Damage and fracture behavior of a metal sheet under in-plane compression–shear deformation
-
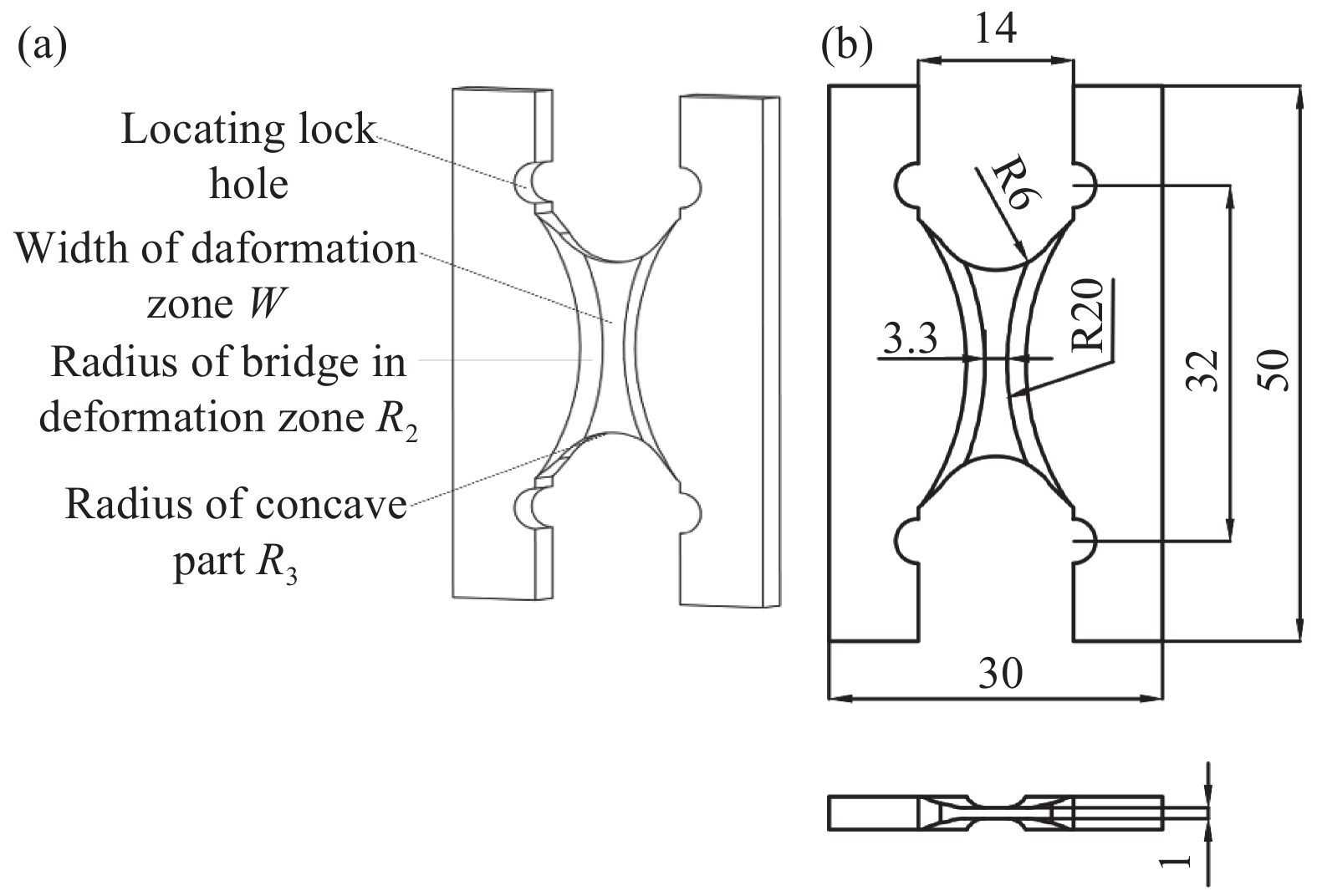
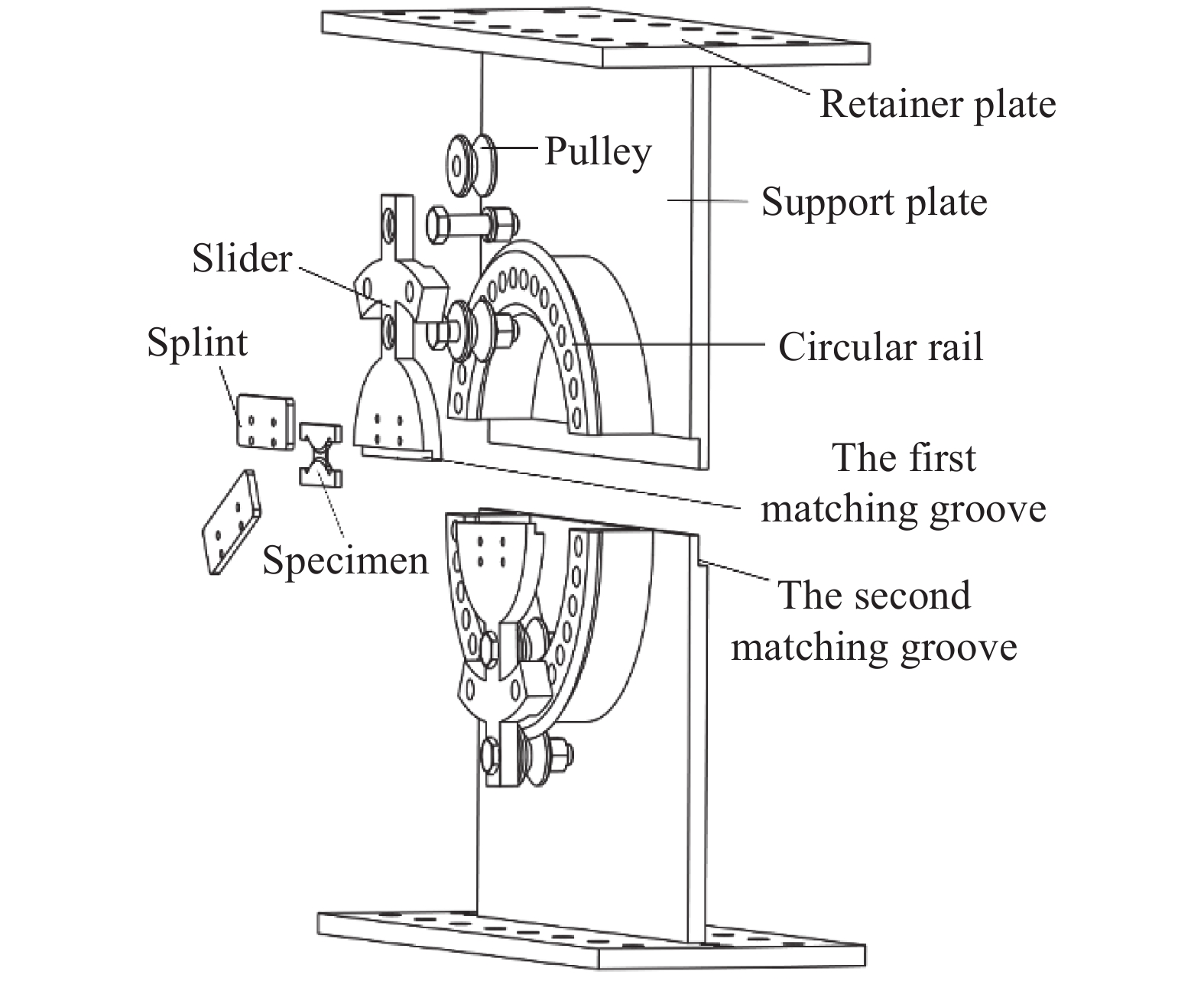
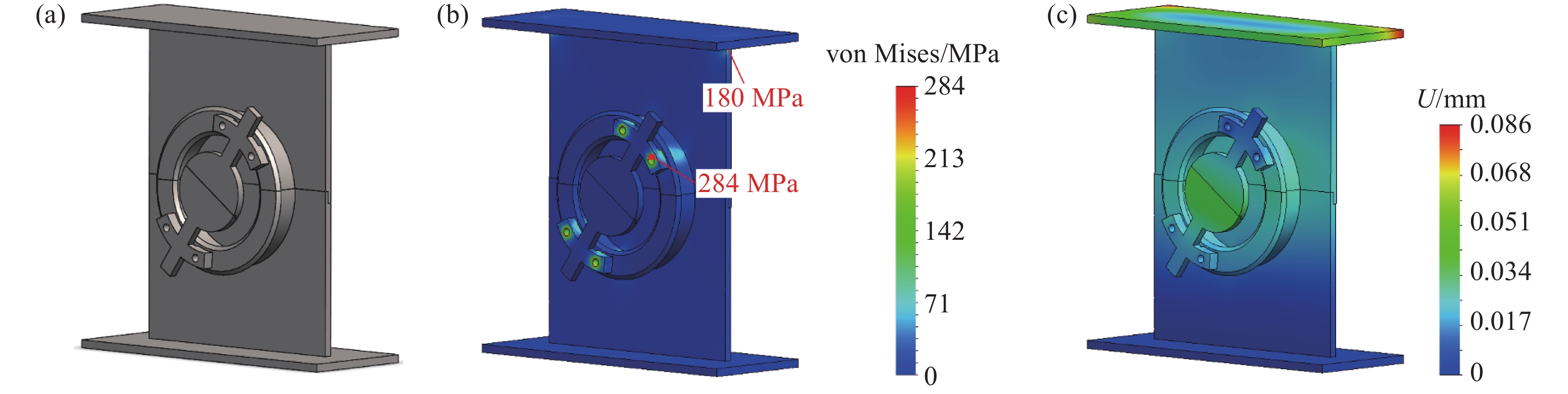
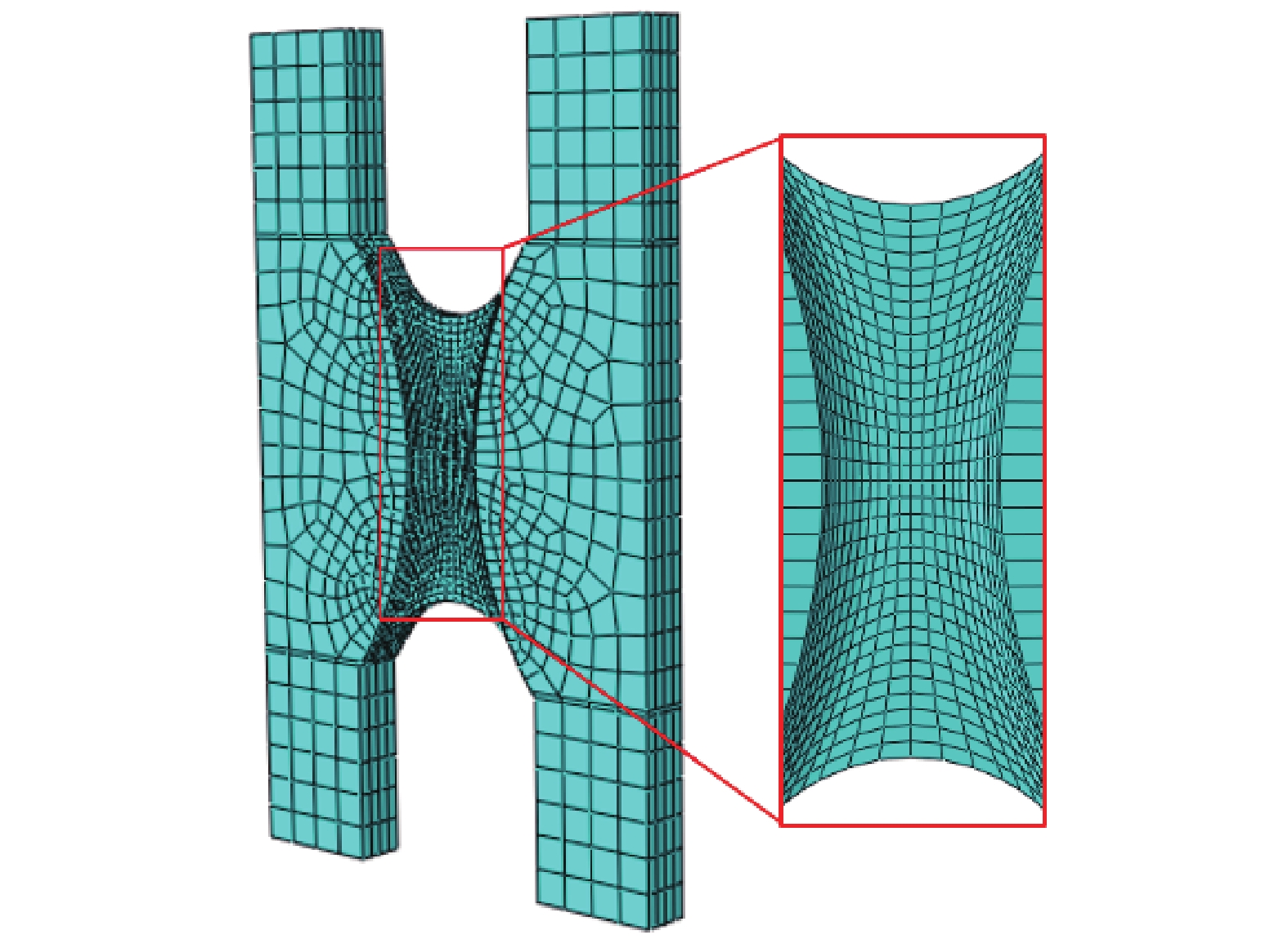
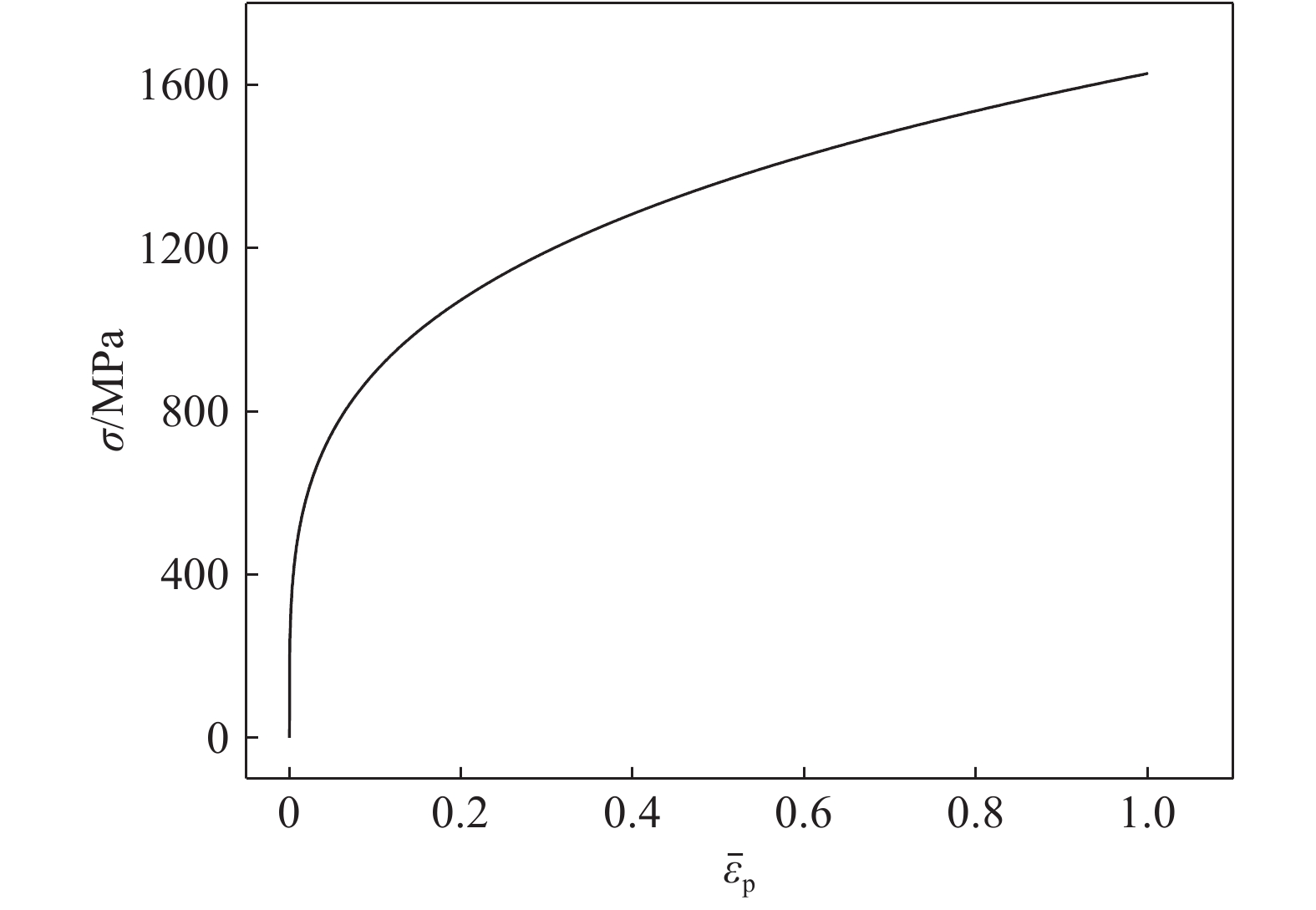
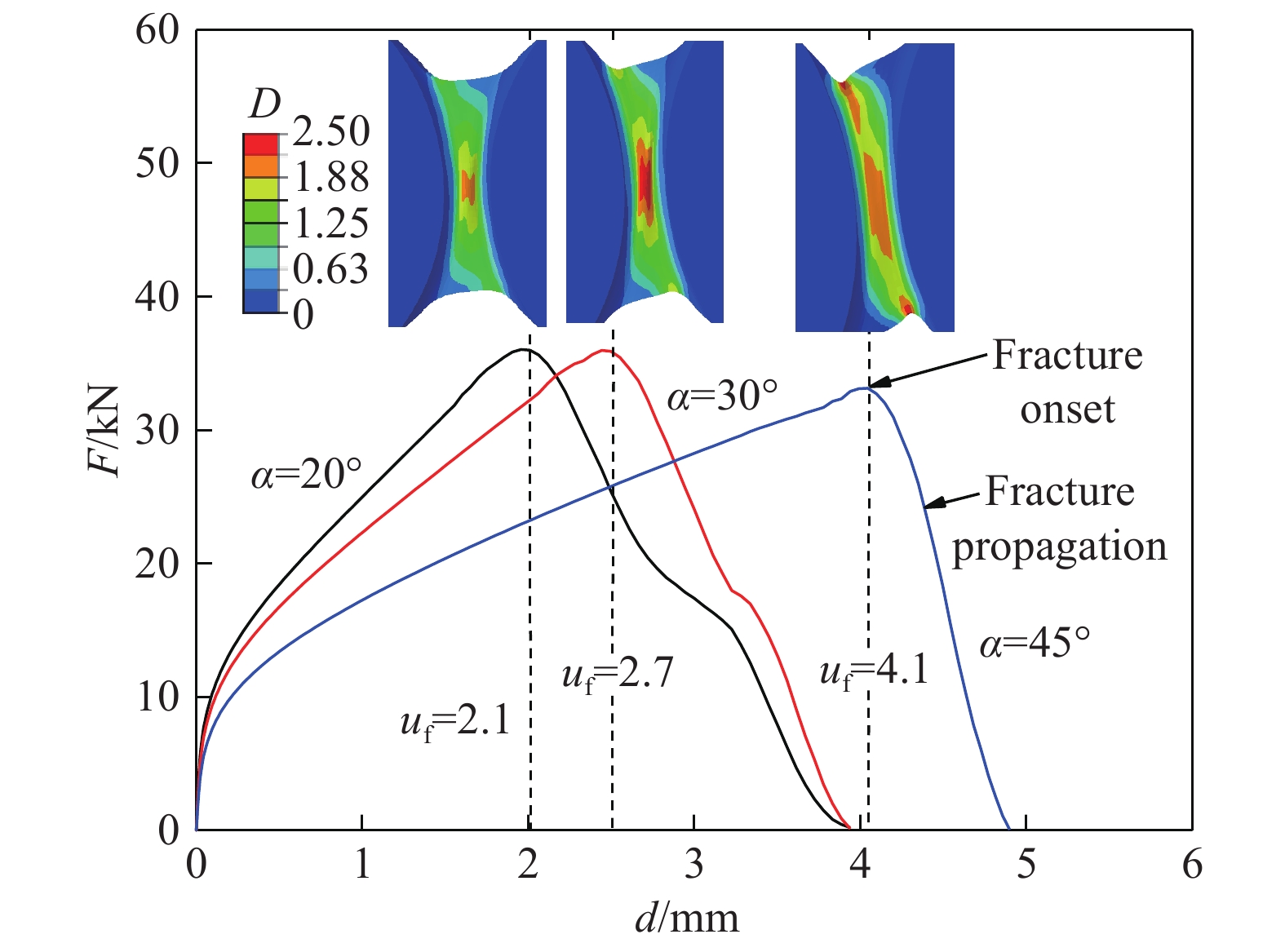
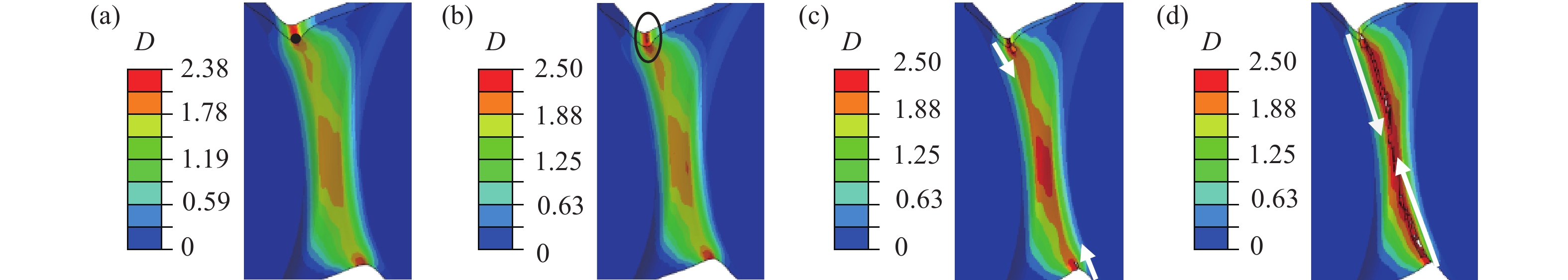
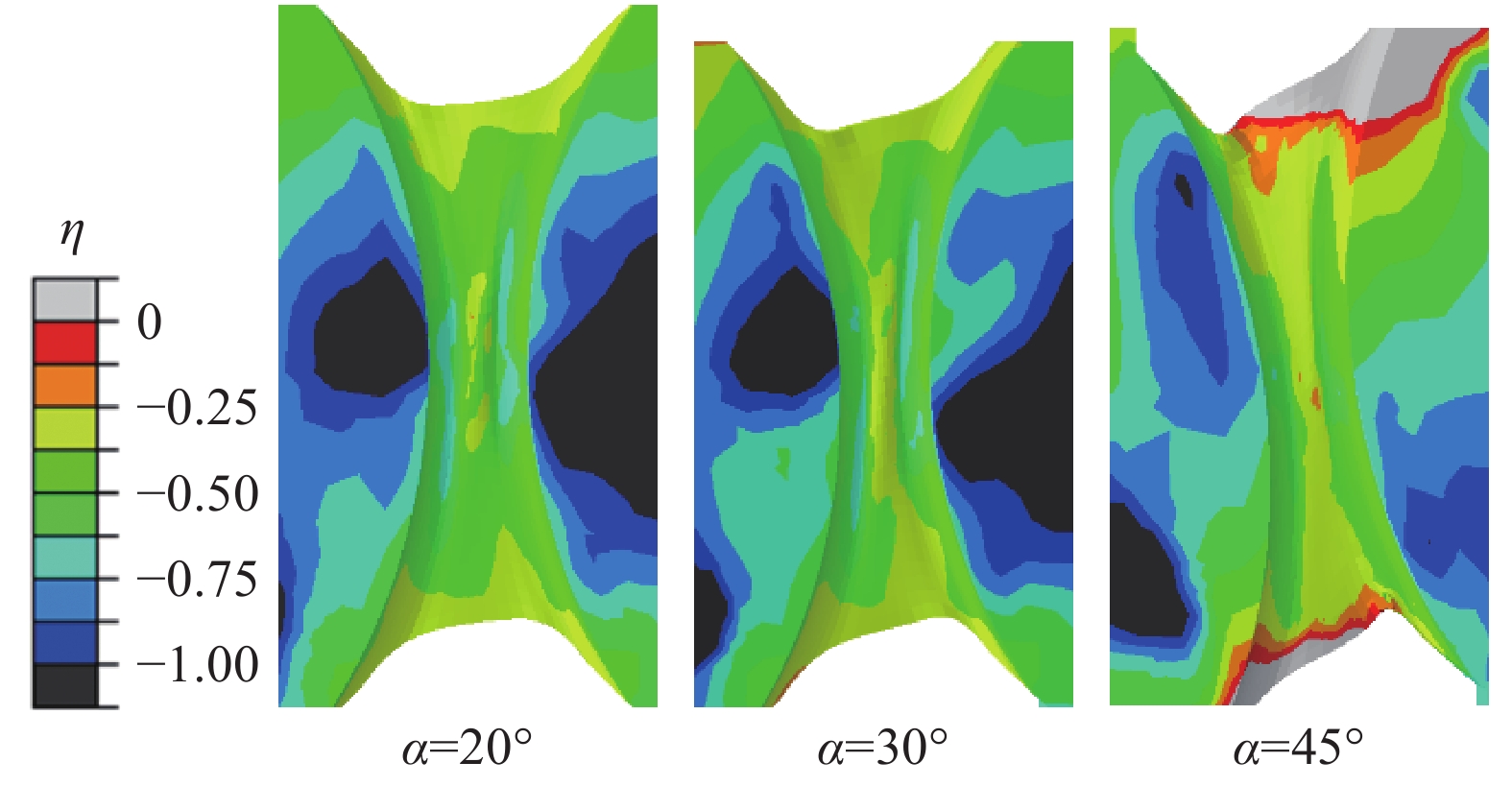
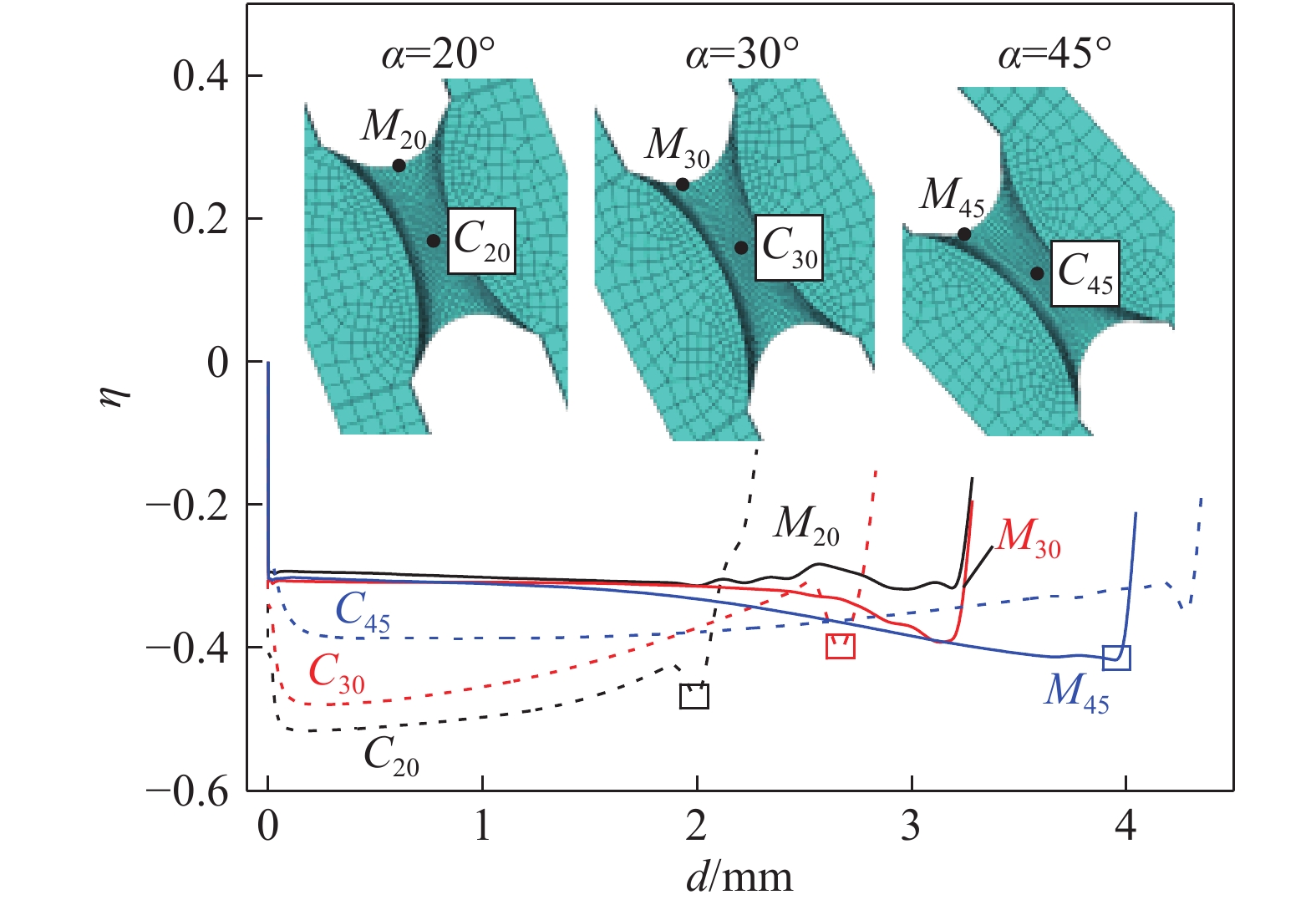
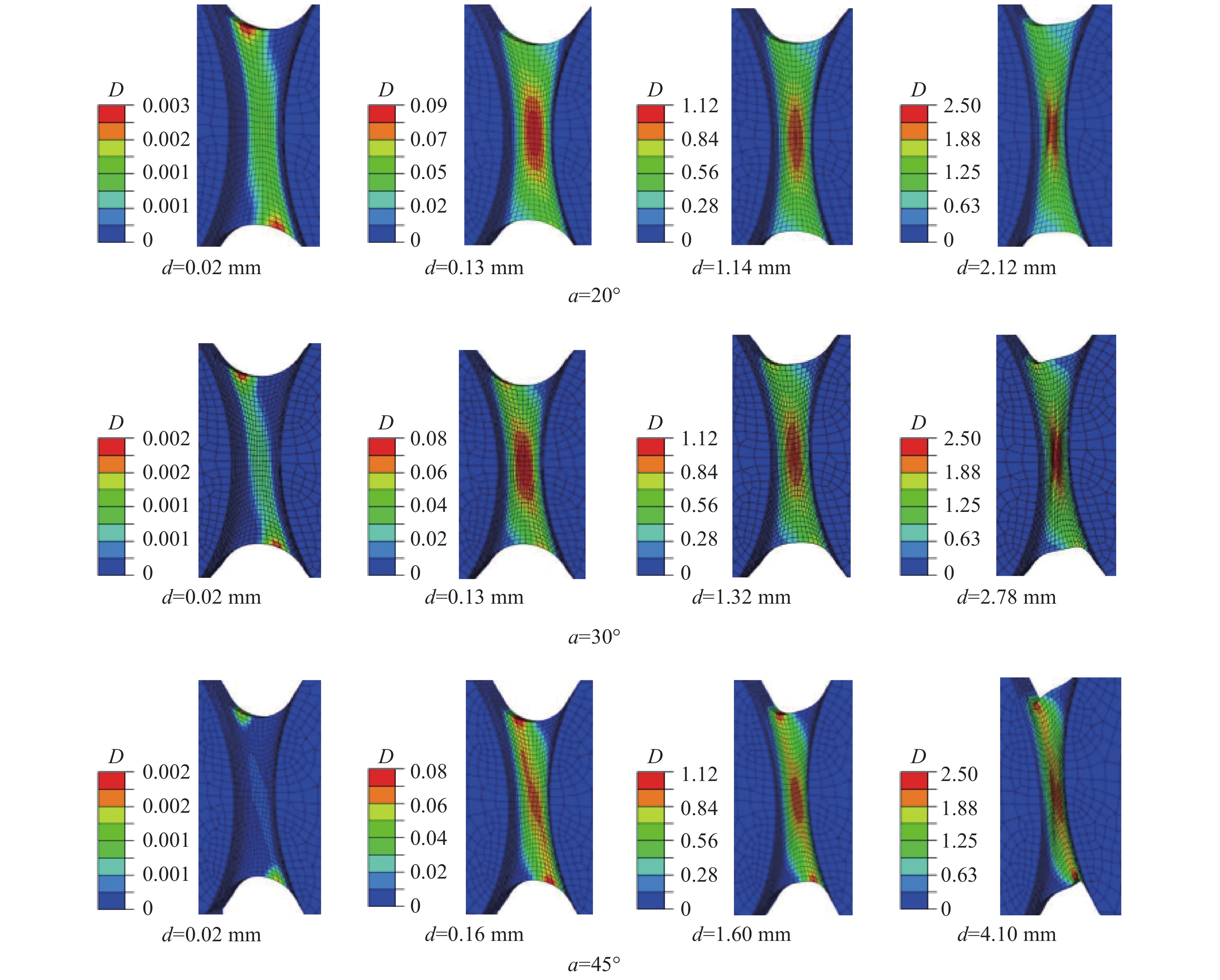
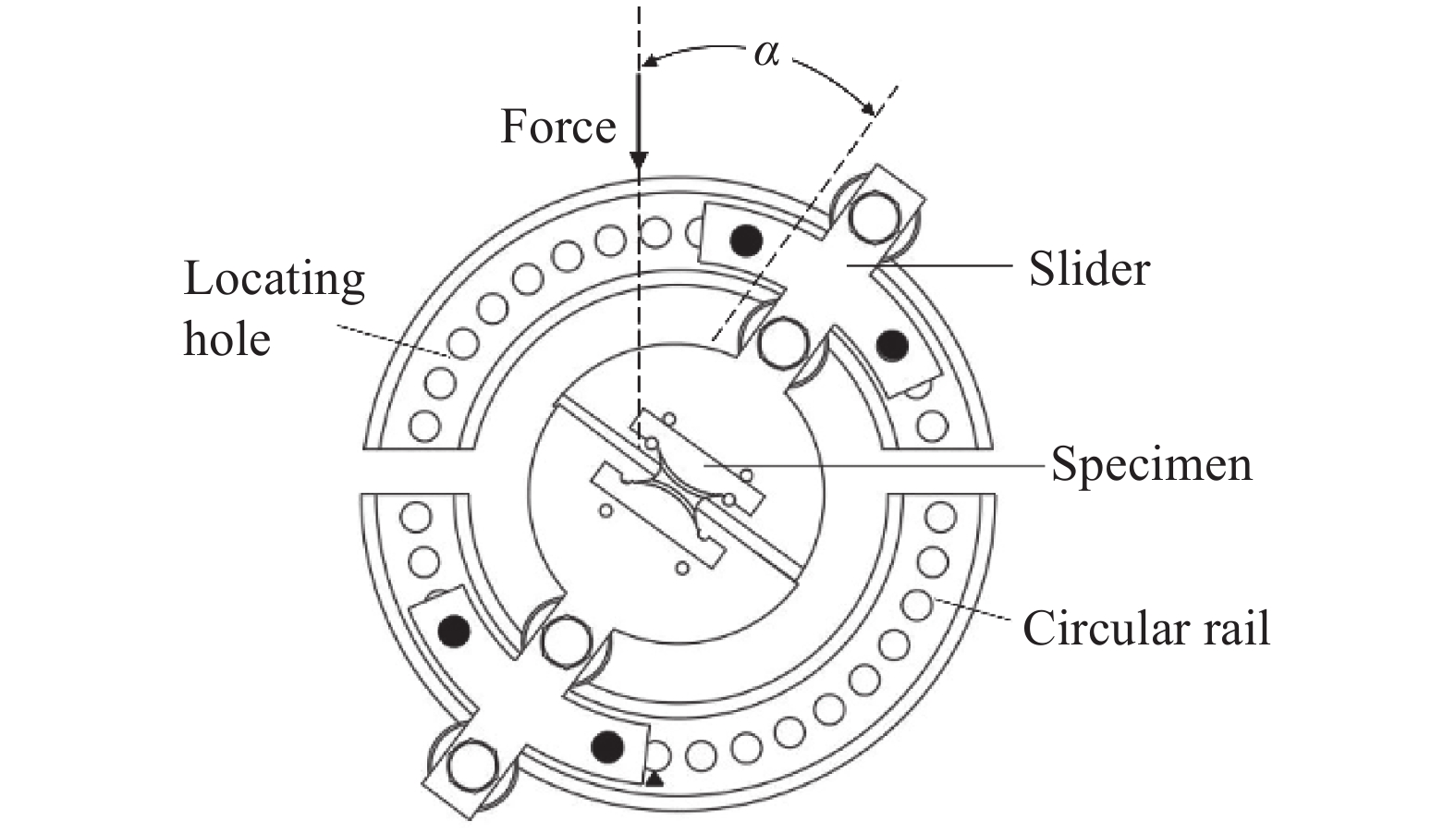
摘要: 相變誘導塑性鋼(TRansformation induced plasticity, TRIP)作為常用的先進高強鋼在汽車等交通工具的輕量化方面有廣泛的應用前景。而對于其復雜零件的成形過程,韌性斷裂是不可忽視的問題之一。本文針對現有實驗裝置不易誘發薄板承受面內壓剪時斷裂失效,從而無法研究板料負應力三軸度區間斷裂行為的問題,以高強鋼TRIP800薄板為研究對象,設計了可在單向試驗機完成壓剪實驗的試樣和夾具。通過調整夾具旋轉角度和試樣裝夾位置可以實現同一種試樣在廣泛的負應力三軸度范圍內進行壓剪斷裂分析。基于ABAQUS/Explicit平臺建立了三個典型加載方向20°、30°和45°對應的壓剪過程有限元模型,分析表明:三種情況的試樣局部變形區域的應力三軸度都小于0且斷裂點的應力三軸度低至?0.485,驗證了設計的裝置可實現負應力三軸度區間的斷裂失效分析,同時基于MMC斷裂準則分析了不同應力狀態的初始損傷情況及損傷擴展路徑。Abstract: Increasing demands for lightweight manufacturing accelerate the application of lightweight materials in the transportation, aviation, and power industries. High-strength steel is a popular candidate among various lightweight materials. Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel, a high-strength, lightweight steel, is promising for forming processes owing to its high strength and toughness. However, the increase in the flow strength of metals will create big challenges for material formability and fracture issues for manufacturing processes. Ductile fracture is still the main failure form during the forming process of TRIP steel. Sheet metal is subject to complex stress states when it undergoes diverse loading paths. Failure modes in metal forming can be mainly classified into the following: tensile, compression, shear, tensile–shear, and compression–shear. Because the metal sheet is prone to buckling failure when it undergoes in-plane compression–shear deformation, it is difficult to induce fracture during the corresponding negative stress triaxiality range. To solve this issue, a novel experimental setup and a specimen were designed to analyze fracture behaviors of an advanced high-strength steel TRIP800 sheet. For the same specimen, the failure behaviors of diverse stress states could be achieved by adjusting the angles between the loading direction and specimen positions. The parallel numerical simulations of in-plane compression–shear deformations under three typical loading angles of 20°, 30°, and 45° were performed on the ABAQUS/Explicit platform. The predicted stress triaxiality in the local deformation region of the three cases was less than zero, and the lowest was up to ?0.485, which verifies that the fracture failure analysis of negative stress triaxiality range could be realized with the designed device. In addition, the fracture onset information and damage evolution were analyzed based on the modified Mohr–Coulomb (MMC) fracture criterion. Furthermore, the fracture strain at the fracture point decreased with the decrease in stress triaxiality when the stress triaxiality was less than ?1/3.
-
Key words:
- TRIP800 /
- in-plane compression–shear /
- stress triaxiality /
- stress state /
- damage evolution
-
表 1 H13鋼和40Cr的材料屬性
Table 1. Material properties of H13 and 40Cr
Material Density/
(kg?m?3)Young’s
modulus/
MPaPoisson’s
ratioYield strength/
MPaTensile strength/
MPaH13 7850 210000 0.3 1550 1800 40Cr 7900 210000 0.28 785 810 表 2 三個方向的厚向異性系數及Hill’48函數的六個各向異性參數
Table 2. Three Lankford ratios and six anisotropic parameters of the Hill’48 function
r0 r45 r90 G K M N P Q 0.87 0.81 1.03 0.452 0.535 0.465 1.5 1.5 1.289 表 3 不同加載角度試樣的初始斷裂應變和應力三軸度關系
Table 3. Initial fracture strain and stress triaxiality at the fracture onset of specimens under different loading angles
Loading angle, α/(°) Displacement Fracture strain Stress triaxiality, η 20 2.1 0.60 ?0.485 30 2.7 0.75 ?0.424 45 4.1 1.06 ?0.419 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Liu W H. Research on Application of High Strength Steel in Automotive Lightweight [Dissertation]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2009.劉文華. 高強度鋼板在汽車輕量化中的應用研究[學位論文]. 武漢: 武漢理工大學, 2009. [2] Chiang J, Lawrence B, Boyd J D, et al. Effect of microstructure on retained austenite stability and work hardening of TRIP steels. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(13-14): 4516 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.032 [3] Lou Y S, Huh H. Prediction of ductile fracture for advanced high strength steel with a new criterion: Experiments and simulation. J Mater Process Technol, 2013, 213(8): 1284 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.03.001 [4] Li Y N, Luo M, Gerlach J, et al. Prediction of shear-induced fracture in sheet metal forming. J Mater Process Technol, 2010, 210(14): 1858 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.06.021 [5] Choi K S, Liu W N, Sun X, et al. Microstructure-based constitutive modeling of TRIP steel: prediction of ductility and failure modes under different loading conditions. Acta Mater, 2009, 57(8): 2592 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2009.02.020 [6] Zhu H, Zhu L, Chen J H, et al. Investigation of fracture mechanism of 6063 aluminum alloy under different stress states. Int J Fract, 2007, 146(3): 159 doi: 10.1007/s10704-007-9158-2 [7] Bao Y B, Wierzbicki T. On fracture locus in the equivalent strain and stress triaxiality space. Int J Mech Sci, 2004, 46(1): 81 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2004.02.006 [8] Shouler D R, Allwood J M. Design and use of a novel sample design for formability testing in pure shear. J Mater Process Technol, 2010, 210(10): 1304 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.03.019 [9] Mu L, Zang Y, Araujo S P M. A micromechanically motivated uncoupled model for ductile fracture prediction. Chin J Eng, 2017, 39(4): 557穆磊, 臧勇, Araujo S P M. 一個基于孔洞演化機制的韌性斷裂預測模型. 工程科學學報, 2017, 39(4):557 [10] Han G Z, Cai L X, Yao D, et al. Fracture criterion and plane-strain fracture toughness of ductile materials. Acta Aeron Astron Sin, 2018, 39(8): 145韓光照, 蔡力勛, 姚迪, 等. 延性材料斷裂準則與平面應變斷裂韌度. 航空學報, 2018, 39(8):145 [11] Jia Z, Mu L, Zang Y. Research progress on the micro-mechanism and prediction models of ductile fracture in metal forming. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(12): 1454賈哲, 穆磊, 臧勇. 金屬塑性成形中的韌性斷裂微觀機理及預測模型的研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2018, 40(12):1454 [12] Zhu Y Z, Kiran R, Xing J H, et al. A modified micromechanics framework to predict shear involved ductile fracture in structural steels at intermediate and low-stress triaxialities. Eng Fract Mech, 2020, 225: 106860 doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106860 [13] Lou Y S, Yoon J W, Huh H. Modeling of shear ductile fracture considering a changeable cut-off value for stress triaxiality. Int J Plast, 2014, 54: 56 [14] Kubík P, ?ebek F, H?lka J, et al. Calibration of ductile fracture criteria at negative stress triaxiality. Int J Mech Sci, 2016, 108-109: 90 [15] Li C. Analysis and Application of the Instability of Thin-Walled Materials in Plastic Forming Process [Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2017李翀. 薄壁材料在塑性加工中的失穩現象分析與應用[學位論文]. 北京: 北京理工大學, 2017 [16] Huang G S, Wang L F, Wang Y X, et al. An Auxiliary Tool for Thin Plate Material Compression and Its Application: China Patent, CN103335883A. 2013-10-02黃光勝, 王利飛, 王艷霞, 等. 一種薄板材料壓縮輔助工具及使用方法: 中國專利, CN103335883A. 2013-10-02 [17] Mohr D, Henn S. Calibration of stress-triaxiality dependent crack formation criteria: a new hybrid experimental–numerical method. Exp Mech, 2007, 47(6): 805 doi: 10.1007/s11340-007-9039-7 [18] Brünig M, Gerke S, Schmidt M. Damage and failure at negative stress triaxialities: Experiments, modeling and numerical simulations. Int J Plast, 2018, 102: 70 [19] Gerke S, Zistl M, Bhardwaj A, et al. Experiments with the X0-specimen on the effect of non-proportional loading paths on damage and fracture mechanisms in aluminum alloys. Int J Solids Struct, 2019, 163: 157 doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2019.01.007 [20] Xu Q S, Zhuang X C, Fang Y Y, et al. A novel test method for symmetrical sheet metal compression-shear. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ, 2015, 49(10): 1510徐芹所, 莊新村, 方勇勇, 等. 一種新的金屬板料雙向壓縮剪切試驗方法. 上海交通大學學報, 2015, 49(10):1510 [21] Wu Y J, Zhuang X C, Zhao Z. Fracture topography analysis of C45 steel under different stress states. J Plast Eng, 2013, 20(3): 106 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2013.03.020吳彥駿, 莊新村, 趙震. 不同應力狀態下45鋼斷口形貌分析. 塑性工程學報, 2013, 20(3):106 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2013.03.020 [22] Wu H, Xu W C, Shan S B, et al. An extended GTN model for low stress triaxiality and application in spinning forming. J Mater Process Technol, 2019, 263: 112 [23] Lou Y S, Yoon J W, Huh H, et al. Correlation of the maximum shear stress with micro-mechanisms of ductile fracture for metals with high strength-to-weight ratio. Int J Mech Sci, 2018, 146-147: 583 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.03.025 [24] Hill R. A theory of the yielding and plastic flow of anisotropic metals. Proc R Soc Lond A, 1948, 193(1033): 281 [25] Qian L Y, Fang G, Zeng P. Modeling of the ductile fracture during the sheet forming of aluminum alloy considering non-associated constitutive characteristic. Int J Mech Sci, 2017, 126: 55 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.03.013 [26] Reis L C, Prates P A, Oliveira M C, et al. Inverse identification of the Swift law parameters using the bulge test. Int J Mater Form, 2017, 10(4): 493 doi: 10.1007/s12289-016-1296-5 [27] Bai Y L, Wierzbicki T. Application of extended Mohr–Coulomb criterion to ductile fracture. Int J Fract, 2010, 161(1): 1 [28] Xue L. Damage accumulation and fracture initiation in uncracked ductile solids subject to triaxial loading. Int J Solids Struct, 2007, 44(16): 5163 -




 下載:
下載: