Reliability life analysis of reinforced concrete in a salt corrosion environment based on a three-parameter Weibull distribution
-
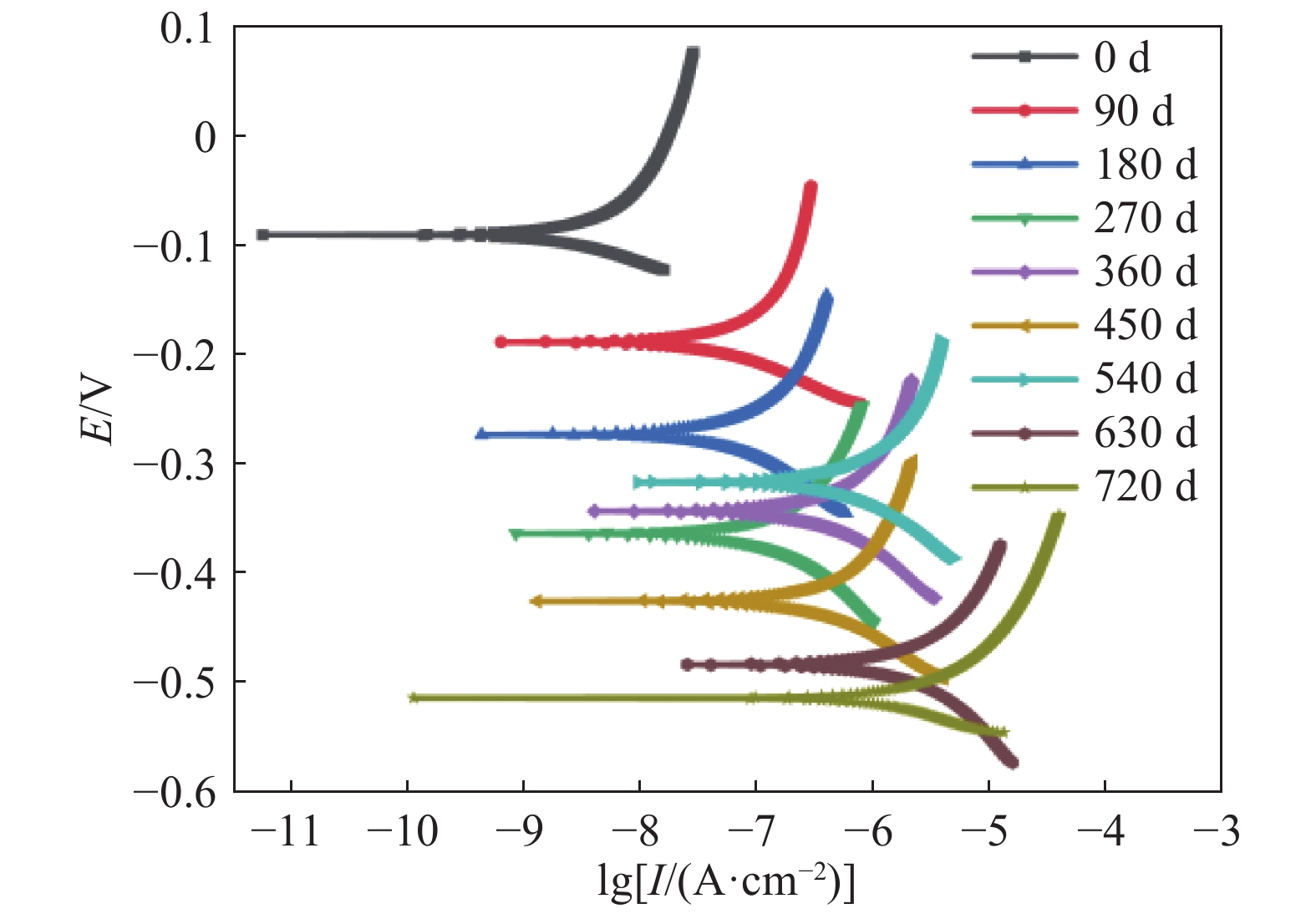
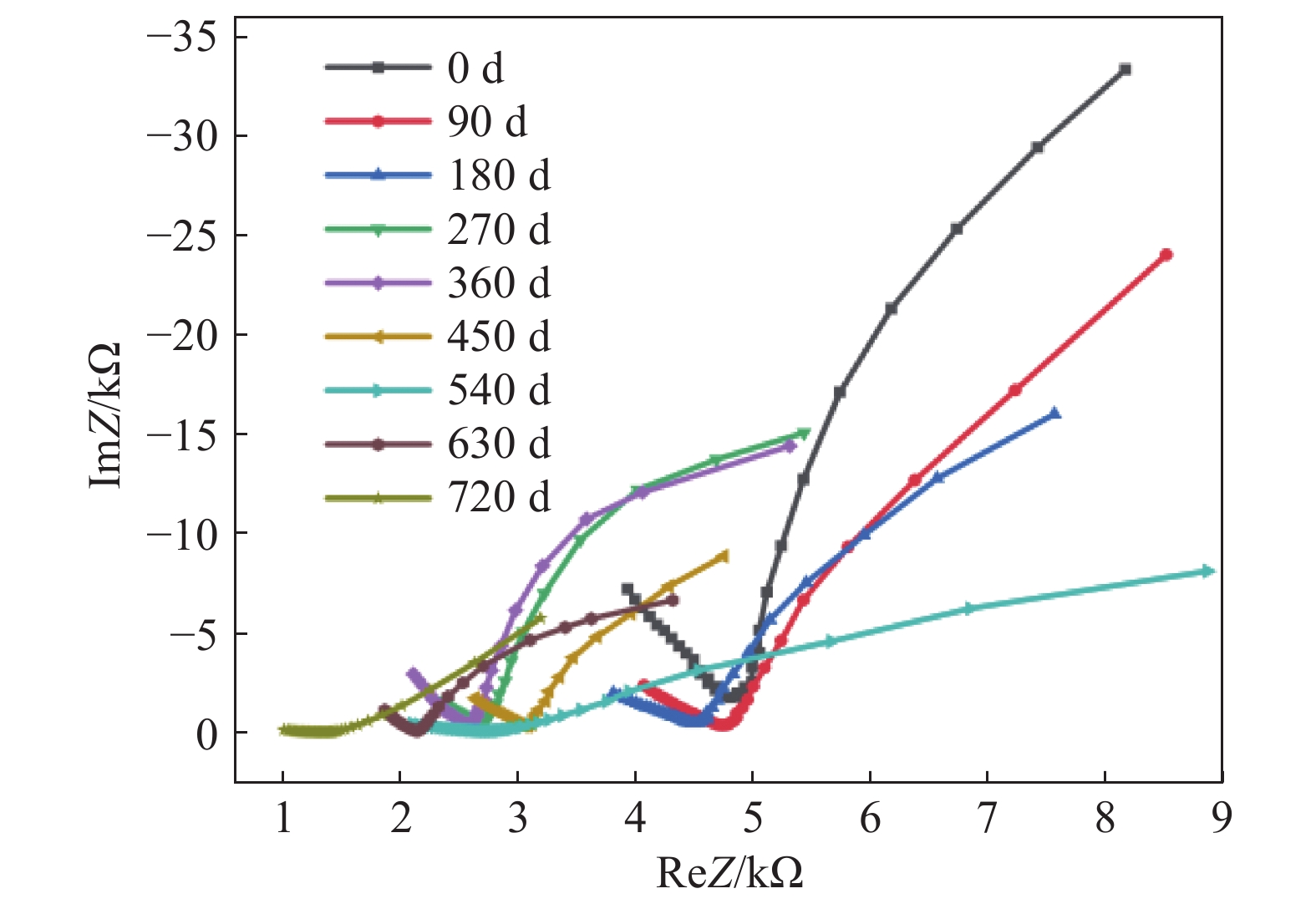
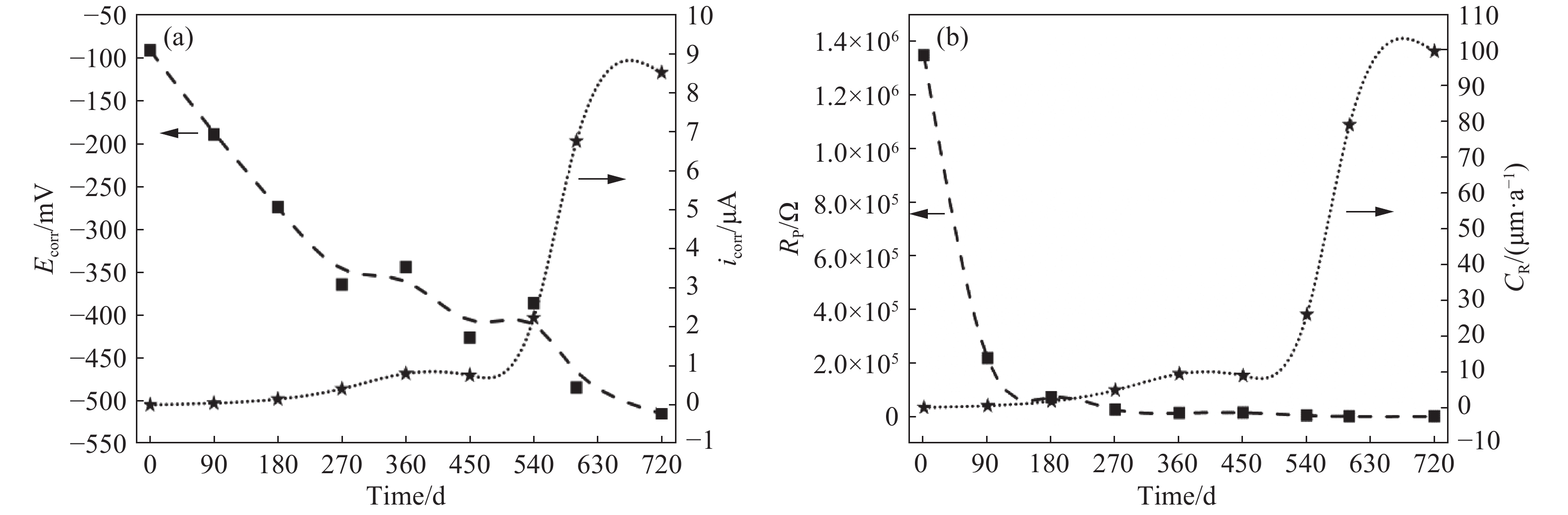
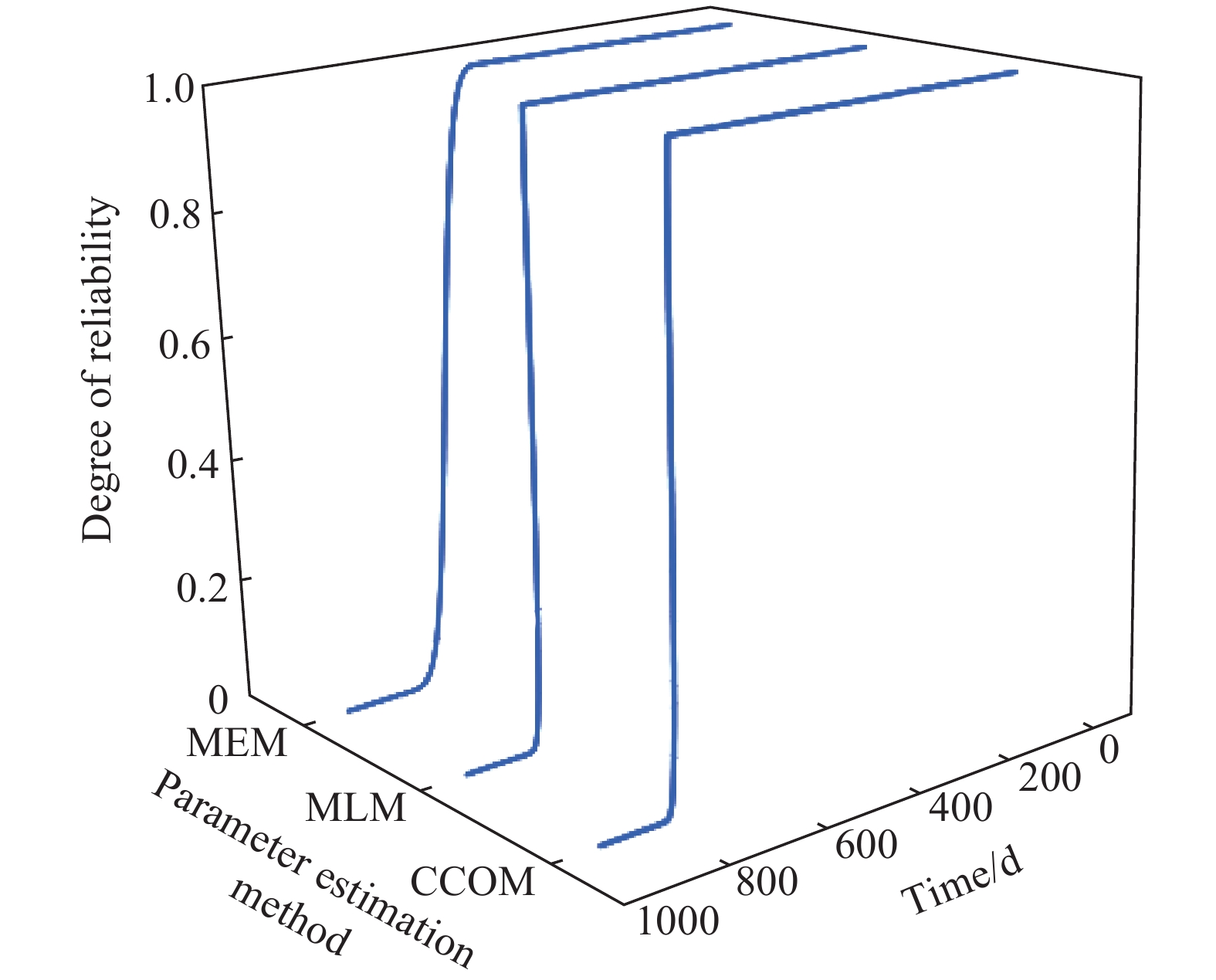
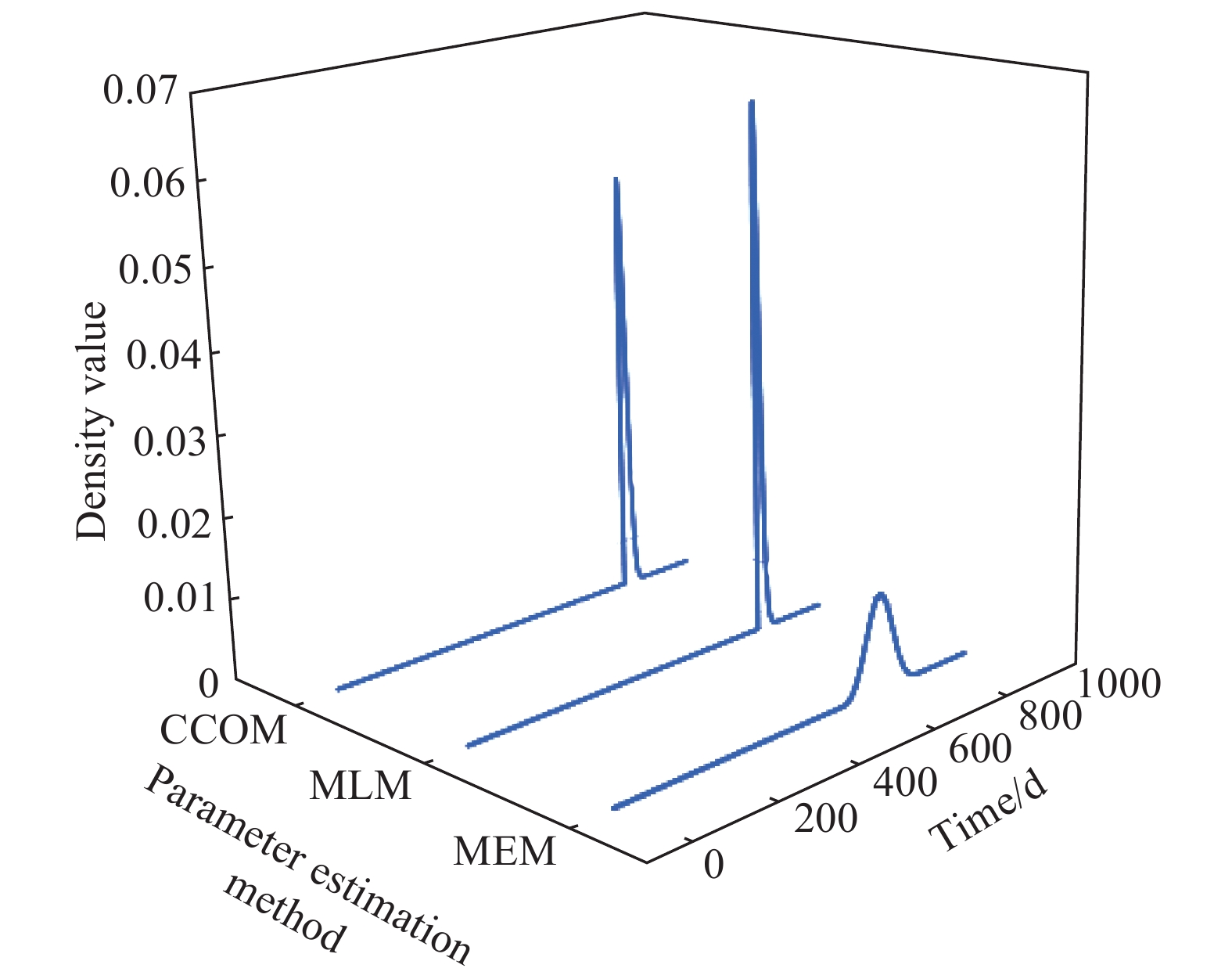
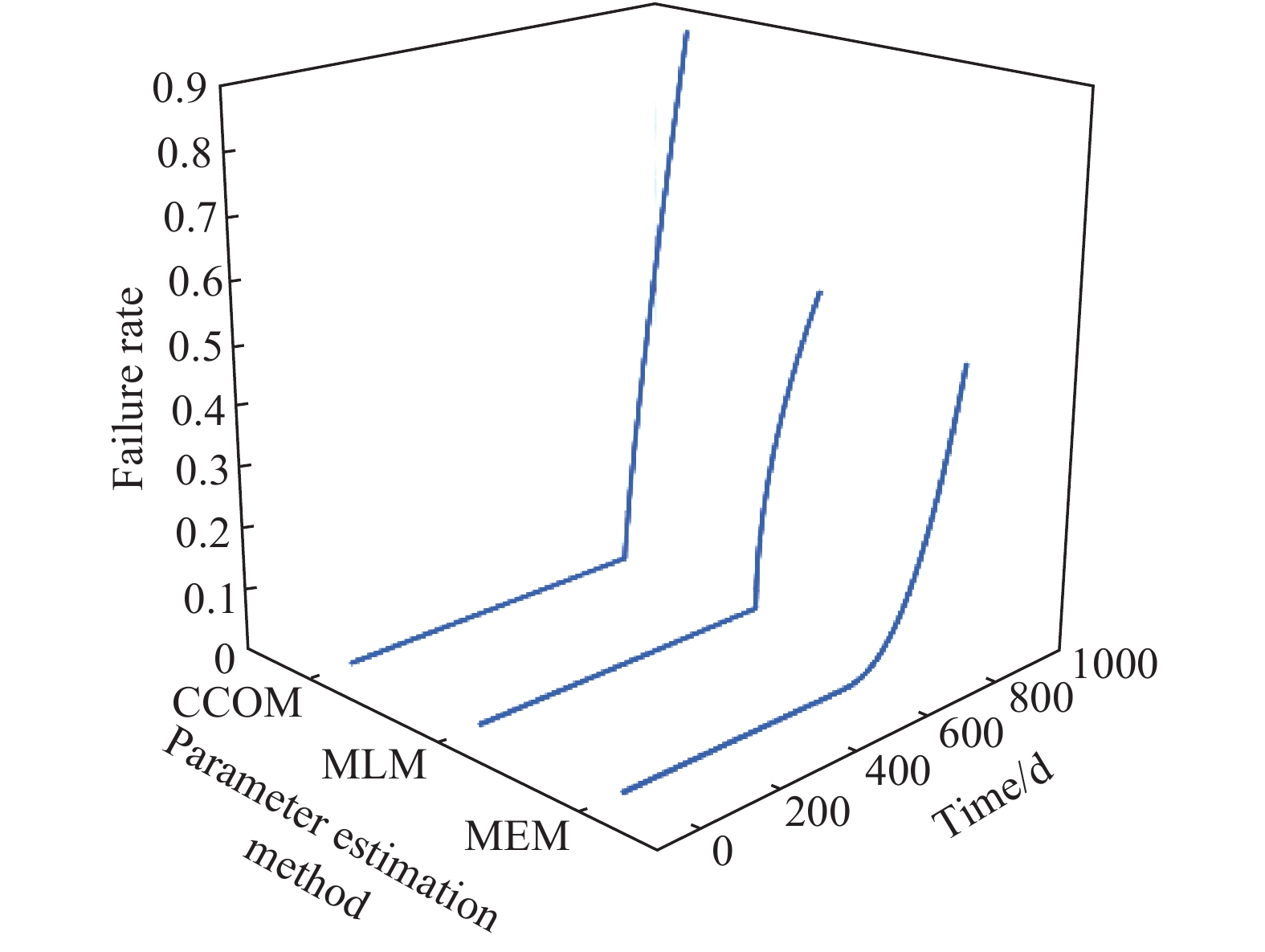
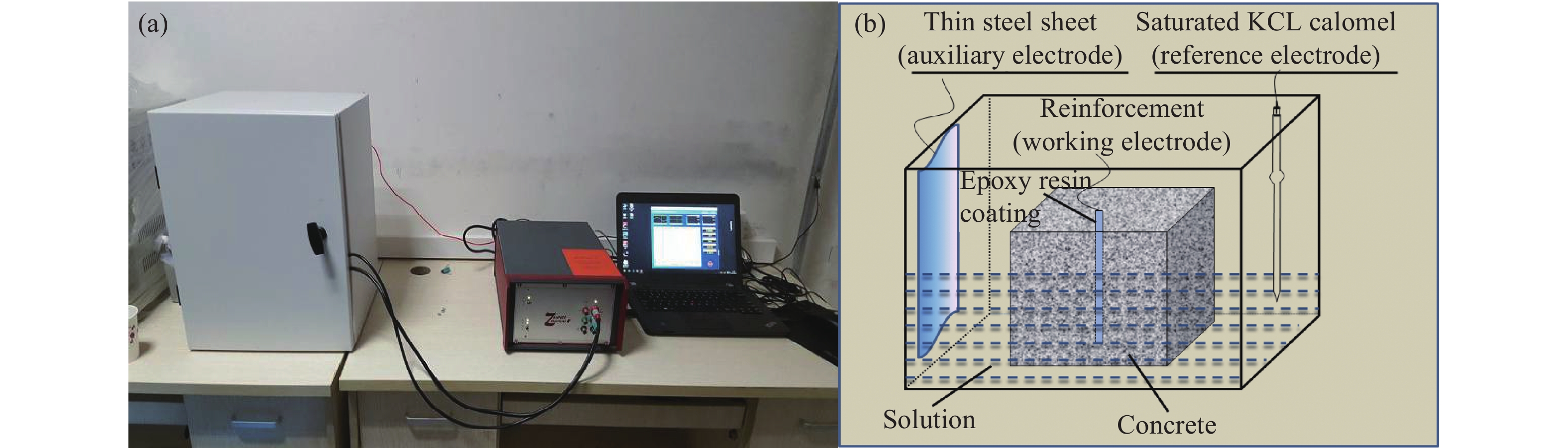
摘要: 為研究鋼筋混凝土在耦合鹽環境中的腐蝕劣化規律及壽命分布,將鋼筋混凝土試件置于0.32 mol·L?1 NaCl和0.4 mol·L?1 MgSO4鹽溶液中,利用電化學工作站定期無損檢測,以極化曲線、交流阻抗圖譜及電化學參數指標進行耐久性分析,選擇3參數Weibull進行可靠性建模,通過Anderson-Darling法(A-D)進行先驗假設檢驗,采用相關系數優化法(CCOM)、極大似然法(MLM)及矩估計法(MEM)進行參數估計,綜合可靠度曲線、密度曲線、失效率曲線對鋼筋混凝土在氯鹽、硫酸鹽、鎂鹽腐蝕環境中的壽命進行分析,研究結果表明:腐蝕離子綜合作用下,極化曲線逐漸向腐蝕電流密度增大和負電位方向移動,交流阻抗圖譜不斷左移并向阻抗實部收縮,鋼筋銹蝕發生的阻力逐漸減小,概率逐漸增大。可靠性壽命曲線初期保持不變,后期加速下降,密度曲線呈單峰對稱狀,失效率曲線初始基本保持不變,后期線性增加。3種參數估計方法中,CCOM和MLM參數估計值相近且穩定準確,所得可靠性壽命曲線相似,MEM參數估計值誤差較大,對于鋼筋混凝土加速試驗得到的小樣本失效數據建議用CCOM和MLM進行參數估計,并進行可靠性壽命分析。C35鋼筋混凝土在硫酸鎂及氯化鈉腐蝕環境中的可靠性壽命周期約為760 d。Abstract: To study the corrosion law and life distribution of reinforced concrete in a coupled salt environment, the reinforced concrete specimens were placed in 0.32 mol·L?1 NaCl and 0.4 mol·L?1 MgSO4 salt solutions. The performance of reinforced concrete was tested regularly using an electrochemical workstation. The durability was analyzed through a polarization curve, an AC impedance spectrum, and electrochemical parameters. A three-parameter Weibull distribution was selected for reliability modeling, and a prior false test was performed by the Anderson-Darling (A-D) method. The parameters were estimated by the correlation coefficient optimization method (CCOM), maximum likelihood method (MLM), and moment estimation method (MEM). The reliability curve, density curve, and failure rate curve were each used to analyze the life of reinforced concrete in chloride, sulfate, and magnesium-based corrosion environments. Results show that under the combined action of corrosion ions, the polarization curve gradually moves toward increasing corrosion current density and negative potential, and the AC impedance spectrum moves to the left and shrinks to the real part of the impedance. The resistance of steel bar corrosion gradually decreases whereas the probability gradually increases. The reliability curve is unchanged at the initial stage and rapidly decreases at the later stage. The density curve is symmetric with a single peak, and the failure rate curve remains unchanged at the initial stage and increases linearly at the later stage. Among the three-parameter estimation methods, CCOM and MLM parameter estimation values are similar, stable, and accurate, and the obtained reliability curves are similar. It is suggested that CCOM and MLM should be used for parameter estimation and reliability analysis of small sample failure data that is obtained from an accelerated test of reinforced concrete. The reliability life of C35 reinforced concrete in magnesium sulfate and sodium chloride corrosion environments is about 760 d.
-
表 1 混凝土配合比設計
Table 1. Concrete mix design
kg·m?3 Cement Fly ash Aggregate Sand Water Corrosion inhibition Water-binder ratio Water reducer Compressive strength/MPa Slump/mm 300 90 1153 621 148.2 36 0.38 1.8 39.6 180 表 2 P.O 42.5水泥及粉煤灰化學成分(質量分數)
Table 2. Chemical composition of P.O 42.5 cement and fly ash
% Raw materials Ignition loss SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 Cement 1.62 26.38 9.61 4.34 50.09 3.16 2.01 Fly ash 5.4 44.36 25.13 12.64 11.94 0.82 1.23 表 3 腐蝕電流密度與鋼筋銹蝕程度的對應關系[17]
Table 3. Corresponding relationship between corrosion current density and corrosion degree of reinforcement[17]
icorr/(μA·cm?2) Corrosion status icorr <0.2 Passivation state 0.2< icorr <0.5 Low corrosion condition state 0.5< icorr <1.0 Moderate corrosion condition state 1.0< icorr <10 Higher corrosion condition state icorr >10 Highest corrosive condition state 表 4 腐蝕電位與鋼筋銹蝕程度的對應關系[18]
Table 4. Corresponding relationship between corrosion potential and corrosion degree of reinforcement[18]
American standard?ASTMC876 Chinese metallurgical ministry standard Potential range/mV Corrosion discriminant Potential range/mV Corrosion discriminant >?200 5% probability of corrosion >?250 No rust (?200)?(?350) 50% probability of corrosion (?250)?(?400) Maybe corroded <?350 95% probability of corrosion <?400 Rust 表 5 鋼筋混凝土試件失效天數匯總表
Table 5. Summary of the failure days of reinforced concrete specimens
Functional form Specimen 1 Specimen 2 Specimen 3 t/d R2 t/d R2 t/d R2 Exponential function 740 0.95105 736 0.94177 729 0.95045 Power function 747 0.95999 741 0.95129 731 0.95884 Cubic function 748 0.96468 742 0.95688 732 0.96425 表 6 參數估計值匯總表
Table 6. Parameter estimate summary
Estimation method U V δ CCOM 725.4 1.83 15.41 MLM 728.0 1.50 11.43 MEM 560.0 3.47 113.44 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Yu Y J, Guo X H, Wang L, et al. Durability evaluation and repair of concrete structure under coupling action of acid and chlorine. Ind Constr, 2019, 49(3): 180于英俊, 郭小華, 王玲, 等. 酸和氯鹽耦合作用下混凝土結構耐久性評估及修復. 工業建筑, 2019, 49(3):180 [2] Wang C, Ge G H, Hou J G, et al. Study of durability of concrete structures and its influencing factors in south region of Xinjiang. Eng J Wuhan Univ, 2017, 50(3): 447王成, 葛廣華, 侯建國, 等. 南疆地區混凝土結構耐久性現狀與影響因素研究. 武漢大學學報(工學版), 2017, 50(3):447 [3] Zhang L, Su X P. Comparison and selection of the durability evaluating parameters of concrete in saline soil region. Adv Mater Res, 2014, 919-921: 1751 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.919-921.1751 [4] Liu Z Q, Pei M, Zhang F Y, et al. The comparison of chemical attack products in different zones of cement paste partially exposed to Na2SO4 solution [J/OL]. J Building Mater (2019-02-28) [2019-12-06]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1764.TU.20190227.0913.014劉贊群, 裴敏, 張豐燕, 等. 水泥凈漿不同部分受硫酸鈉侵蝕產物對比分析[J/OL]. 建筑材料學報(2019-02-28)[2019-12-06]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1764.TU.20190227.0913.014 [5] Zhu J J, Gao J M, Chen F, et al. Corrosion mechanism of cement mortars partially immersed in combined NaCl?Na2SO4 solution. J Southeast Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2019, 49(5): 964 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2019.05.021朱健健, 高建明, 陳菲, 等. 水泥砂漿半浸泡在NaCl?Na2SO4混合溶液中的侵蝕機理. 東南大學學報(自然科學版), 2019, 49(5):964 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2019.05.021 [6] Yao M B, Li J P. Distribution behavior of sulfate erosion in concrete piles under water pressure. J Tongji Univ Nat Sci, 2019, 47(8): 1131 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2019.08.007姚明博, 李鏡培. 水壓作用下硫酸鹽在混凝土樁中的侵蝕分布規律. 同濟大學學報(自然科學版), 2019, 47(8):1131 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2019.08.007 [7] Jiang L, Niu D T. Study of constitutive relation of concrete under sulfate attack and drying-wetting cycles. J China Univ Min Technol, 2017, 46(1): 66姜磊, 牛荻濤. 硫酸鹽侵蝕與干濕循環下混凝土本構關系研究. 中國礦業大學學報, 2017, 46(1):66 [8] Zhao G W, Li J P, Fan H H, et al. Influence of chloride-sulfate attack on degradation and sulfate diffusion of cast-in-situ concrete structures subjected to wet-dry cycles. J Tongji Univ Nat Sci, 2018, 46(12): 1637 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.12.004趙高文, 李鏡培, 樊恒輝, 等. 干濕循環下氯鹽對現澆混凝土硫酸鹽腐蝕劣化及擴散影響. 同濟大學學報(自然科學版), 2018, 46(12):1637 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.12.004 [9] Cefis N, Comi C. Damage modelling in concrete subject to sulfate attack. Frattura e Integrita Strutturale, 2014, 8(29): 222 doi: 10.3221/IGF-ESIS.29.19 [10] Andrade J J O, Possan E, Dal Molin D C C. Considerations about the service life prediction of reinforced concrete structures inserted in chloride environments. J Build Pathol Rehabil, 2017, 2(1): 6 doi: 10.1007/s41024-017-0025-x [11] Zhang J H, Wang W, Guan Z G. Service life prediction of reinforced concrete bridge deck under chloride attack. Mater Rep, 2016, 30(Suppl 2): 401張菊輝, 王偉, 管仲國. 基于氯鹽侵蝕的鋼筋混凝土橋面板壽命預測. 材料導報, 2016, 30(增刊 2):401 [12] Akiyama M, Frangopol D M, Takenaka K. Reliability-based durability design and service life assessment of reinforced concrete deck slab of jetty structures. Struct Infrastruct Eng, 2017, 13(4): 468 doi: 10.1080/15732479.2016.1164725 [13] Wang Z M, Ren L N, Duan H Y, et al. Reliability assessment of cutting-tool for machine tools with three-parameter Weibull distribution under variable machining conditions. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ, 2018, 52(4): 77王智明, 任麗娜, 段紅燕, 等. 耐用度服從三參數Weibull分布的機床刀具在變加工條件下的可靠性評估. 西安交通大學學報, 2018, 52(4):77 [14] Mendez-Gonzalez L C, Rodriguez-Picon L A, Valles-Rosales D J, et al. Reliability analysis for electronic devices using beta‐Weibull distribution. Qual Reliab Eng Int, 2017, 33(8): 2521 doi: 10.1002/qre.2214 [15] Liang C, Yao J W, Zhang K X, et al. Railway equipment reliability test based on Weibull distribution. Appl Mech Mater, 2016, 851: 340 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.851.340 [16] Li L. Corrosion monitoring of reinforced concrete structure based on electrochemical theory. J Nanoelectron Optoelectron, 2018, 13(4): 572 doi: 10.1166/jno.2018.2306 [17] Erdo?du ?, Bremner T W, Kondratova I L. Accelerated testing of plain and epoxy-coated reinforcement in simulated seawater and chloride solutions. Cem Concr Res, 2001, 31(6): 861 doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00487-2 [18] Huang R. Durability Research of Reinforced Concrete under the Western Environment [Dissertation]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017黃冉. 西部環境下結構混凝土耐久性研究[學位論文]. 南京: 東南大學, 2017 [19] Yu Y, Si X S, Hu C H, et al. Data driven reliability assessment and life-time prognostics: a review on covariate models. Acta Autom Sin, 2018, 44(2): 216喻勇, 司小勝, 胡昌華, 等. 數據驅動的可靠性評估與壽命預測研究進展: 基于協變量的方法. 自動化學報, 2018, 44(2):216 [20] Almalki S J, Nadarajah S. Modifications of the Weibull distribution: a review. Reliab Eng Syst Saf, 2014, 124: 32 doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2013.11.010 [21] Zhang T L, Li W X, Dwight R. Modeling failure data by 3-parameter Weibull distribution models // 2016 11th International Conference on Reliability, Maintainability and Safety (ICRMS). Hangzhou, 2016: 1 [22] Voinov V, Alloyarova R, Pya N. A modified Chi-squared goodness-of-fit test for the three-parameter Weibull distribution and its applications in reliability // Mathematical Methods in Survival Analysis, Reliability and Quality of Life. Wiley, 2010 [23] Liu Y, Rong X Q, Bu S P. Life expectancy of smart meter with Weibull distribution. Electr Meas Instrum, 2019, 56(3): 148劉勇, 榮雪琴, 卜樹坡. 基于Weibull分布的智能電能表壽命預計. 電測與儀表, 2019, 56(3):148 [24] Freels J K, Timme D A, Pignatiello J J, et al. Maximum likelihood estimation for the poly-Weibull distribution. Qual Eng, 2019, 31(4): 545 doi: 10.1080/08982112.2018.1557685 [25] Zhao H Q, Liu R Y. Moment estimation equation of the three-parameter Weibull distribution under censored samples. College Math, 2005, 21(1): 49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1454.2005.01.012趙海清, 劉瑞元. 在定數截尾樣本下三參數威布爾分布的矩估計方程. 大學數學, 2005, 21(1):49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1454.2005.01.012 [26] Cran G W. Moment estimators for the 3-parameter Weibull distribution. IEEE Trans Reliab, 1988, 37(4): 360 doi: 10.1109/24.9839 -




 下載:
下載: