): 33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2006.06.008于旭光, 邱竹賢. 熔鹽電解制備稀土鋁合金的研究. 稀土, 2006, 27(6): 33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2006.06.008 [55] Liao C F, Luo L S, Wang X, et al. Preparation for Al-Nd intermediate alloy by molten-salt electrolysis method and its mechanism. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2015, 25(12): 3523 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201512031.htm廖春發, 羅林生, 王旭, 等. 熔鹽電解制備鋁釹中間合金及其機理. 中國有色金屬學報, 2015, 25(12): 3523 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201512031.htm [56] Zhan L. Practice of RE-Al alloys production with pre-baked Al reduction pot. Gansu Metall, 2012, 34(6): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2012.06.010詹磊. 150 kA預焙鋁電解槽生產稀土鋁中間合金生產實踐. 甘肅冶金, 2012, 34(6): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2012.06.010 [57] Pang S M, Yan S H, Li Z A, et al. Development on molten salt electrolytic methods and technology for preparing rare earth metals and alloys in China. Chin J Rare Met, 2011, 35(3): 440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2011.03.022龐思明, 顏世宏, 李宗安, 等. 我國熔鹽電解法制備稀土金屬及其合金工藝技術進展. 稀有金屬, 2011, 35(3): 440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2011.03.022 [58] Li G Y, Yang S H, Li J D, et al. Preparation of Al-Sc alloys by molten salt electrolysis. Light Met, 2007(5): 54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2007.05.015李廣宇, 楊少華, 李繼東, 等. 熔鹽電解法制備鋁鈧合金的研究. 輕金屬, 2007(5): 54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2007.05.015 [59] Guo R, Cao W L, Zhai X J, et al. Preparation of Al-Sc application alloys by molten salt electrolysis method. Chin J Rare Met, 2008, 32(5): 645 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2008.05.021郭瑞, 曹文亮, 翟秀靜, 等. 熔鹽電解法制備Al-Sc應用合金的工藝研究. 稀有金屬, 2008, 32(5): 645 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2008.05.021 [60] Teng G C, Zhai X J, Li J F, et al. Study on preparation of Al-Sc alloys by molten electrolysis. Non-Ferrous Min Metall, 2009, 25(1): 26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2009.01.008縢國春, 翟秀靜, 李俊福, 等. 鋁鈧合金的熔鹽電解法制備研究. 有色礦冶, 2009, 25(1): 26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2009.01.008 [61] Liu Q C, Xue J L, Zhu J, et al. Processing Al-Sc alloys at liquid aluminum cathode in KF-AlF3 molten salt. ECS Trans, 2013, 50(11): 483 doi: 10.1149/05011.0483ecst [62] Yang S. The Research on Direct Electrolytic Al-Sc Alloys in Molten Salt[Dissertation]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2003楊昇. 電解法生產鋁鈧合金的研究[學位論文]. 鄭州: 鄭州大學, 2003 [63] Qian Y. Fundamental Studies on Preparation of Al-Sc-Zr Alloys by Electrolysis in Molten Salts[Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017錢義. 熔鹽電解法制備鋁鈧鋯合金的基礎研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2017 [64] Qian Y, Xue J L, Liu Q C, et al. Preparing Al-Sc-Zr alloys in aluminum electrolysis process//TMS 2013 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. San Antonio, 2013: 1311 [65] Jung J G, Lee S H, Lee J M, et al. Improved mechanical properties of near-eutectic Al-Si piston alloy through ultrasonic melt treatment. Mater Sci Eng A, 2016, 669: 187 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.05.087 [66] Puga H, Barbosa J, Costa S, et al. Influence of indirect ultrasonic vibration on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Al-Si-Cu alloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 560: 589 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.106 [67] Feng H K, Yu S R, Li Y L, et al. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on microstructures of hypereutectic Al-Si alloy. J Mater Process Technol, 2008, 208(1-3): 330 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.121 [68] Qiu Z X, Zhang M J, Wang J, et al. Preparation of aluminum-magnesium master alloys by electrolysis of magnesium oxide in fluoride melts//TMS 1990 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. New Orleans, 1990: 349 [69] Yang S H. Study on Preparation Al-Mg Alloy by Molten Salt Electrolysis Method from Magnesium Oxide[Dissertation]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2008楊少華. 以氧化鎂為原料熔鹽電解法制備Al-Mg合金的研究[學位論文]. 沈陽: 東北大學, 2008 [70] Yang S H, Ban Y G, Guo Y H, et al. Preparation of aluminum-magnesium alloys from magnesium oxide. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 2007, 28(6): 839 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2007.06.020楊少華, 班允剛, 郭玉華, 等. 以氧化鎂為原料生產鋁鎂合金的研究. 東北大學學報(自然科學版), 2007, 28(6): 839 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2007.06.020 [71] Yang S, Wu L, Yang F L, et al. Preparation of aluminum-magnesium alloy from magnesium oxide in RECl3-KCl-MgCl2 electrolyte by molten salts electrolysis method//TMS 2012 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. Orlando, 2012: 63 [72] Qiu Z X, Yu Y X, Zhang M J. Prepare Al-Ti alloy in aluminium reduction cell. Light Met, 1986(4): 32 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS198604006.htm邱竹賢, 于亞鑫, 張明杰. 在鋁電解槽中生產Al-Ti合金. 輕金屬, 1986(4): 32 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS198604006.htm [73] Yu X G, Qiu Z X. Preparation of Al-Ti alloy by electrolysing TiO2 in aluminium bath. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 2004, 25(11): 1088 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX200411019.htm于旭光, 邱竹賢. TiO2電解制取Al-Ti合金. 東北大學學報(自然科學版), 2004, 25(11): 1088 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX200411019.htm [74] Wang M X, Liu Z Y, Song T F, et al. Test of producing low-Ti aluminum alloy by reduction and analysis of Ti distribution uniformity in the product. Light Met, 2003(4): 41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2003.04.013王明星, 劉智勇, 宋天福, 等. 電解生產低鈦鋁合金工業試驗及產品中鈦分布的均勻性分析. 輕金屬, 2003(4): 41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2003.04.013 [75] Fan G X, Wang M X, Liu Z Y, et al. Grain refinement effects of titanium added to commercial pure aluminum by electrolysis and by master alloys. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2004, 14(2): 250 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2004.02.018范廣新, 王明星, 劉志勇, 等. 電解加鈦與熔配加鈦對工業純鋁晶粒細化的作用. 中國有色金屬學報, 2004, 14(2): 250 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2004.02.018 [76] Yu X G, Qiu Z X. Preparation of Al-Si alloy by molten salt electrolysis. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 2004, 25(5): 442 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2004.05.010于旭光, 邱竹賢. 熔鹽電解法制取Al-Si合金. 東北大學學報(自然科學版), 2004, 25(5): 442 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2004.05.010 [77] Ma S L, Xu M, Lin Y S, et al. Research on Al-Si alloy produced from large aluminum reduction cell. Nonferrous Met (Extract Metall), 2011(5): 20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2011.05.005馬紹良, 許敏, 林玉勝, 等. 大型鋁電解槽直接生產鋁硅合金的研究. 有色金屬(冶煉部分), 2011(5): 20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2011.05.005 [78] Yang G Q, Yang S, Yang Q F, et al. A review on production of Al-Si-Ti alloy by electrolysis. Foundry, 1999(4): 51 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-2249.1999.04.018楊冠群, 楊升, 楊巧芳, 等. 電解法生產鋁硅鈦多元合金述評. 鑄造, 1999(4): 51 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-2249.1999.04.018 [79] Zhou R M, Zhang Z M, Wang J N, et al. Direct production of the aluminum-manganese alloy with the addition of the black manganese in industrial aluminum electrolytic cells. J Tangshan Inst Eng Technol, 1988(2): 33 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBLG198802003.htm周瑞銘, 張自銘, 王家乃, 等. 在工業鋁電解槽中添加氧化錳直接生產鋁-錳合金. 唐山工程技術學院學報, 1988(2): 33 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBLG198802003.htm [80] Yin Y J, Chen F H, Wen C Z. Industrial test of preparing Al-Mn alloy by electrolysis. Jiangxi Metall, 1988, 9(3): 43 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXYE198803019.htm尹英健, 陳芳華, 溫承志. 電解法制取鋁錳合金工業試驗研究. 江西冶金, 1988, 9(3): 43 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXYE198803019.htm [81] Huang Y K, Xiao H Z, Peng D Q. Industrial test of preparing Al-Si-Ti alloy by electrolysis. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 1995, 5(2): 75 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ502.018.htm黃英科, 肖輝照, 彭德泉. 電解法直接制取Al-Si-Ti合金工業試驗. 中國有色金屬學報, 1995, 5(2): 75 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ502.018.htm [82] Liao C F, Luo L S, Wang X. Preparation of Al-Cu intermediate alloy by molten-salt electrolytic. Nonferrous Met Sci Eng, 2015, 6(3): 1 https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10407-1016244374.htm廖春發, 羅林生, 王旭. 熔鹽電解法制備Al-Cu中間合金. 有色金屬科學與工程, 2015, 6(3): 1 https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10407-1016244374.htm [83] Tang H. Study on Preparation of Al-Cu-Y Intermediate Alloy and Electrochemical Mechanism by Molten Salt Electrolysis[Dissertation]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2016湯浩. 熔鹽電解法制備Al-Cu-Y中間合金及電化學機理研究[學位論文]. 贛州: 江西理工大學, 2016 [84] Luo L S. Research on Mechanism and Preparation of Al-Cu-Nd Alloy by Molten Salt Electrolysis[Dissertation]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2015羅林生. 熔鹽電解法制備Al-Cu-Nd三元合金及機理研究[學位論文]. 贛州: 江西理工大學, 2015 -




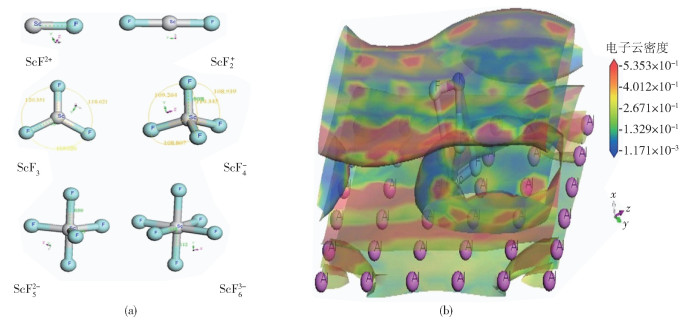
 下載:
下載: