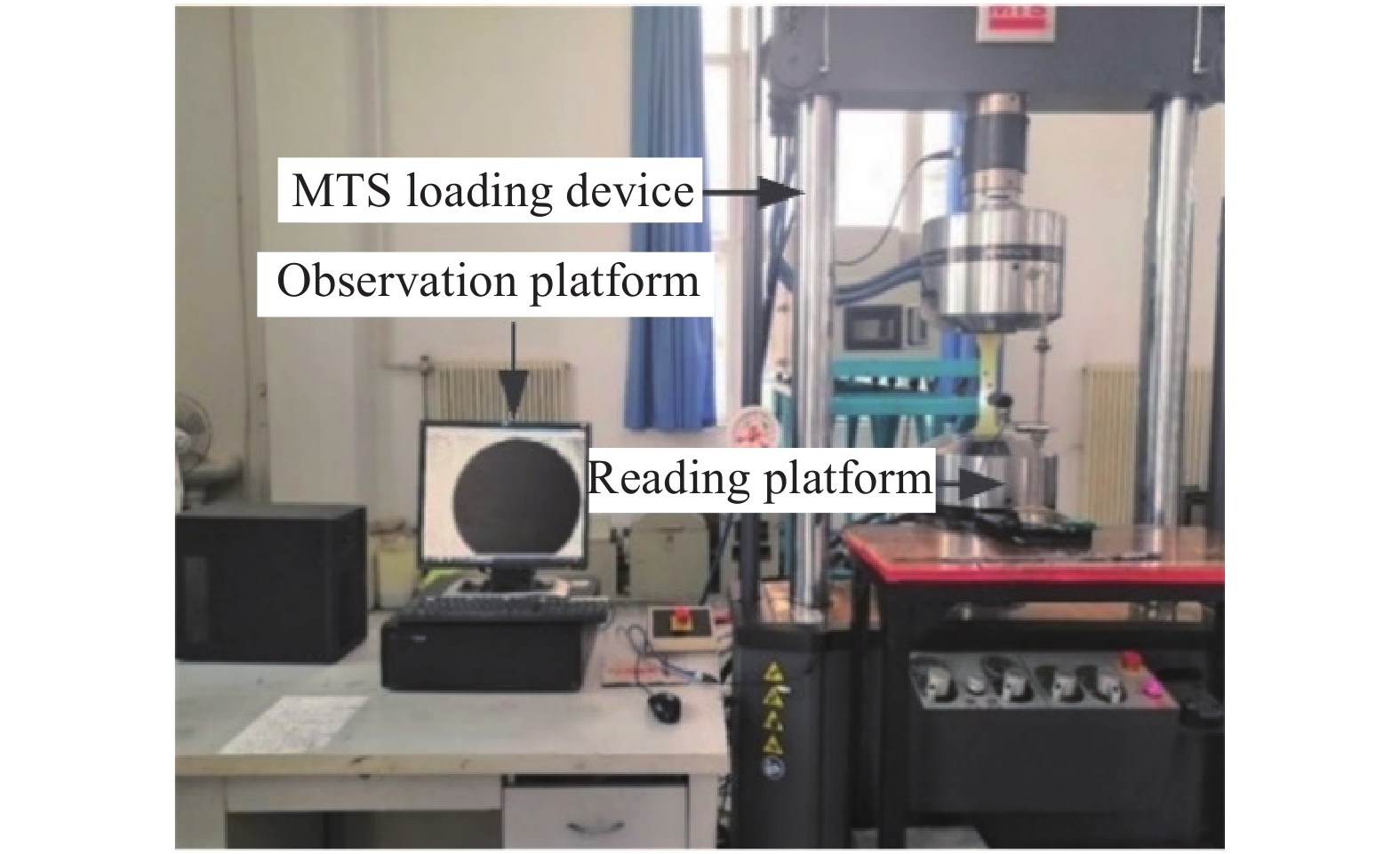
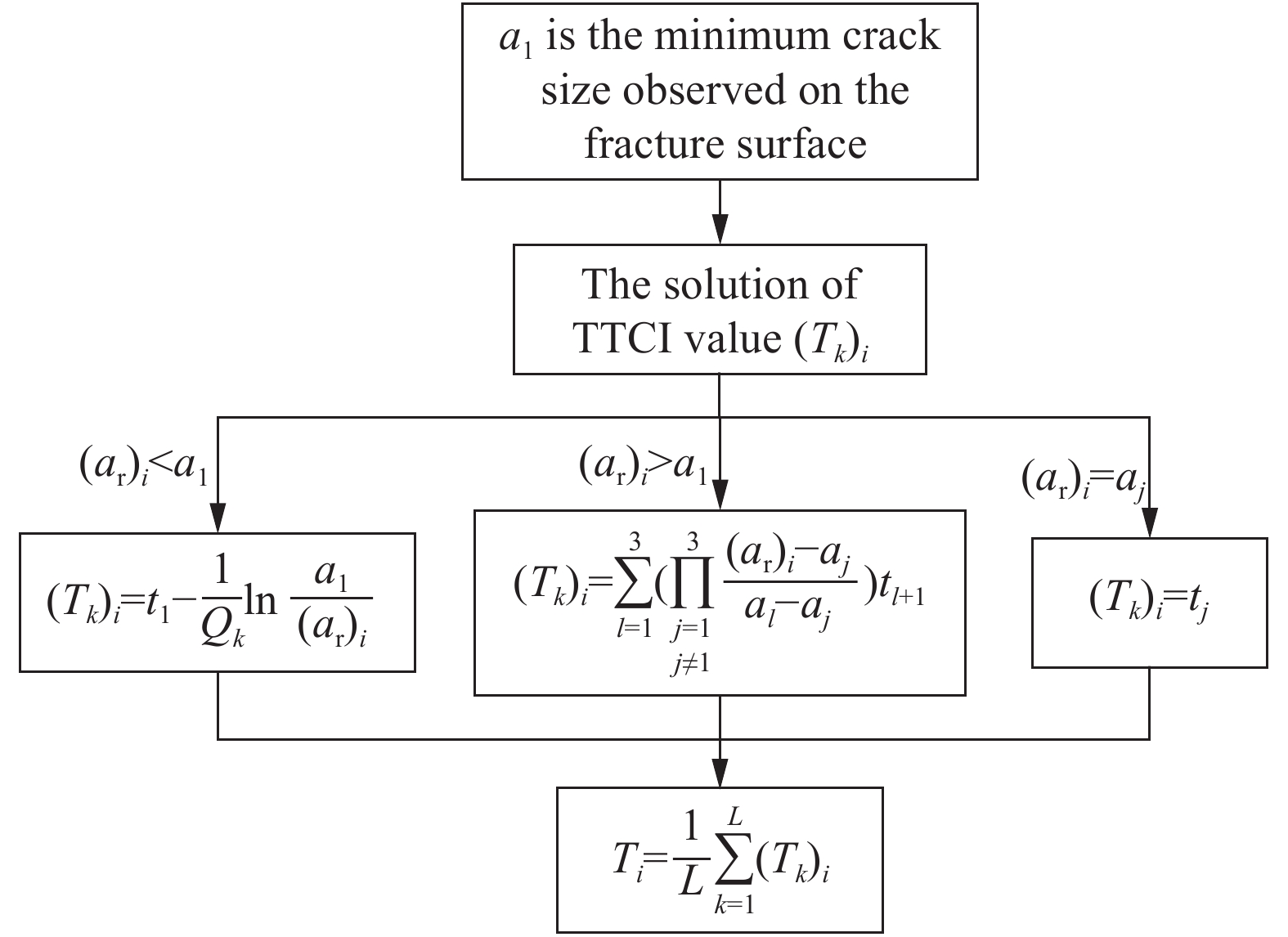
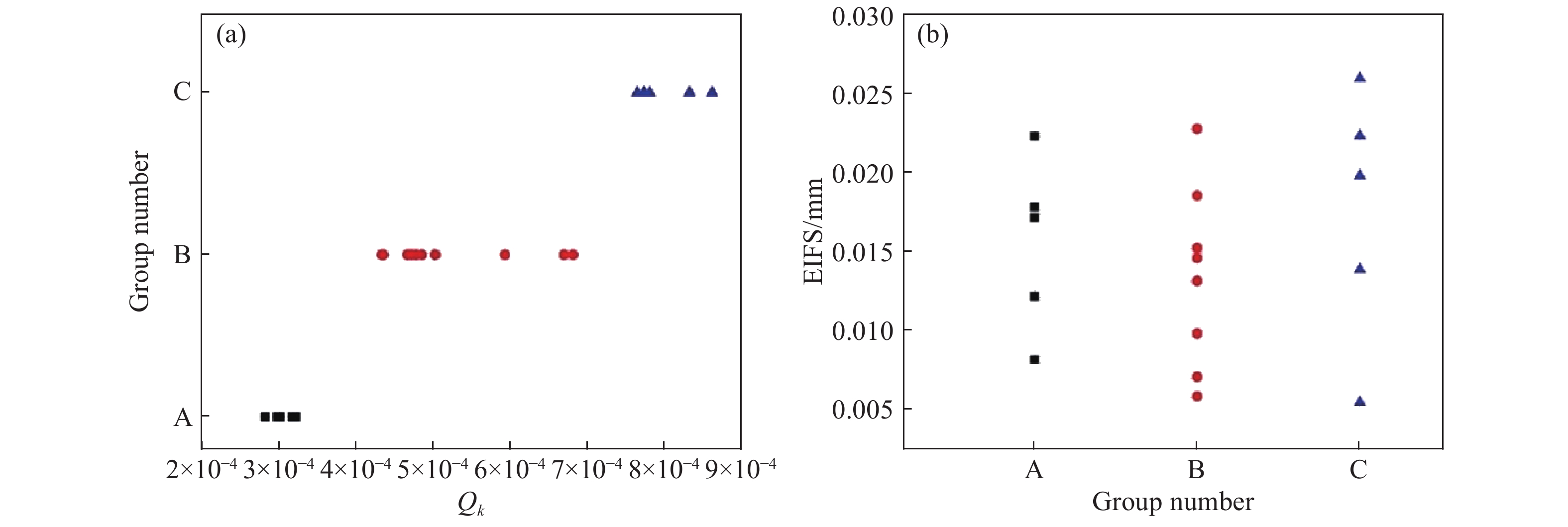
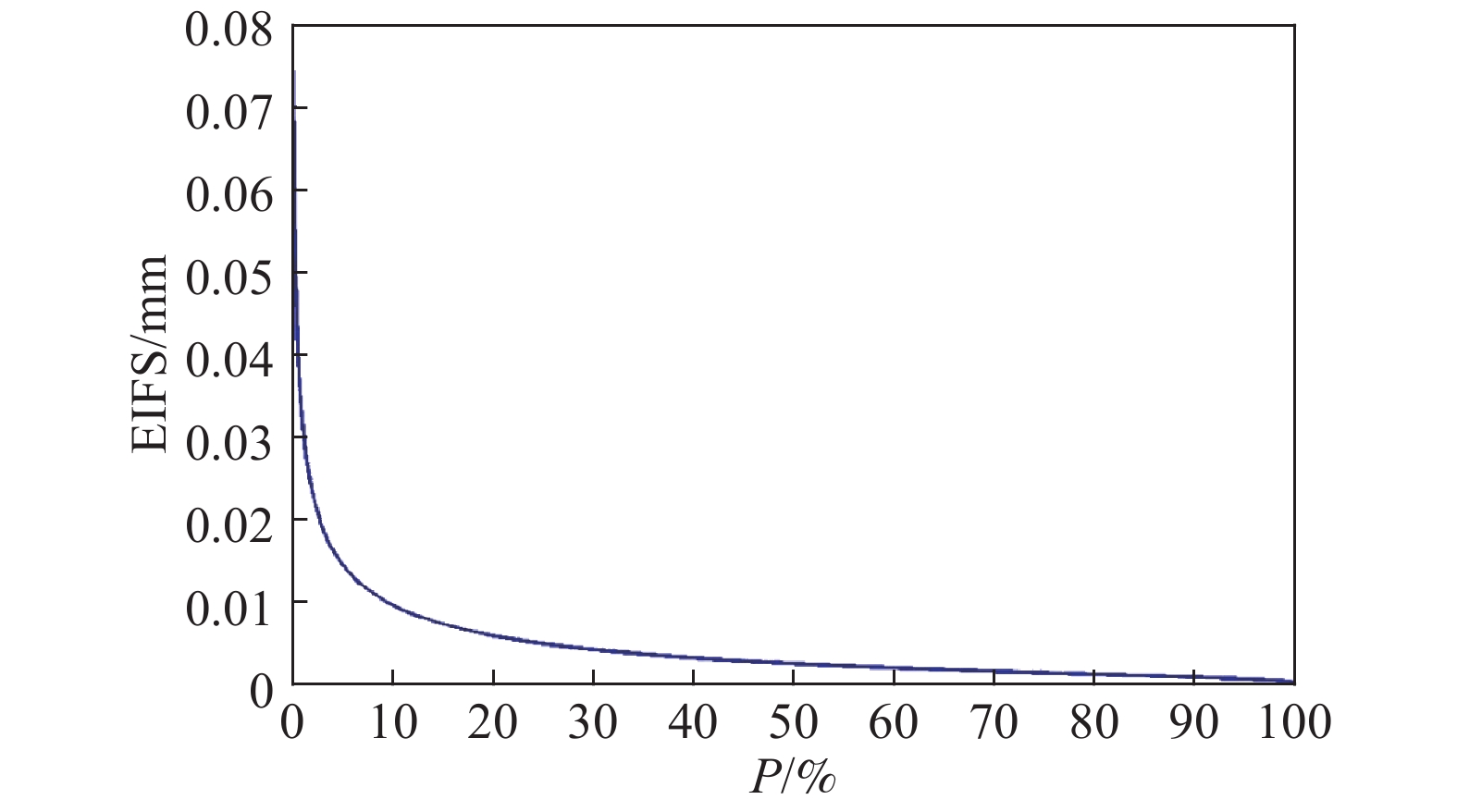
Evaluation method of initial fatigue quality of aircraft wing flange fastener holes
-
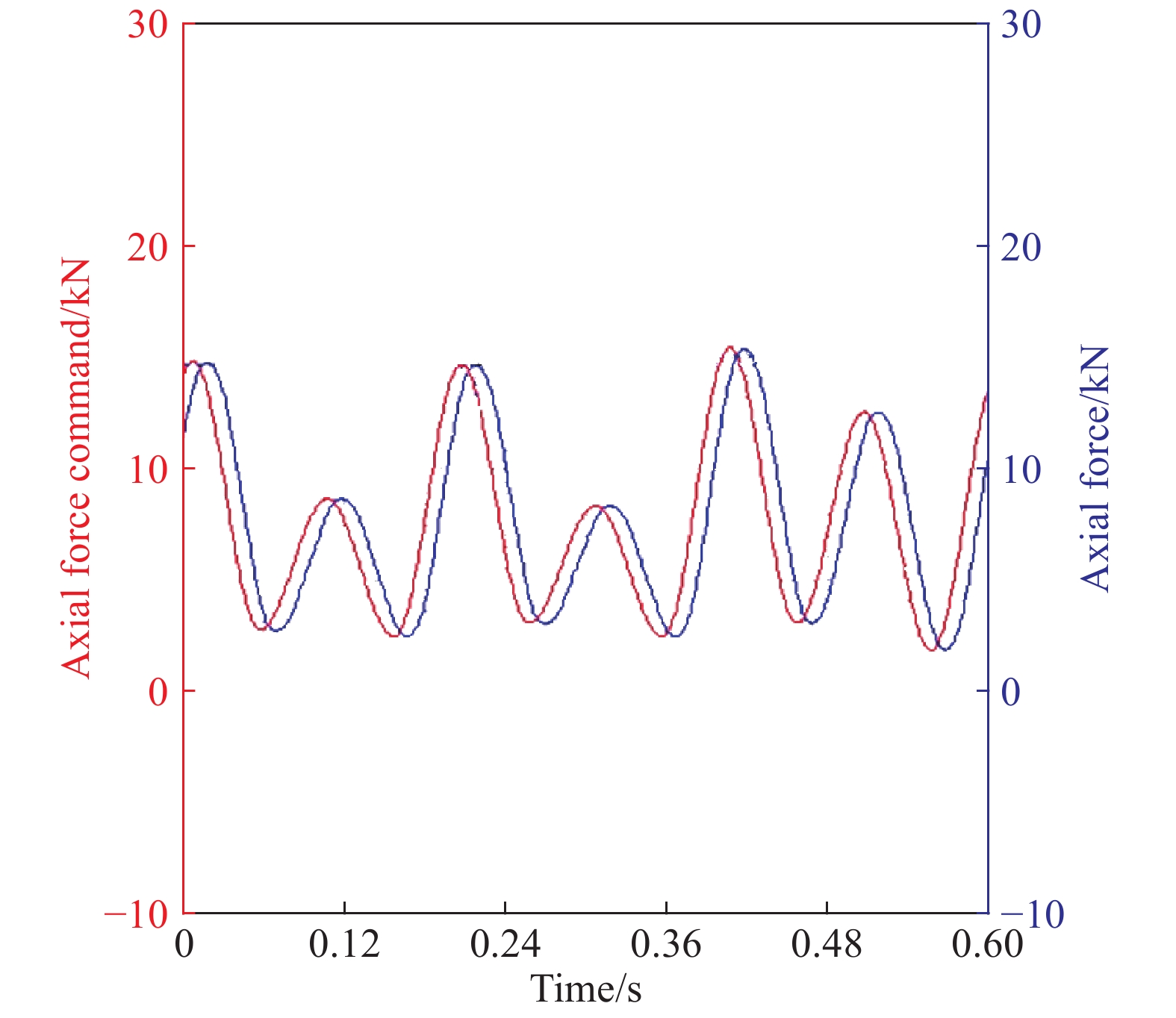
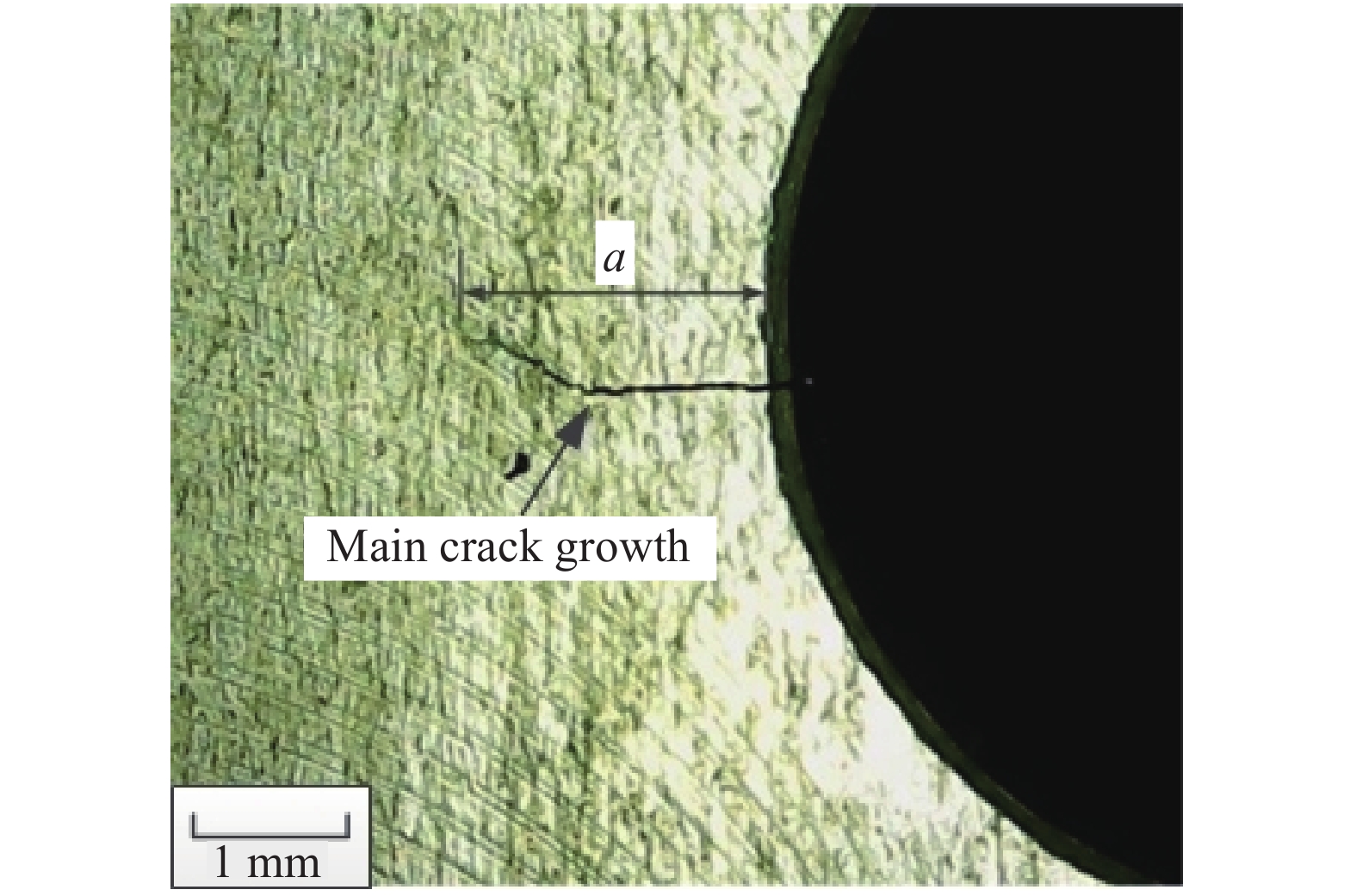
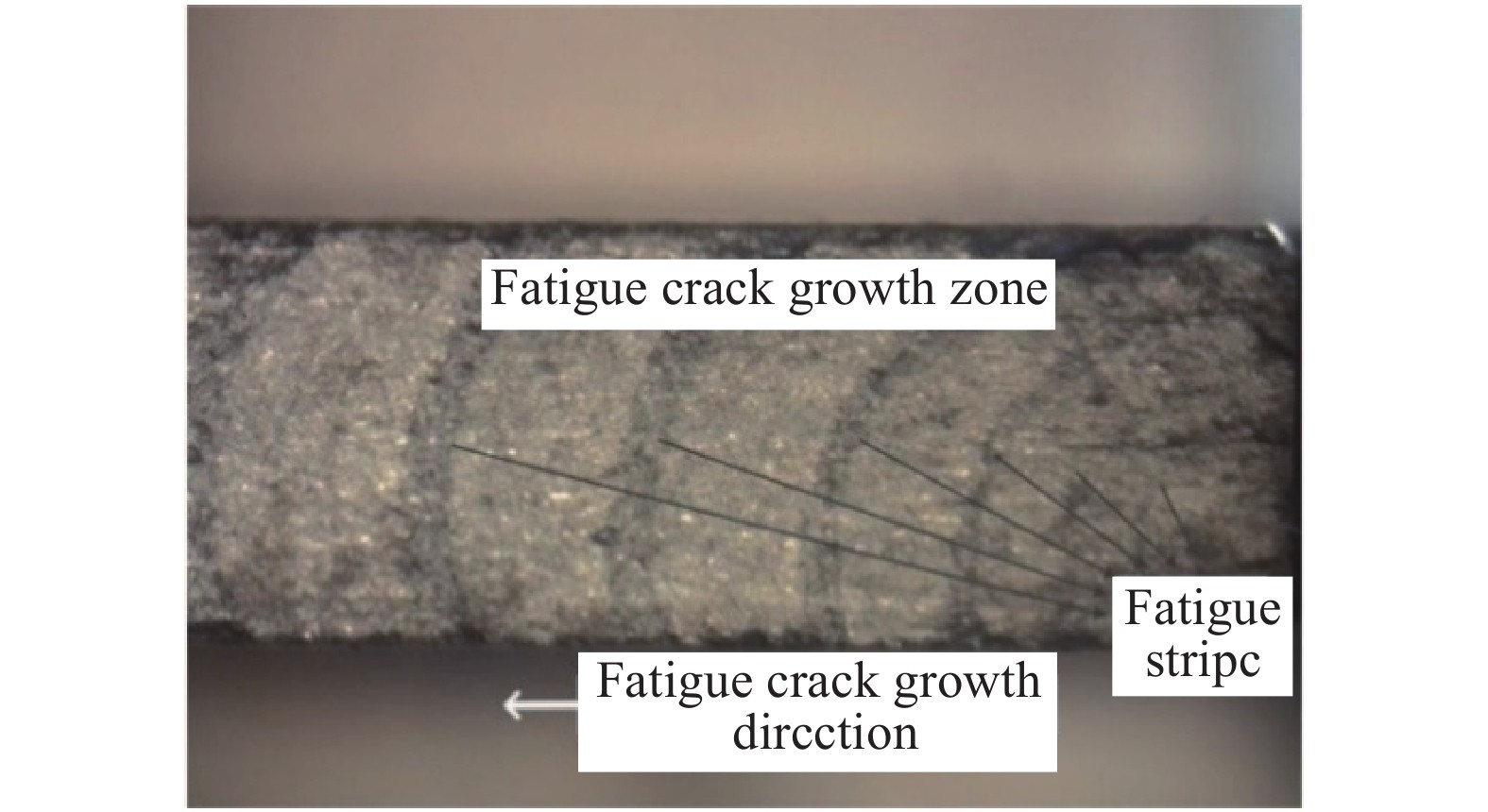
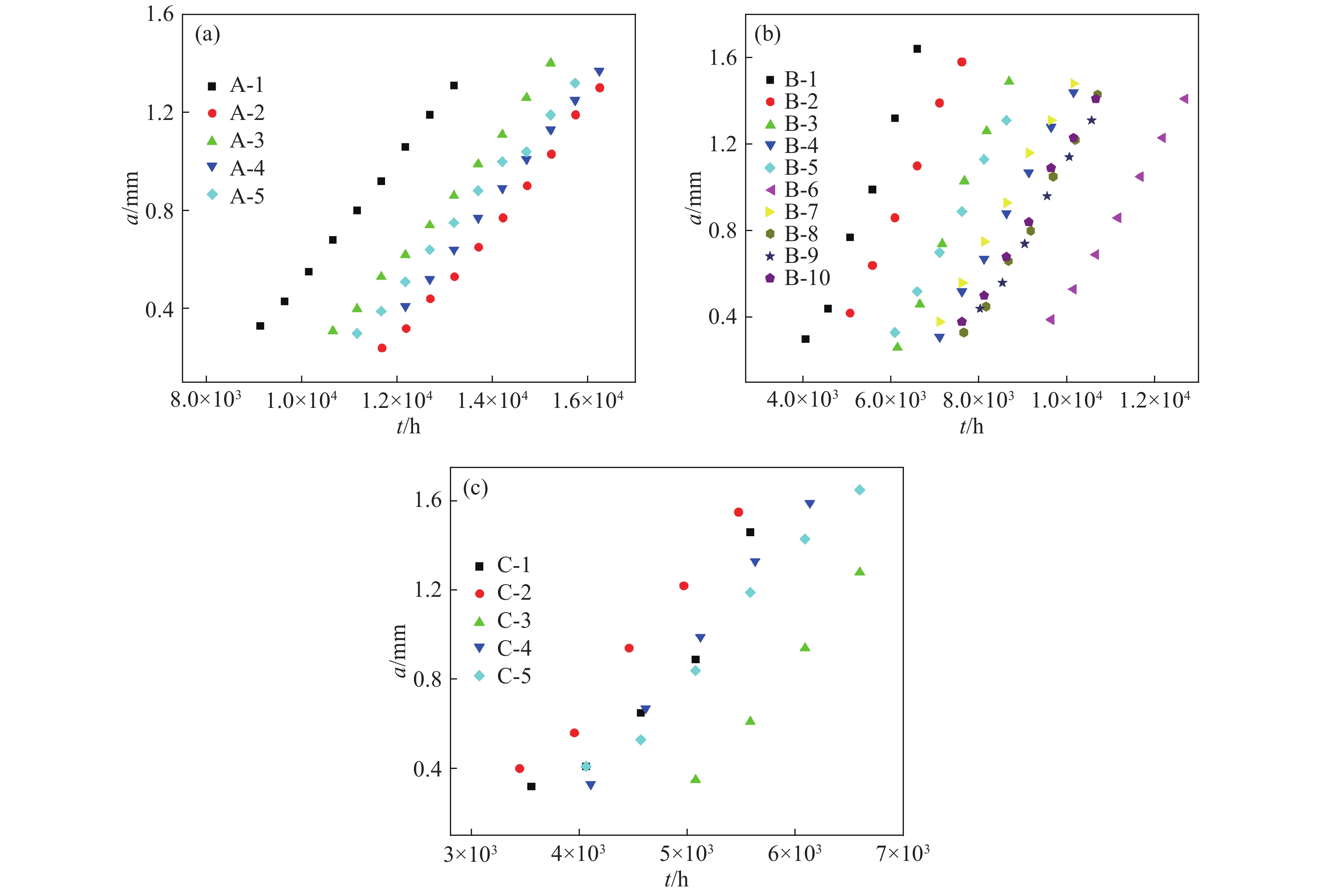
摘要: 為了對飛機機翼緣條緊固孔細節原始疲勞質量進行評估,本文首先對飛機機翼緣條結構中常用的BXXX鋁合金緊固孔試件分別開展了高、中、低3種應力水平下的疲勞試驗,通過斷口判讀和反推得到3組關于裂紋長度a和疲勞壽命t的(a?t)數據,在此基礎上應用當量初始缺陷尺寸(EIFS)控制方程對每個試件的EIFS值進行計算并初步評估,驗證了在不同應力水平下緊固孔結構細節的EIFS無顯著性差異;得到了緊固孔結構細節的裂紋萌生時間(TTCI)分布,在指定應力水平下對緊固孔結構細節95%置信水平下的經濟壽命進行預測,并與設計壽命進行對比,提出了一種不同超越概率P下的結構細節當量初始缺陷尺寸模型,基于給定5%的裂紋超越概率,對結構細節的通用EIFS分布進行評估。通過以上對飛機機翼緣條緊固孔細節原始疲勞質量的三重評估,得到綜合評估結果:飛機機翼緣條緊固孔細節原始疲勞質量滿足要求。Abstract: On analyzing the details of kinetic links of parts and structures of aircrafts, one can find few bad links. But fastener hole is the weakest link where abnormal stress is produced and initiation of crack occurs. The initial fatigue quality of aircraft wing flange fastener is the key parameter, which affects the durability of aircraft structure. The initial fatigue quality of structural details is usually characterized by the equivalent initial defect size (EIFS) and the time to crack initiation (TTCI). To evaluate the initial fatigue quality of aircraft wing flange fastener hole details, this paper first carried out fatigue tests at high-, medium- and low-stress levels on the BXXX aluminum alloy fastener hole specimens generally used in aircraft wing flange structures, and obtained three groups of (a?t) datasets about crack length a and fatigue life t through fracture interpretation and back stepping. On this basis, the EIFS governing equation was used to evaluate the EIFS value of each specimen, and it is found out that there is no significant difference in equivalent initial flaw size under different stress levels; TTCI distribution of structural details is obtained, and the economic life of specified stress level under 95% confidence level of fastener hole structural details was predicted, and compared with the design life; a structural detail equivalent to initial flaw size model under different exceedance probability P was proposed. Based on the given 5% crack exceedance probability, the general EIFS distribution of structural details was evaluated. The comprehensive evaluation results were obtained through the above triple evaluation of the initial fatigue quality of the fastener hole details: the general EIFS distribution and the EIFS value of each test piece are less than the allowable value, and the economic life is greater than the allowable value, so the original fatigue quality of the details of the fastening holes of the aircraft flange meets the stringent requirements.
-
表 1 方差分析表
Table 1. Analysis of variance
Source Sum of deviation squares Degree of freedom Mean square deviation F value Between groups 0.0000350 2 0.0000175 0.341 Within Groups 0.0008733 17 0.00005137 Total 0.0000908 19 — Note: The degree of freedom refers to the number of variables whose values are not restricted when calculating a certain statistic. Usually the degree of freedom takes df=n-k, where n is the number of samples and k is the number of restricted conditions or variables. 表 2 TTCI分布參數
Table 2. TTCI distribution parameters
Group number $ \beta $ $ \varepsilon $ $ \alpha $ A 17956 453 6.529 B 10558 267 C 6832 172 表 3 經濟壽命
$ {T}_{\mathrm{e}} $ Table 3. Economic life
$ {T}_{\mathrm{e}} $ Group number Economic life, Te/h A 11829 B 6956 C 4501 表 4 通用EIFS分布參數
Table 4. General EIFS distribution parameters
Group number Qi/10?4 Qβ $ \alpha $ A 3.04 5.446 6.529 B 5.17 C 7.99 表 5 綜合評估結果
Table 5. Comprehensive assessment results
Evaluation EIFS value of each specimen/mm General EIFS distribution/mm TTCI/h Calculated value 0.00545–0.02599 0.02194 4501 Allowable value 0.125 0.125 4000 Evaluation conclusion IFQ meets requirements IFQ meets requirements IFQ meets requirements 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Chikmath L, Ramanath M N, Dattaguru B. Fatigue life benefits of cold worked holes in fastener joints. Procedia Struct Integr, 2019, 14: 922 doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2019.07.072 [2] Correia J A F O, Blasón S, De Jesus A M P, et al. Fatigue life prediction based on an equivalent initial flaw size approach and a new normalized fatigue crack growth model. Eng Fail Anal, 2016, 69: 15 doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.04.003 [3] Zhao T L, Liu Z Y, Du C W, et al. Modeling for corrosion fatigue crack initiation life based on corrosion kinetics and equivalent initial flaw size theory. Corros Sci, 2018, 142: 277 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018.07.031 [4] Chinese Aviation Institute. Military Aircraft Fatigue, Damage Tolerance and Durability Design Manual. Beijing: Chinese Aviation Institute Press, 1994中國航空研究院. 軍用飛機疲勞·損傷容限·耐久性設計手冊. 北京: 中國航空研究院出版社, 1994 [5] Liu W T, Zheng M Z, Fei B J. Probability Fracture Mechanics and Probabilistic Damage Tolerance/Durability. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1999劉文珽, 鄭旻仲, 費斌軍. 概率斷裂力學與概率損傷容限/耐久性. 北京: 北京航空航天大學出版社, 1999 [6] Fawaz S A. Equivalent initial flaw size testing and analysis of transport aircraft skin splices. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 2003, 26(3): 279 doi: 10.1046/j.1460-2695.2003.00637.x [7] Makeev A, Nikishkov Y, Armanios E. A concept for quantifying equivalent initial flaw size distribution in fracture mechanics based life prediction models. Int J Fatigue, 2007, 29(1): 141 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.01.018 [8] Wang Z Z, Wang P X, Nie X Z. Evaluation approach to initial fatigue quality of fastener hole. Acta Aeron Astron Sin, 1998, 19(4): 88王志智, 王普選, 聶學洲. 一種緊固孔細節原始疲勞質量評定方法. 航空學報, 1998, 19(4):88 [9] Zhang Y T. Durability Analysis of An Aircraft Wing Box[Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008張永濤. 某型飛機機翼盒段耐久性分析[學位論文]. 南京: 南京航空航天大學, 2008 [10] Xiang Y B, Lu Z Z, Liu Y M. Crack growth-based fatigue life prediction using an equivalent initial flaw model. Part I: uniaxial loading. Int J Fatigue, 2010, 32(2): 341 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2009.07.011 [11] Nicolas A, Co N E C, Burns J T, et al. Predicting fatigue crack initiation from coupled microstructure and corrosion morphology effects. Eng Fracture Mech, 2019, 220: 106661 doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106661 [12] Rudd J L. Application of the Equivalent Initial Quality Method AFFDL-TM-76-83-FBE. Dayton: Wright AFB, 1977 [13] Rudd J L, Gray T D. Quantification of fastener-hole quality. J Aircraft, 1978, 15(3): 143 doi: 10.2514/3.58332 [14] Yang J N. Statistical Estimation of Economic Life for Aircraft Structures. J Aircraft, 1980, 17(7): 528 doi: 10.2514/3.57935 [15] Wang D Y. An Investigation of Initial Fatigue Quality: STPZ8860S. West Conshohochen: ASTM Special Technical Publication, 1982 [16] AFFD System Engineering Office of the Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics. The Background Information of USAF Durability Design Handbook: Vol.Ⅷ. Xi’an: AFFD System Engineering Office of the Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1989航空航天部 AFFD 系統辦公室. 美國空軍耐久性手冊背景材料: 第Ⅷ卷. 西安: 航空航天部 AFFD 系統辦公室, 1989 [17] Moreira P M G P, de Matos P F P, de Castro P M S T. Fatigue striation spacing and equivalent initial flaw size in Al 2024-T3 riveted specimens. Theoret Appl Fract Mech, 2005, 43(1): 89 doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2004.12.005 [18] Shahani A R, Kashani H M. Assessment of equivalent initial flaw size estimation methods in fatigue life prediction using compact tension specimen tests. Eng Fract Mech, 2013, 99: 48 doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2013.01.007 [19] Wu Y Z, Xu Y W, Guo X, et al. Fatigue life prediction based on equivalent initial flaw size for Al-Li alloy 2297 under spectrum loading. Int J Fatigue, 2017, 103: 39 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.04.015 [20] Cao C N, Wang Z Z, Zhao X M. Evaluation and coincidence check for initial fatigue quality of fastener hole. J Northwest Polytech Univ, 2000, 18(1): 15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2000.01.004曹昌年, 王志智, 趙選民. 緊固孔原始疲勞質量評定及符合性檢查. 西北工業大學學報, 2000, 18(1):15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2000.01.004 [21] Zhang S, He Y T, Zhang T, et al. Assessment on initial fatigue quality of aircraft typical connected structure. J Mech Strength, 2016, 38(3): 480張勝, 何宇廷, 張騰, 等. 飛機典型連接結構原始疲勞質量評估. 機械強度, 2016, 38(3):480 [22] Zhou J J, Wang S N. Initial fatigue quality assessment for aircraft wing panel fastener hole. J Northwest Polytech Univ, 2018, 36(1): 91 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2018.01.013周俊杰, 王生楠. 飛機機翼壁板緊固孔細節原始疲勞質量評估. 西北工業大學學報, 2018, 36(1):91 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2018.01.013 [23] He Y T, Zhang T, Cui R H, et al. Theory and Technology of Aircraft Structural Life Control. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017何宇廷, 張騰, 崔榮洪, 等. 飛機結構壽命控制原理與技術. 北京: 國防工業出版社, 2017 [24] Provan J W. Probabilistic Fracture Mechanics and Reliability. Leiden: Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, 1987 [25] Gao Z T. Fatigue Application Statistics. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1986高鎮同. 疲勞應用統計學. 北京: 國防工業出版社, 1986 [26] Chen Z L, Chen Y Z, Gong X Q, et al. Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University Press, 2016陳振龍, 陳宜治, 龔小慶, 等. 概率論與數理統計. 杭州: 浙江工商大學出版社, 2016 -




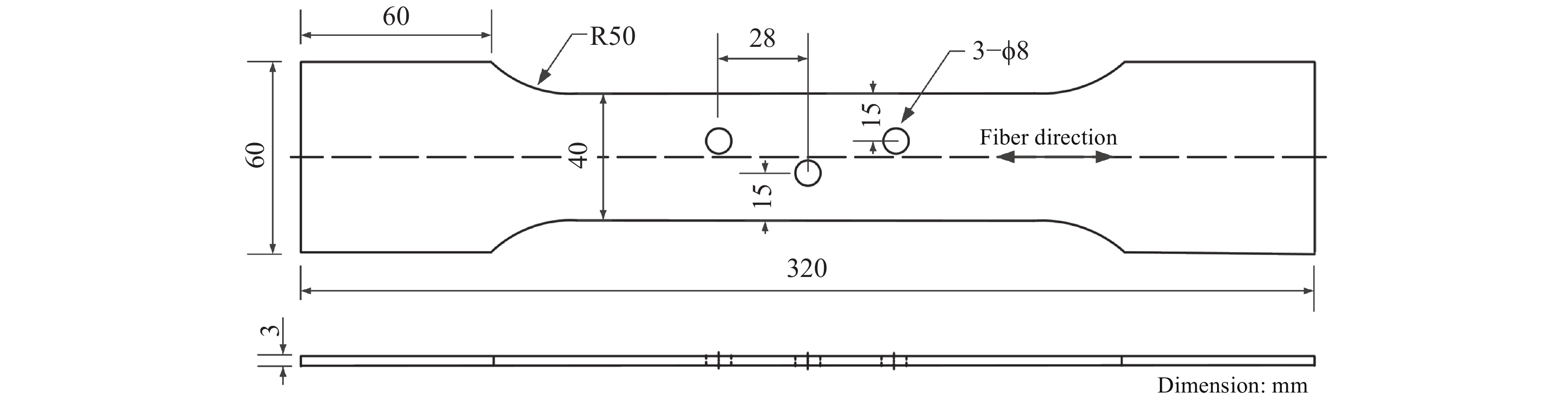
 下載:
下載: