-
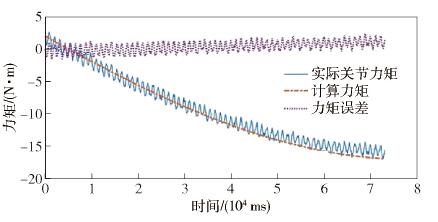
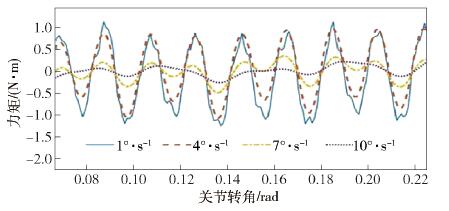
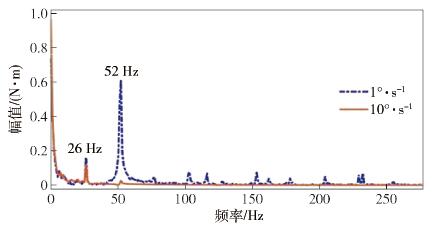
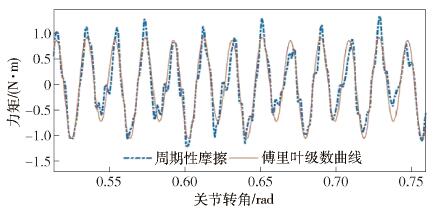
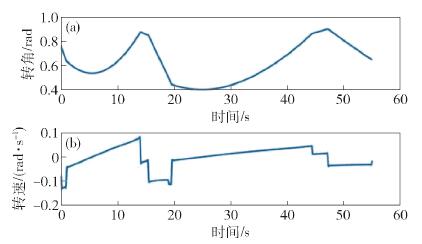
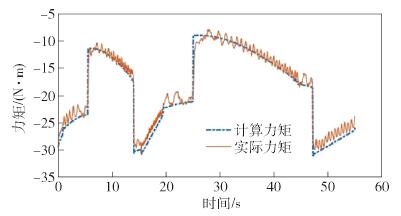
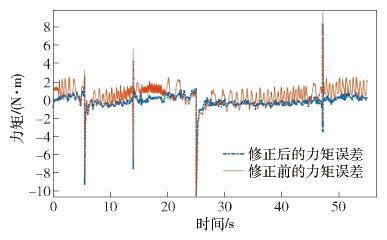
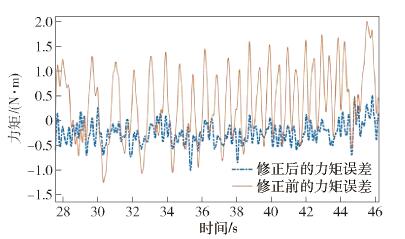
摘要: 針對機器人諧波減速器關節在轉動過程中存在的波動摩擦力矩, 提出一種基于傅里葉級數函數和BP神經網絡的建模方法, 并完善機器人的動力學模型, 修正了因波動摩擦力矩帶來的關節力矩計算誤差. 通過研究諧波減速器關節的波動摩擦力矩在不同影響因素下的變化特性, 采用傅里葉級數與BP神經網絡結合的方法對波動摩擦力矩進行建模. 通過添加傅里葉級數函數作為BP神經網絡的輔助輸入, 克服了力矩誤差曲線因存在高頻周期性波動而難以擬合的困難. 在離線環境下訓練神經網絡, 完成對關節波動摩擦力矩的建模, 進而完善機器人的動力學模型和修正關節中存在的波動摩擦力矩. 驗證實驗表明, 使用完善后的動力學模型可以有效計算諧波減速器關節的波動摩擦力矩, 并使修正后的力矩誤差維持在[-0.5, 0.5] N·m的范圍之內, 方差為0.1659 N2·m2, 是修正前的24.23%.Abstract: For sensorless force control of a robot such as by drag-teaching and collision detection, the control accuracy depends on the accuracy of the robot dynamics model. The error of the robot dynamics model comes from two aspects, modeling and identification errors and from unmodeled dynamics. Among the unmodeled dynamics, one of the important sources of unmodeled dynamic is the friction inside the robot reducer. When the reducer rotates, there is mutual extrusion and friction between the internal components of the reducer. This kind of friction will change as the gear meshing state transforms, resulting in the phenomenon of wave friction torque. A remarkable feature of wave friction torque is that it has a periodic relationship with the joint location and it is often modeled by the Fourier series function. Wave friction torque is obvious when the rotational speed of the joint is low and decreases with the increase in rotational speed. In order to improve the accuracy of the robot dynamics model, the wave friction torque needs to be modeled and eliminated. Aiming at the wave friction of the robot harmonic joint during the rotation process, a modeling method based on a Fourier series function and BP neural network was proposed, the dynamic model of the robot was optimized, and the calculation error of the joint torque caused by the wave friction was corrected. By studying the variation characteristics of the wave friction of the harmonic reducer joint under different influencing factors, the combination of the Fourier series and BP neural network was used to model the wave friction. By adding the Fourier series function as the auxiliary input of the BP neural network, the difficulty of fitting the torque error curve due to the presence of high frequency periodic fluctuations was overcome. The neural network was trained in the off-line environment to complete the modeling of the wave friction, and then to improve the dynamic model of the robot and correct the wave friction. The experimental results show that the improved dynamic model can effectively predict the wave friction of the harmonic reducer joint and keep the corrected torque error within the range of[-0.5, 0.5] N·m, and the variance is 0.1659 N2·m2, which is 24.23% before the correction.
-
表 1 傅里葉級數參數
Table 1. Fourier series parameters
a0/
(N·m)a1/
(N·m)b1/
(N·m)a2/
(N·m)b2/
(N·m)w0/
(rad·s-1)0.0005784 0.1666 -0.02131 -0.8926 -0.1009 162 表 2 各軌跡點的三維坐標(單位:m)
Table 2. -dimensional coordinates of each track point (unit: m)
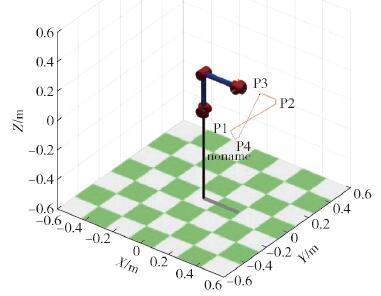
示教點 X Y Z P1 0.3199 -0.1666 0.06901 P2 0.3309 0.2487 0.04331 P3 0.2469 0.2080 0.09832 P4 0.3785 -0.1641 0.04621 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Iwatani M, Kikuuwe R. Some improvements in elastoplastic friction compensator. SICE J Control Meas Syst Integration, 2017, 10(3): 141 doi: 10.9746/jcmsi.10.141 [2] De Luca A, Mattone R. Sensorless robot collision detection and hybrid force/motion control//Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Barcelona, 2005: 999 [3] Haddadin S, De Luca A, Albu-Schaffer A. Robot collisions: A survey on detection, isolation, and identification. IEEE Trans Rob, 2017, 33(6): 1292 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2723903 [4] Gandhi P S, Ghorbel F H, Dabney J. Modeling, identification, and compensation of friction in harmonic drives//Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision & Control. Las Vegas, 2002: 160 [5] Liao H B, Fan S X, Fan D P. Friction compensation of harmonic gear based on location relationship. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part I J Syst Control Eng, 2016, 230(8): 695 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/304070594_Friction_compensation_of_harmonic_gear_based_on_location_relationship [6] Wu W X. Joint Friction Analysis and Low-speed Hight-precision Motion Control of Multi-DOF Serial Robots[Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013吳文祥. 多自由度串聯機器人關節摩擦分析與低速高精度運動控制[學位論文]. 杭州: 浙江大學, 2013 [7] Zhu S Q, Wu W X, Wang X Y, et al. Slow motion control of serial robots with harmonic drives considering friction compensation. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach, 2013, 44(11): 293 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.11.050朱世強, 吳文祥, 王宣銀, 等. 考慮摩擦的諧波驅動機器人低速運動控制方法. 農業機械學報, 2013, 44(11): 293 doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.11.050 [8] Liu J. The application of BP neural network in multidimensional nonlinear function. J Shangluo Univ, 2014, 28(6): 19 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLSF201406009.htm劉俊. BP神經網絡在多維非線性函數擬合中的應用. 商洛學院學報, 2014, 28(6): 19 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLSF201406009.htm [9] Lin Y F, Deng H M, Shi X Y. Application of BP neural network based on newly improved particle swarm optimization algorithm in fitting nonlinear function. Comput Sci, 2017, 44(11A): 51 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.11A.009林宇鋒, 鄧洪敏, 史興宇. 基于新的改進粒子群算法的BP神經網絡在擬合非線性函數中的應用. 計算機科學, 2017, 44(11A): 51 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.11A.009 [10] Wu W X, Zhu S Q, Jin X L. Dynamic identification for robot manipulators based on modified Fourier series. J Zhejiang Univ Eng Sci, 2013, 47(2): 231 doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2013.02.006吳文祥, 朱世強, 靳興來. 基于改進傅里葉級數的機器人動力學參數辨識. 浙江大學學報: 工學版, 2013, 47(2): 231 doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2013.02.006 [11] Khalil W, Gautier M, Lemoine P. Identification of the payload inertial parameters of industrial manipulators//Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Roma, 2007: 4943 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/224705850_Identification_of_the_payload_inertial_parameters_of_industrial_manipulators [12] Sousa C D, Cortes?o R. Physical feasibility of robot base inertial parameter identification: a linear matrix inequality approach. Int J Rob Res, 2014, 33(6): 931 doi: 10.1177/0278364913514870 [13] Xu F Y. Design method of filter for audio noise reduction based on application of Matlab. Audio Eng, 2017, 41(2): 28 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJS201702006.htm徐帆云. 基于Matlab的音頻降噪濾波器設計. 電聲技術, 2017, 41(2): 28 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJS201702006.htm [14] Yuan F. Comparison of several filtering methods based on MATLAB. Power Supply Technol Appl, 2013(10): 50 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201401029.htm遠飛. 基于MATLAB的幾種濾波方法比較. 電源技術應用, 2013(10): 50 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201401029.htm [15] Taghirad H D, Belanger P R. Modeling and parameter identification of harmonic drive systems. J Dyn Syst Meas Control, 1998, 120(4): 439 doi: 10.1115/1.2801484 [16] Gandhi P S. Modeling and Control of Nonlinear Transmission Attributes in Harmonic Drive Systems[Dissertation]. Houston: Rice University, 2001 [17] Ye H W, Yang L F, Liu X Z. Optimizing weight and threshold of BP neural network using SFLA: applications to nonlinear function fitting//Fourth International Conference on Emerging Intelligent Data and Web Technologies. Xi'an, 2013: 211 [18] Liu S, Gang T Q. Adaptive back-stepping control of the harmonic drive system with LuGre model-based friction compensation. AIP Conf Proc, 2018, 1944: 020027-1 http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2018AIPC.1944b0027L -




 下載:
下載: