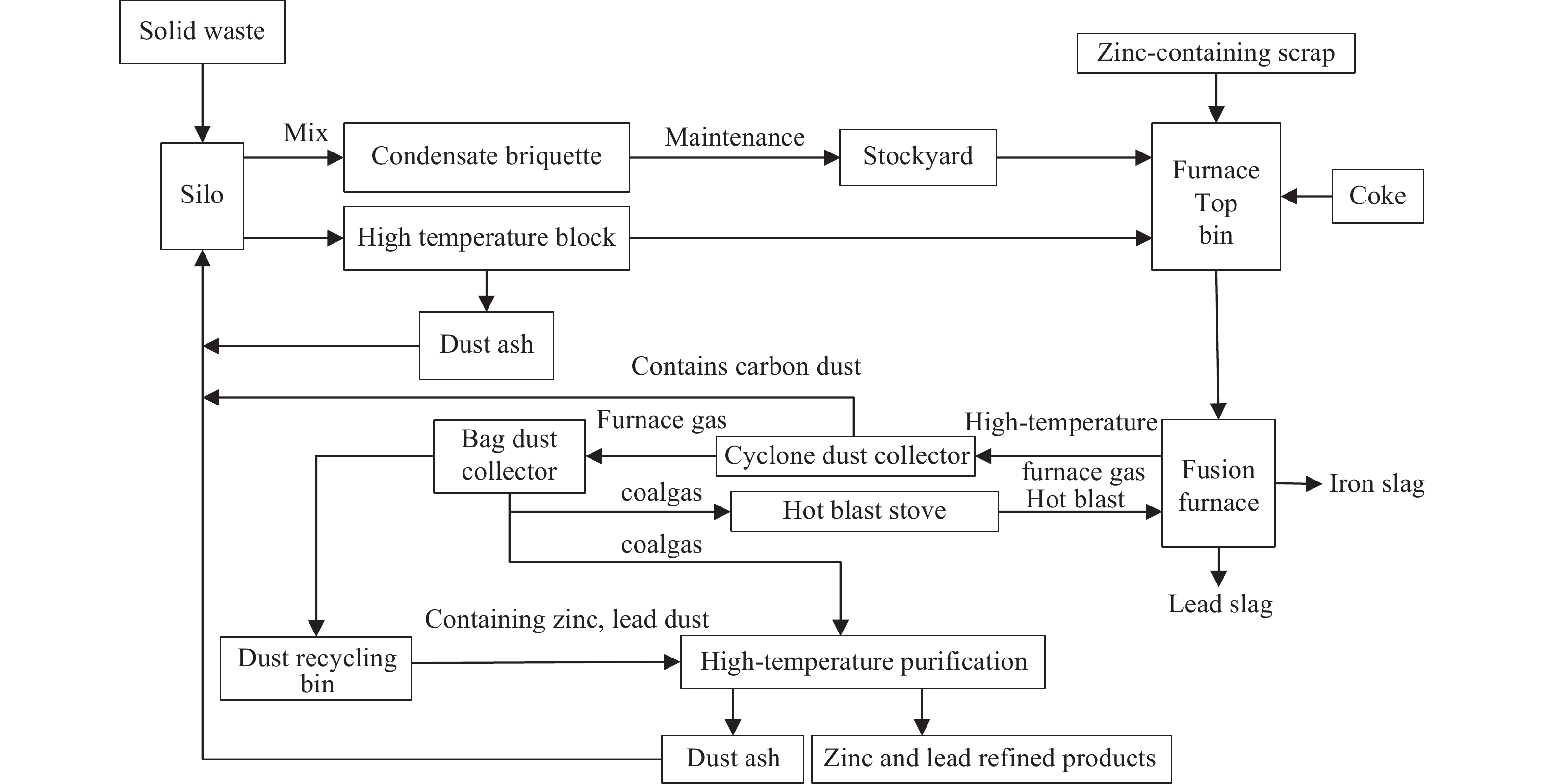
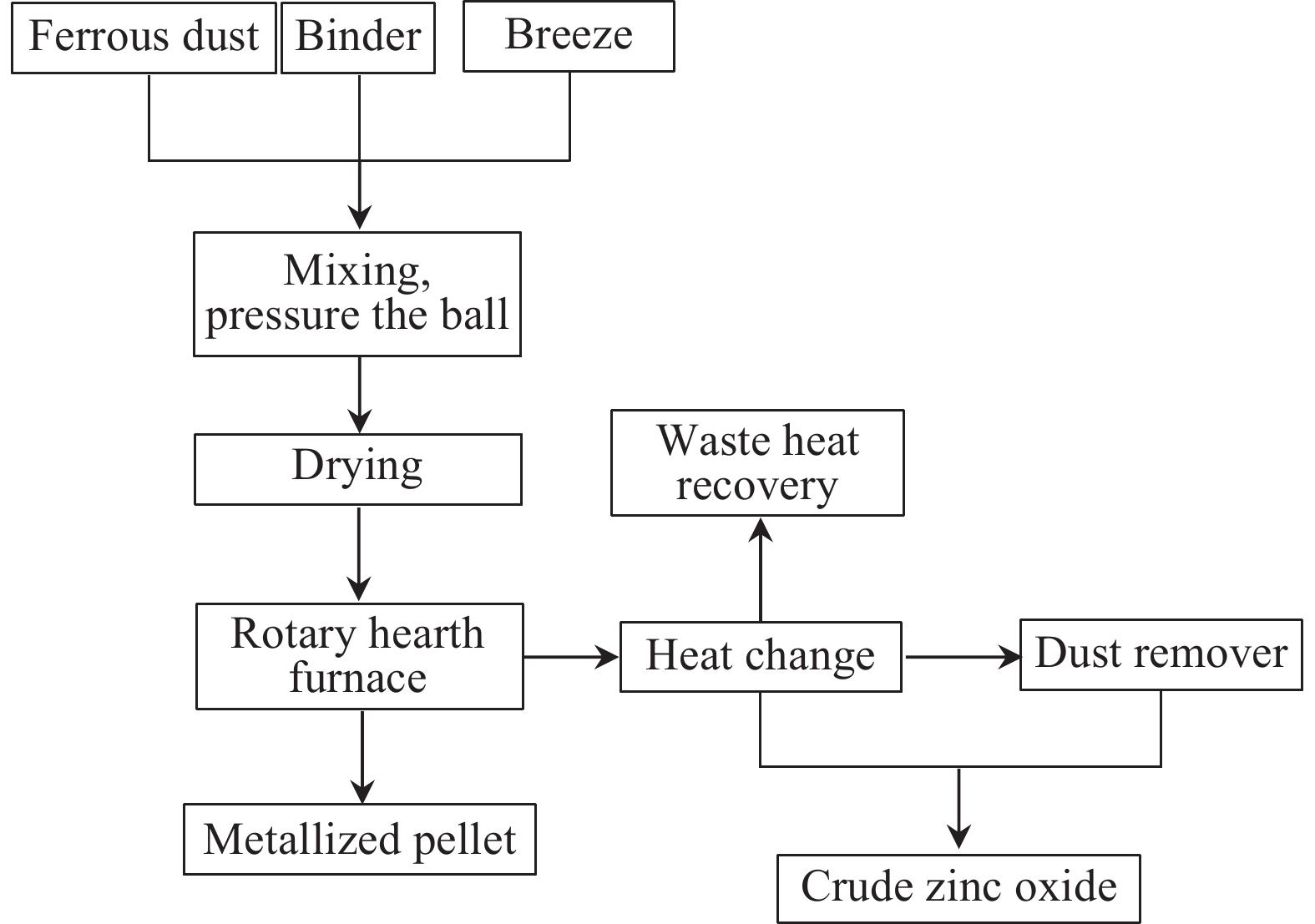
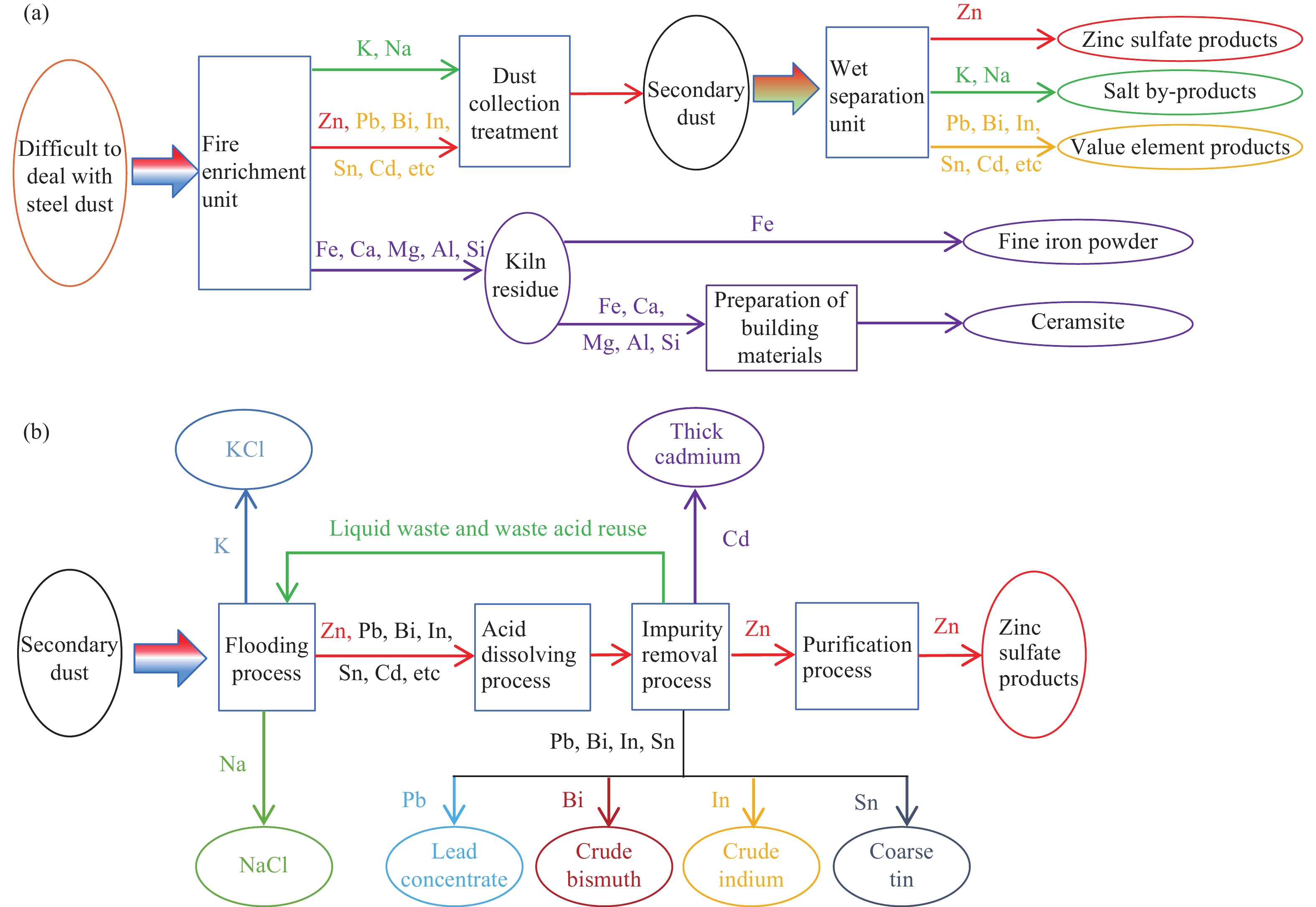
Progress in treating difficult-to-handle dust and sludge and full-scale resource utilization in an iron and steel industry cluster
-
摘要: 簡述了鋼鐵冶金塵泥現有的處理工藝,具體介紹了回轉窯工藝、Oxycup工藝、轉底爐工藝。鋼鐵冶金塵泥目前的處理工藝主要停留在塵泥資源化回收利用的前3個階段,往往只針對含量較高的部分元素進行分離回收。鋼鐵產業集聚區的塵泥除了含有 Fe、Zn、Pb、K、Na 等元素,還富集了大量 In、Bi、Sn、Cd等具有高附加值的稀散元素,是寶貴的有價資源。隨著國家環保法規和產業政策的要求,鋼鐵冶金塵泥已經到了必須100%全部回收利用的新階段。鑒于此,提出了根據各自的成分特征進行基于產品設計的各種塵泥間的協同搭配、單元技術間的科學耦合和系統集成,實現多組分梯級分離和全量利用的技術方案,希望能夠為鋼鐵企業冶金塵泥的全量資源化利用提供參考。Abstract: Iron and steel metallurgical dust is a solid waste produced in the production process of the iron and steel industry. It has the characteristics of many types, large quantities, complex components, and many valuable elements. Japan and Germany have realized the centralized treatment and comprehensive utilization of metallurgical solid wastes, and China’s current technological level is still far behind them. This paper briefly described the existing treatment processes of iron and steel metallurgical dust and mud and specifically introduced the most widely used pyrotechnic processes in enterprises, including the rotary kiln, Oxycup, and rotary hearth furnace processes. The current treatment process of iron and steel metallurgical dust and sludge mainly stays in the first three stages of dust and sludge resource recycling and often only separates and recovers some elements with high contents. In addition to elements such as Fe, Zn, Pb, K, and Na, dust and mud in an iron and steel industry agglomeration area are also enriched with large amounts of valuable and rare elements with high added values such as In, Bi, Sn, and Cd, which are precious materials. The ineffective treatment and recycling of a huge volume of iron and steel metallurgical dust and mud will cause serious air, water, and soil pollutions; affect the ecological environment; and endanger human life. Moreover, it will cause a considerable loss of valuable resources, which is not conducive to the rapid development of China’s industries. With the requirements of the national environmental protection regulations and industrial policies, steel metallurgical dust and sludge have reached a new stage where 100% of all dust and sludge must be recycled. In response to this, a technical solution established on the product design based on the coordination of various types of dust and mud, scientific coupling, and system integration among unit technologies was proposed according to their respective composition characteristics to achieve multicomponent cascade separation and full utilization. The full resource utilization of metallurgical dust and sludge in iron and steel enterprises provides a reference.
-
表 1 某鋼鐵廠典型粉塵的化學成分(質量分數)
Table 1. Chemical composition of typical dust in a steel plant
% Type TFe SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 K Na C Zn Sintering head ash 28.50 3.00 5.20 1.00 1.70 26.20 1.36 2.25 1.12 Blast furnace dry ash 17.03 2.87 2.18 0.70 2.49 0.76 0.28 34.00 16.60 Converter OG mud 58.19 1.98 10.28 3.47 1.83 0.19 0.21 1.65 0.25 Rolling line sludge 71.73 1.39 0.02 0.03 1.19 0.14 0.36 1.12 0.13 Electric furnace ash 44.73 2.06 2.92 1.38 0.56 1.32 1.32 1.14 2.61 表 2 某廠二次灰的化學成分(質量分數)
Table 2. Chemical composition of secondary ash from a factory
% Zn Pb Bi In Sn Cd 49.150 6.410 0.240 0.042 0.350 0.073 表 3 某鋼鐵廠典型粉塵的粒度組成和比表面積
Table 3. Particle size composition and specific surface area of typical dust from a steel plant
Type X10/μm X50/μm X90/μm Specific surface area/(m2·g?1) Blast furnace dry ash 3.940 17.041 58.550 0.730 Converter OG Mud 0.631 1.207 2.508 6.521 Rolling line sludge 3.772 27.846 84.268 0.667 Electric furnace ash 0.888 1.941 4.068 4.350 Notes: X10 is the particle size corresponding to a cumulative particle size distribution of 10% of the sample; X50 is the particle size corresponding to a cumulative particle size distribution of 50% of the sample; X90 is the particle size corresponding to a cumulative particle size distribution of 90% of the sample. 表 4 火法工藝中發生的化學反應方程式
Table 4. Chemical reaction equations that occur in the pyrometallurgical process
Element Reaction equation Reduction reaction first Oxidation reaction in the second step Zn ZnO(s) + CO(g) = Zn(g) + CO2(g) 2Zn(g) + O2(g) = 2ZnO(g) Pb PbO(s) +CO(g) =Pb(g) +CO2(g) 2Pb(g) +O2(g) =2PbO(g) In In2O3(s) + 3CO(g) = 2In(g) + 3CO2(g) 4In(g) + 3O2(g) = 2In2O3(g) Sn SnO2(s) + 2CO(g) = Sn(g) + 2CO2(g) Sn(l) + O2(g) = SnO2(g) Cd CdO(s) + CO(g) = Cd(g) + CO2(g) 2Cd(g) + O2(g) = 2CdO(g) Bi Bi2O3(s) + 3CO(g) = 2Bi(g) + 3CO2(g) 4Bi(g) + 3O2(g) = 2Bi2O3(g) Fe FeO(s) + CO(g) = Fe(g) + CO2(g) — 表 5 國內典型企業轉底爐生產工藝情況
Table 5. Production process of a rotary hearth furnace in typical domestic enterprises
Company Technology Source of technology Production time Implementation effect Shanxi Jicheng 7×104 t·a?1 USTB 2004 — Sinosteel Taiwan 1.3×105 t·a?1, driquetting Nippon Steel 2007.12 Initial dissatisfaction,
regular maintenanceTianjin Rongcheng 4×105 t·a?1 SHENWU 2009 — Ma Steel 2×105 t·a?1, disc pelletizing Nippon Steel 2009.6 Initial dissatisfaction, high energy consumption, currently running stable PANGANG 1×105 t·a?1 SHENWU — — Rizhao Steel 2×105 t·a?1, briquetting CISRI 2010.5 High operating energy consumption SHAGANG 4.2×105 t·a?1, briquetting SHENWU 2010.10 High equipment failure rate, low operation rate LAIGANG 3.2×105 t·a?1, briquetting USTB 2011.3 Bonding and clogging of the boiler in the initial flue gas system BAOWU Zhanjiang 2×105 t·a?1, metalized pellets MCC 2016.6 Dezincification rate>85% BAOWU SHAOGANG 2.5×105 t·a?1 SMDRI 2020 Normal production SHOUGANG
JINGTANG3×105 t·a?1 MCC 2020.7 Normal production ZHANJIANG Phase II 2×105 t·a?1, metalized pellets MCC 2021.4 Stable operation of system and equipment BAOWU BAOSHAN 5×105 t·a?1, metalized pellets MCC — Successful hot test in January 2021 Note: USTB stands for the University of Science and Technology Beijing; SHENWU corresponds to Shenwu Technology Group Corp; CISRI refers to China Iron & Steel Research Institute Group; MCC is CISDI Engineering Co., Ltd; and SMDRI is Shanghai Meishan Industrial and Civil Engineering Design & Research Institute Co., Ltd. 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Oda H, Ibaraki T, Abe Y. Dust recycling system by the rotary hearth furnace. Nippon Steel Technical Report, 2006(94): 147 [2] Yang X F, Chu M S, Shen F M, et al. Mechanism of zinc damaging to blast furnace tuyere refractory. Acta Metall Sin (Engl Lett) , 2009, 22(6): 454 doi: 10.1016/S1006-7191(08)60123-4 [3] Guo X J, Shu X W, Liang G, et al. Iron-bearing dust and sludge treatment technology in iron and steel enterprise. Environ Eng, 2011, 29(2): 96郭秀鍵, 舒型武, 梁廣, 等. 鋼鐵企業含鐵塵泥處理與利用工藝. 環境工程, 2011, 29(2):96 [4] Havlík T, Vidor e Souza B, Bernardes A M, et al. Hydrometallurgical processing of carbon steel EAF dust. J Hazard Mater, 2006, 135(1-3): 311 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.067 [5] Wang Q. Research on Zinc Removal from Metallurgy Dust Containing Iron [Dissertation]. Tangshan: Hebei Union University, 2014王瓊. 含鐵塵泥還原脫鋅過程的研究[學位論文]. 唐山: 河北聯合大學, 2014 [6] Smith S M, Zhou X, Nassaralla C L. A novel process for recycling steelmaking dust. Iron steelmaker, 2000, 27(2): 69 [7] Zhang J L, Li Y, Yuan X, et al. Present situation and prospect of dust treatment in Chinese iron and steel enterprises. Iron Steel, 2018, 53(6): 1張建良, 李洋, 袁驤, 等. 中國鋼鐵企業塵泥處理現狀及展望. 鋼鐵, 2018, 53(6):1 [8] Itoh S, Tsubone A, Matsubae-Yokoyama K, et al. New EAF dust treatment process with the aid of strong magnetic field. ISIJ Int, 2008, 48(10): 1339 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.48.1339 [9] He H Y, Tang Z Y, Pei W B, et al. Preparation of metallization pellets with BF gas dust and converter sludge. Chin J Process Eng, 2012, 12(1): 92何環宇, 唐忠勇, 裴文博, 等. 高爐瓦斯灰和轉爐污泥造塊制備金屬化球團. 過程工程學報, 2012, 12(1):92 [10] She X F. Fundamental Research on the Process of Direct Reduction Treatment of Zinc-containing Dust and Sludge in Iron and Steel Plants With Rotary Hearth Furnace [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2011佘雪峰. 轉底爐直接還原處理鋼鐵廠含鋅塵泥工藝基礎研究 [學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2011 [11] Zhang G Z. Thoughts on strengthening the planning and construction of industrial clusters [N/OL]. Anyang News (2009-11-02) [2021-11-10].https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&filename=AYRB200911020014張廣智. 加強產業集聚區規劃和建設的思考[N/OL]. 安陽日報(2009-11-02) [2021-11-10].https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&filename=AYRB200911020014 [12] Mantovani M C, Takano C. The strength and the high temperature behaviors of self-reducing pellets containing EAF dust. ISIJ Int, 2000, 40(3): 224 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.224 [13] Bruckard W J, Davey K J, Rodopoulos T, et al. Water leaching and magnetic separation for decreasing the chloride level and upgrading the zinc content of EAF steelmaking baghouse dusts. Int J Miner Process, 2005, 75(1-2): 1 doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2004.04.007 [14] Tian W, Yue C S, Peng B. Analysis of the characteristics and disposal technology of metallurgical dust. Conserv Util Miner Resour, 2019, 39(3): 105田瑋, 岳昌盛, 彭犇. 鋼鐵冶金塵泥的產生及處置利用技術分析. 礦產保護與利用, 2019, 39(3):105 [15] Liu N, Zhao B G, Xin G S. Process optimization of converter in Baogang steelmaking plant. China Metall, 2017, 27(9): 38劉南, 趙保國, 辛廣勝. 包鋼煉鋼廠轉爐工藝優化. 中國冶金, 2017, 27(9):38 [16] Dutra A J B, Paiva P R P, Tavares L M. Alkaline leaching of zinc from electric arc furnace steel dust. Miner Eng, 2006, 19(5): 478 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005.08.013 [17] Chen Y X, Feng W J. On the centralized treatment and comprehensive utilization of metallurgical dust. Sinter Pelletizing, 2005, 30(5): 42陳硯雄, 馮萬靜. 鋼鐵企業粉塵的綜合處理與利用. 燒結球團, 2005, 30(5):42 [18] Wolf C, Jensen J. Recycling of dusts from the electric-arc furnace. Asia Steel, 1999: 123 [19] Ding Y G, Wang J S, Zeng H, et al. Research on reduction kinetics of carbon-bearing pellets of BOF dust and sludge. Chin J Process Eng, 2010, 10(Suppl 1): 73丁銀貴, 王靜松, 曾暉, 等. 轉爐塵泥含碳球團還原動力學研究. 過程工程學報, 2010, 10(增刊1): 73 [20] Shang H X, Li H M, Wei R F, et al. Present situation and prospect of iron and steel dust and sludge utilization technology. Iron Steel, 2019, 54(3): 9尚海霞, 李海銘, 魏汝飛, 等. 鋼鐵塵泥的利用技術現狀及展望. 鋼鐵, 2019, 54(3):9 [21] Zhang L, Guo X Y, Tian Q H, et al. Selective separation of arsenic from high-arsenic dust in the NaOH-S system based on response surface methodology. J Sustainable Metall, 2021, 7: 684 doi: 10.1007/s40831-021-00372-0 [22] Ruiz O, Clemente C, Alonso M, et al. Recycling of an electric arc furnace flue dust to obtain high grade ZnO. J Hazard Mater, 2007, 141(1): 33 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.079 [23] Peng B, Zhang C F, Peng J, et al. Treatment of electric arc furnace dust. Multipurp Util Miner Resour, 2000(4): 33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2000.04.010彭兵, 張傳福, 彭及, 等. 電弧爐粉塵的治理. 礦產綜合利用, 2000(4):33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2000.04.010 [24] She X F, Xue Q G, Wang J S, et al. Comprehensive utilization of Zinc-containing dust in iron and steel plants and comparison of related treatment processes. Ironmaking, 2010, 29(4): 56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1471.2010.04.016佘雪峰, 薛慶國, 王靜松, 等. 鋼鐵廠含鋅粉塵綜合利用及相關處理工藝比較. 煉鐵, 2010, 29(4):56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1471.2010.04.016 [25] Yamada S, Itaya H, Hara Y. Simultaneous recovery of zinc and iron from electric arc furnace dust with a coke-packed bed smelting-reduction process. Iron Steel Eng, 1998, 75(8): 64 [26] Wang J S, Yang H X, She X F, et al. Study on mechanism of Zn, K, Na removal and flue gas formation in RHF direct reduction treat metallurgical dust process. J Chongqing Univ, 2011, 34(3): 82 doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2011.03.014王靜松, 楊慧賢, 佘雪峰, 等. 轉底爐處理冶金粉塵工藝的鋅鉀鈉脫除及煙氣形成. 重慶大學學報, 2011, 34(3):82 doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2011.03.014 [27] Zhu Y P. Practice of recovery indium, zinc and bismuth from gas ash from blast furnace. Nonferrous Met (Extr Metall) , 2009(6): 14朱耀平. 高爐瓦斯灰中銦鋅鉍的回收實踐. 有色金屬(冶煉部分), 2009(6):14 [28] Mao R, Zhang J L, Liu Z J, et al. Characteristic and resource utilization technique of dust and sludge containing iron from steel production process. J Central South Univ (Sci Technol) , 2015, 46(3): 774 doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.03.003毛瑞, 張建良, 劉征建, 等. 鋼鐵流程含鐵塵泥特性及其資源化. 中南大學學報(自然科學版), 2015, 46(3):774 doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.03.003 [29] Matsui H, Matsuo K, Yamamoto T. Waste treatment and metal recycling system for stainless steel making plant. Electric Furnace Steel, 2009, 80(2): 199 [30] Zeng G W. Review on utilization technologies of blast-furnace gas sludge. Environ Prot Chem Ind, 2015, 35(3): 279 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2015.03.011曾冠武. 高爐瓦斯泥綜合利用技術述評. 化工環保, 2015, 35(3):279 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2015.03.011 [31] Niu F S, Ni W, Zhang J X, et al. Current situation and development of comprehensive utilization of metallurgical dusts and slimes in China. Iron Steel, 2016, 51(8): 1牛福生, 倪文, 張晉霞, 等. 中國鋼鐵冶金塵泥資源化利用現狀及發展方向. 鋼鐵, 2016, 51(8):1 [32] Liu Y. Mathematical Model Investigation of Direct Reduction of Carbon-Containing Pellets Made of Metallurgical Dust in a Rotary Hearth Furnace [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015劉穎. 轉底爐內冶金粉塵含碳球團直接還原過程數學模型研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2015 [33] Strohmeier G, Bonestell J E. Steelworks residues and the Waelz kiln treatment of electric arc furnace dust. Iron Steel Eng, 1996, 73(4): 87 [34] Wang Z Y, Gao W C, Weng J K, et al. Research progress in the recovery of valuable metals from zinc leaching residue and its total material utilization. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(11): 1400王振銀, 高文成, 溫健康, 等. 鋅浸出渣有價金屬回收及全質化利用研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(11):1400 [35] Antrekowitsch J, Rosler G, Steinacker S. State of the Art in steel Mill Dust Recycling. Chem Ing Tech, 2015, 87(11): 1498 doi: 10.1002/cite.201500073 [36] Vermeulen I, Caneghem J V, Block C, et al. Environmental impact of incineration of calorific industrial waste: Rotary kiln vs. cement kiln. Waste Manage, 2012, 32(10): 1853 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.05.035 [37] Puta W D. The Recovery of Zinc from EAF dust by the waltz process. Steel Times, 1989, 217(3): 194 [38] Zhang Q M, Duan Z J, Yao T L, et al. Treatment process of Benxi Steel’s high-zinc iron-containing dust and mud rotary kiln. Mater Rev, 2014, 28(5): 109張慶明, 段志軍, 幺田林, 等. 本鋼高鋅含鐵塵泥回轉窯處理工藝. 材料導報, 2014, 28(5):109 [39] Ju J T, Dang Y J. Present state and development of zinc-bearing dust treatment process in iron and steel plants. Mater Rev, 2014, 28(9): 109巨建濤, 黨要均. 鋼鐵廠含鋅粉塵處理工藝的現狀及發展. 材料導報, 2014, 28(9):109 [40] Liu Z M, Rao L, Gui M C. Research and practice of comprehensive utilization of Fe-containing dust in Masteel. China Metall, 2018, 28(9): 71劉自民, 饒磊, 桂滿城, 等. 馬鋼含鐵塵泥綜合利用研究與實踐. 中國冶金, 2018, 28(9):71 [41] He S Z, Ye W C. Oxycup oxygen-enriched shaft furnace process-melting steelmaking ore powder and dust to produce molten iron and slag. TISCO Translation, 2012(4): 7賀淑珍, 葉文成. Oxycup富氧豎爐工藝-熔融煉鋼礦粉、塵泥生產鐵水及爐渣. 太鋼譯文, 2012(4):7 [42] Mao R, Zhang J L, Liu Z J, et al. How to deal with iron-containing dust sludge is more economical and environmentally friendly? [N/OL]. China Metallurgical News (2014-07-17) [2021-11-10]. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&filename=CYJB201407170060毛瑞, 張建良, 劉征建, 等. 含鐵塵泥如何處理更經濟環保? [N/OL]. 中國冶金報 (2014-07-17) [2021-11-10].https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&filename=CYJB201407170060 [43] Lü D R. Latest developments on treatment process for zinc-bearing dust caused by iron & steel enterprises in China and outlook of the process. Angang Technol, 2019(3): 7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2019.03.002呂冬瑞. 中國鋼鐵企業含鋅粉塵處理工藝現狀及展望. 鞍鋼技術, 2019(3):7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2019.03.002 [44] Zhang X W, Liao H Q, Bao X J, et al. Centralized treatment and resource utilization technology of dust removal ash. Metall Environ Prot, 2007, 5: 32張向偉, 廖洪強, 包向軍, 等. 除塵灰集中處理與資源化利用技術. 冶金環境保護, 2007, 5:32 [45] Zhang J L, Liu Z J, Li S Q, et al. Technical Method for Processing Steel Plant Zinc and Iron-bearing Dust Through Shaft Furnace Process: China Patent, 201710981905.5. 2017-10-20張建良, 劉征建, 李世欽, 等. 一種豎爐法處理鋼鐵廠含鋅、鐵塵泥工藝方法: 中國專利, 201710981905.5. 2017-10-20 [46] Zhu X P. Wisdom leads and makes extraordinary: The green road of Tangshan Hexing waste comprehensive utilization technology Co., Ltd. China High Tech, 2019(17): 51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4137.2019.17.026朱曉蘋. 智慧引領 鑄就不凡——記唐山鶴興廢料綜合利用科技有限公司綠色之路. 中國高新科技, 2019(17):51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4137.2019.17.026 [47] Zhu R, Ren J T, Liu G, et al. Development and practice on the rotary hearth furnace ironmaking process. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2007, 29(Suppl 1): 171朱榮, 任江濤, 劉綱, 等. 轉底爐工藝的發展與實踐. 北京科技大學學報, 2007, 29(增刊1): 171 [48] Nagata K, Kojima R, Murakami T, et al. Mechanisms of pig-iron making from magnetite ore pellets containing coal at low temperature. ISIJ Int, 2001, 41(11): 1316 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.41.1316 [49] Sawa Y, Yamamoto T, Takeda K, et al. New coal-based process to produce high quality DRI for the EAF. ISIJ Int, 2001, 41(Suppl): S17 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.41.Suppl_S17 [50] Xiao S. Itmk3—The third generation coal-based direct reduction ironmaking technology. Iron Steel, 2002, 37(8): 40曉蘇. ITmk3——第三代煤基直接還原煉鐵技術. 鋼鐵, 2002, 37(8):40 [51] Tsuge O, Kikuchi S, Tokuda K, et al. Successful iron nuggets production at ITmk3 pilot plant // 61st Ironmaking Conference Proceedings. Nashville, 2002: 511 [52] Wang X J. Theoretical Analysis and Experimental Research of RHF Treatment on Matallurgical Zinc-Bearing Wastes [Dissertation]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012王賢君. 轉底爐處理冶金含鋅塵泥的理論分析及實驗研究[學位論文]. 重慶: 重慶大學, 2012 [53] Wang D Y, Wang W Z, Chen W Q, et al. Present state and development trend of disposal technique of in-plant Zn?Pb?bearing dust. Iron Steel, 1998, 33(1): 65 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.1998.01.017王東彥, 王文忠, 陳偉慶, 等. 含鋅鉛鋼鐵廠粉塵處理技術現狀和發展趨勢分析. 鋼鐵, 1998, 33(1):65 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.1998.01.017 [54] Zhang J L, Yan Y F, Xu M, et al. Research on removal of Zn from blast furnace dust. Iron Steel, 2006, 41(10): 78 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.10.019張建良, 閆永芳, 徐萌, 等. 高爐含鋅粉塵的脫鋅處理. 鋼鐵, 2006, 41(10):78 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.10.019 [55] She X F, Xue Q G, Dong J J, et al. Study on basic properties of typical industrial dust from iron and steel plant and analysis of its utilization. Chin J Process Eng, 2009, 9(Sup 1): 7佘雪峰, 薛慶國, 董杰吉, 等. 鋼鐵廠典型粉塵的基本物性與利用途徑分析. 過程工程學報, 2009, 9(增刊1): 7 [56] She X F, Wang J S, Han Y H, et al. Comprehensive mathematical model of direct reduction for rotary hearth furnaces. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(12): 1580佘雪峰, 王靜松, 韓毅華, 等. 轉底爐直接還原工藝綜合數學模型. 北京科技大學學報, 2013, 35(12):1580 [57] An X W, Wang J S, She X F, et al. Reduction model of carbon-containing pellets made of zinc-bearing dust. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(2): 155安秀偉, 王靜松, 佘雪峰, 等. 含鋅粉塵內配碳球團還原模型. 北京科技大學學報, 2013, 35(2):155 [58] She X F, Kong L T. Development and function of rotary hearth furnace. Shandong Metall, 2015, 37(6): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4620.2015.06.001佘雪峰, 孔令壇. 轉底爐的發展及其功能. 山東冶金, 2015, 37(6):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4620.2015.06.001 [59] Gao G, Li J X, Long H M, et al. Experimental study on improving strength of dust and sludge carbon-containing pellets after drying. J Anhui Univ Technol (Nat Sci) , 2011, 28(4): 319高崗, 李家新, 龍紅明, 等. 提高塵泥含碳球團烘干后強度的實驗研究. 安徽工業大學學報(自然科學版), 2011, 28(4):319 [60] Lin X L, Peng Z W, Yan J X, et al. Pyrometallurgical recycling of electric arc furnace dust. J Cleaner Prod, 2017, 149: 1079 [61] Kawaguchi T, Kashiwaya Y. Preface to the special issue on “recycling of wastes and environmental problems”. ISIJ Int, 2000, 40(3): 211 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.211 [62] Rutherford S D, Kopflfle J T. Mesabi nugget: the world’s fifirst commercial ITmk3 plant. Iron Steel Technol. 2010, 7(3): 38 [63] Li W, Tan B F, Li K J, et al. Research status and development trend of zinc-containing solid waste recycling in iron and steel plants. Energy Sav Nonferrous Metall, 2021, 37(1): 8李威, 譚炳富, 栗克建, 等. 鋼鐵廠含鋅固廢資源循環利用研究現狀及發展態勢. 有色冶金節能, 2021, 37(1):8 [64] Zhang L F. Study on treatment of Zn-containing dust of iron and steel plants by rotary hearth furnace process in China. Sinter Pelletizing, 2012, 37(3): 57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2012.03.017張魯芳. 我國轉底爐處理鋼鐵廠含鋅粉塵技術研究. 燒結球團, 2012, 37(3):57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2012.03.017 [65] Du X E, Wang Z Y, Wang J S, et al. Problem of rotary hearth furnace and development advice. Metall Collect, 2013(2): 42杜續恩, 王再義, 王俊山, 等. 轉底爐工藝技術存在的問題與發展建議. 冶金叢刊, 2013(2):42 [66] Wang D B, Liang J L, Li H, et al. A review of recovery of zinc oxide from metallurgical zinc dust. China Nonferrous Metall, 2018, 47(6): 39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2018.06.012王冬斌, 梁精龍, 李慧, 等. 冶金含鋅粉塵中回收氧化鋅的工藝綜述. 中國有色冶金, 2018, 47(6):39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2018.06.012 [67] Hu J G, Du X E, Zhou W T. Present situation of industrialized RHF technology and its review. Sinter Pelletizing, 2013, 38(1): 36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2013.01.010胡俊鴿, 杜續恩, 周文濤. 工業化轉底爐煉鐵技術的現狀及評述. 燒結球團, 2013, 38(1):36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2013.01.010 [68] Wang G, Xue Q G, She X F, et al. Effect of BOF fine dust on the performance of carbon-contained pellets for RHF direct reduction process. J Wuhan Univ Sci Technol, 2014, 37(6): 424王廣, 薛慶國, 佘雪峰, 等. 轉爐細灰對轉底爐直接還原含碳球團性能的影響. 武漢科技大學學報, 2014, 37(6):424 [69] Sofili? T, Rastovcan-Mioc A, Cerjan-Stefanovi? S, et al. Characterization of steel mill electric-arc furnace dust. J Hazard Mater, 2004, 109(1-3): 59 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.02.032 [70] Guo Y H, Zhang C X, Fan B, et al. Analysis and evaluation on utilization ways of zinc-bearing sludge and dust from iron and steel enterprises. Environ Eng, 2010, 28(4): 83郭玉華, 張春霞, 樊波, 等. 鋼鐵企業含鋅塵泥資源化利用途徑分析評價. 環境工程, 2010, 28(4):83 [71] Wu K, Yang T J, Gudenau H. Treatment of recycling fine dust formed in ironmaking and steelmaking processes with injecting method. Iron Steel, 1999, 34(12): 60吳鏗, 楊天鈞, Gudenau H W. 采用噴吹方法處理鋼鐵廠的細粉塵. 鋼鐵, 1999, 34(12):60 [72] Wu K, Dou L W, Yao K H, et al. Research on the foaming process of smelting reduction of blast furnace dust and sludge in iron bath. China Environ Sci, 2001, 21(4): 335 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2001.04.012吳鏗, 竇力威, 姚克虎, 等. 高爐粉塵在鐵浴熔融還原發泡過程的研究. 中國環境科學, 2001, 21(4):335 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2001.04.012 [73] Hu X J, Guo T, Zhou G Z. Development and current states of techniques of disposal zinc-containing dust in metallurgical industry. J Iron Steel Res, 2011, 23(7): 1胡曉軍, 郭婷, 周國治. 含鋅冶金粉塵處理技術的發展和現狀. 鋼鐵研究學報, 2011, 23(7):1 [74] Gao J T, Li S Q, Zhang Y L, et al. Separation technology of Fe and Zn from blast furnace dust at non-molten state. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2012, 34(11): 1268高金濤, 李士琦, 張延玲, 等. 高爐粉塵Fe和Zn非熔態分離工藝. 北京科技大學學報, 2012, 34(11):1268 [75] Peng C, Guo Z C, Zhang F L. Discovery of potassium chloride in the sintering dust by chemical and physical characterization. ISIJ Int, 2008, 48(10): 1398 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.48.1398 [76] Peng C, Zhang F L, Guo Z C. Separation and recovery of potassium chloride from sintering dust of ironmaking works. ISIJ Int, 2009, 49(5): 735 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.49.735 [77] Peng C, Guo Z C, Zhang F L. Existing state of potassium chloride in agglomerated sintering dust and its water leaching kinetics. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2011, 21(8): 1847 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60940-0 [78] Turan M D, Altundo?an H S, Tümen F. Recovery of zinc and lead from zinc plant residue. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 75(1-4): 169 doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2004.07.008 [79] Yang Y, Deng Z G, Wei C, et al. Preparation of iron oxide red by sinking iron slag in zinc smelting hematite process. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(10): 1325楊源, 鄧志敢, 魏昶, 等. 利用濕法煉鋅赤鐵礦法沉鐵渣制備鐵紅工藝. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(10):1325 [80] Xing Q R, Ma Y, Li Y. Effect of CaO sources derived from different solid waste on the minerals and properties of prepared anorthite ceramics. Nonferrous Met Sci Eng, 2021, 12(1): 39邢芩瑞, 馬遠, 李宇. 不同CaO源固廢對鈣長石全固廢陶瓷礦相和性能的影響. 有色金屬科學與工程, 2021, 12(1):39 -




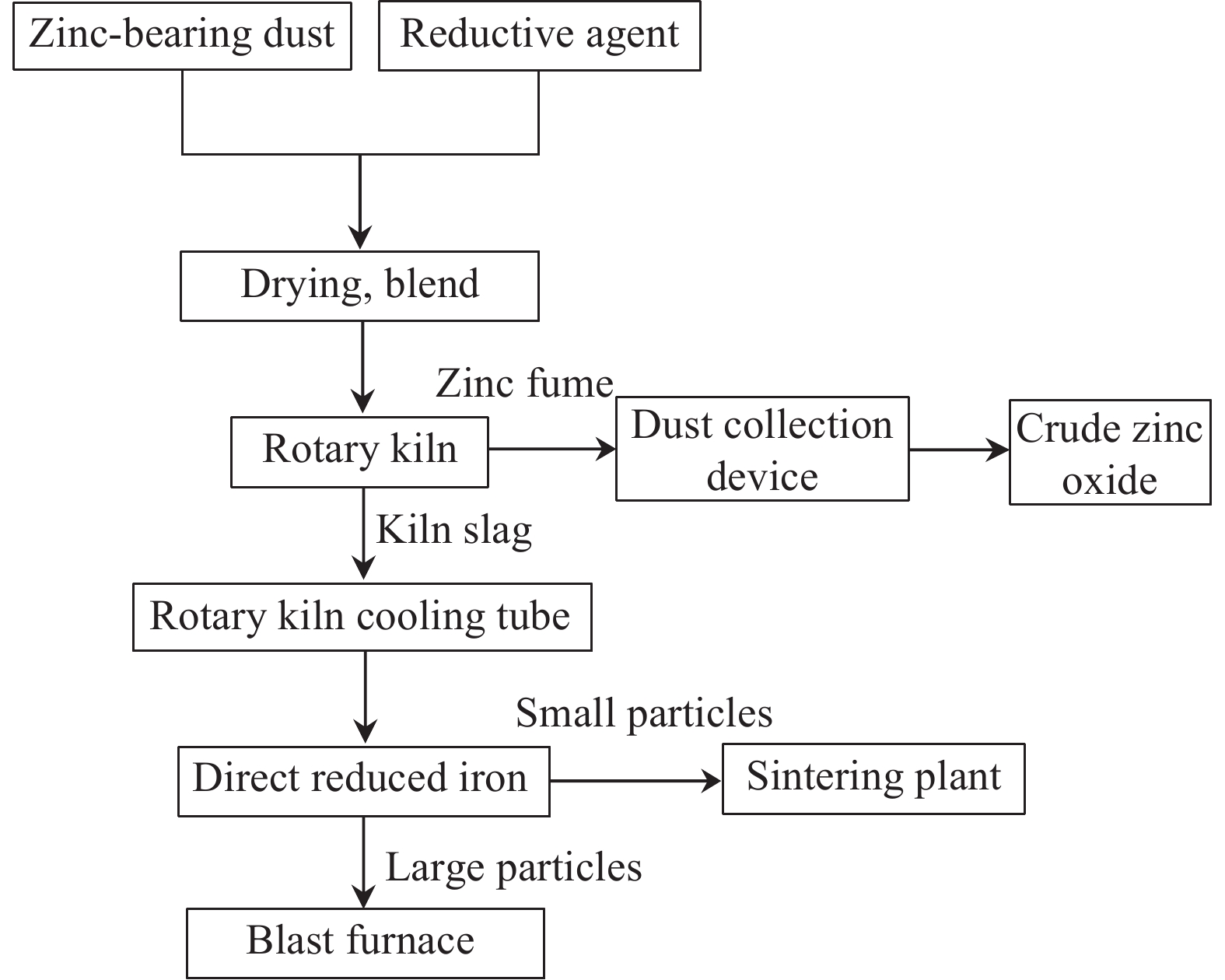
 下載:
下載: