-
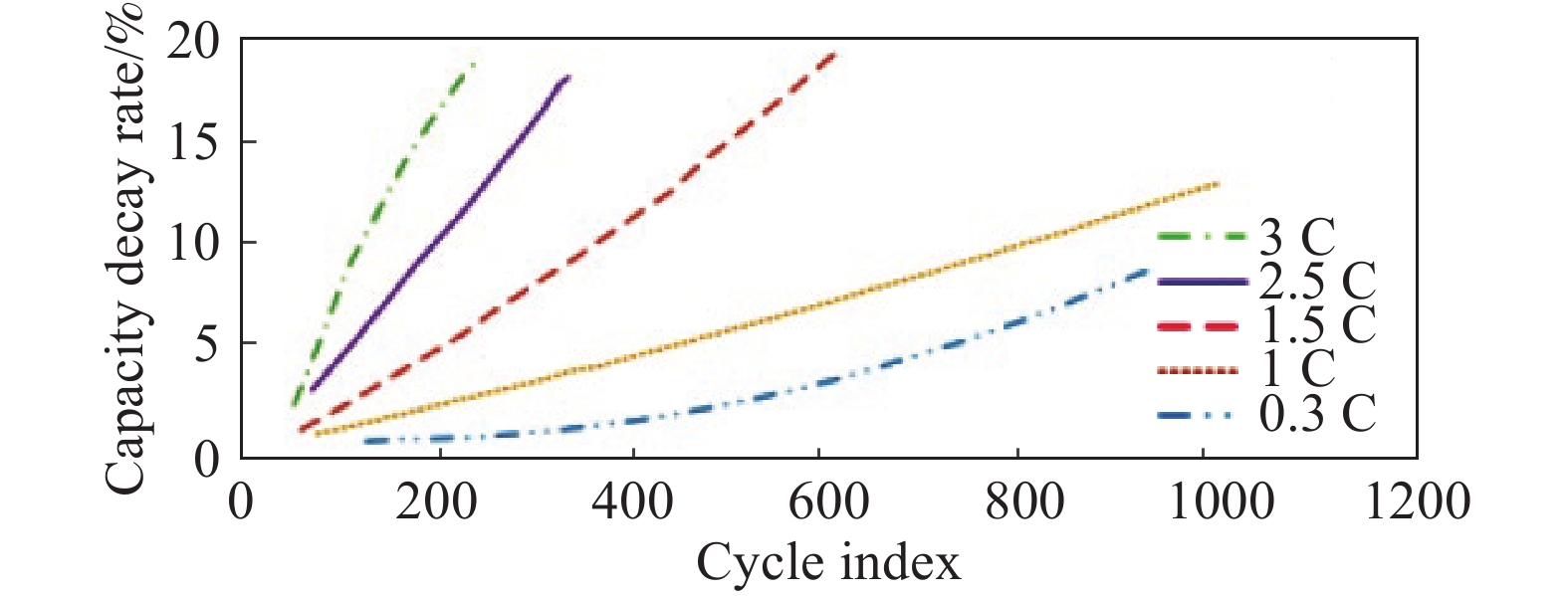
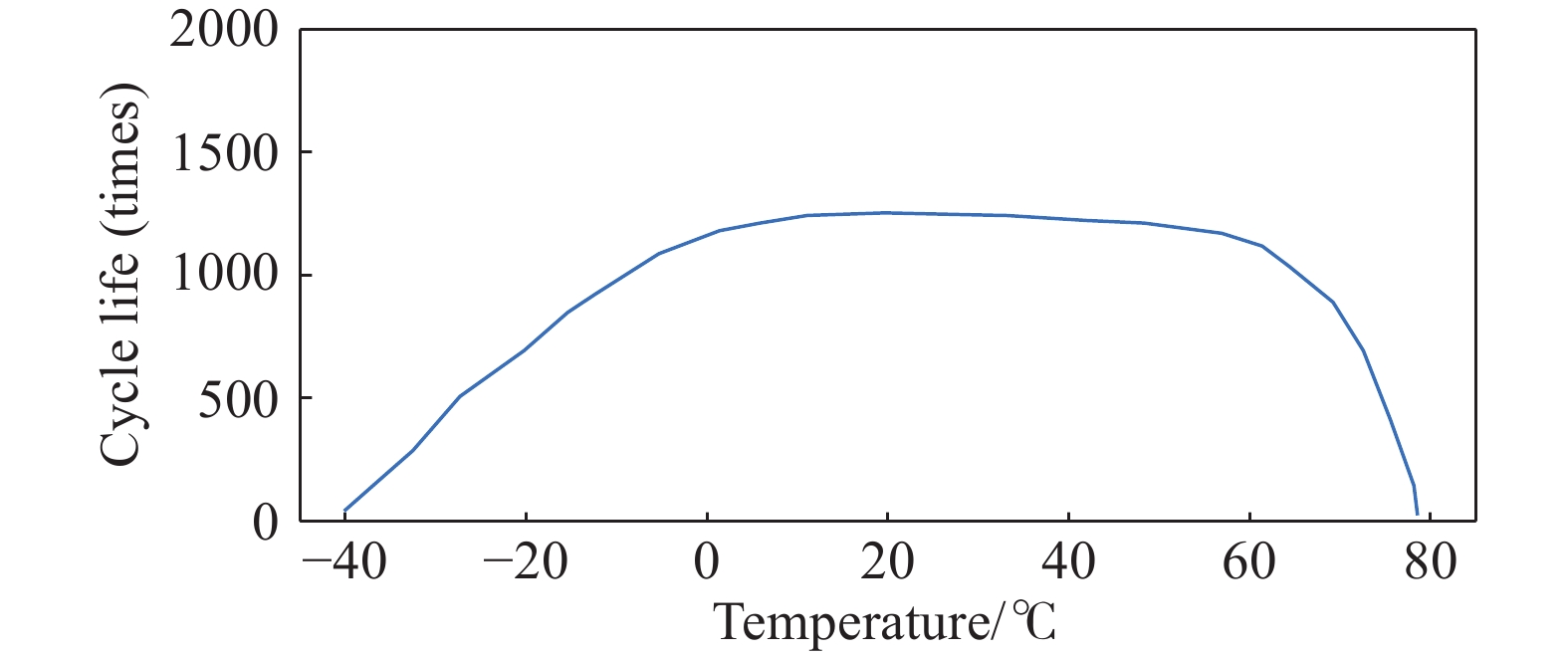
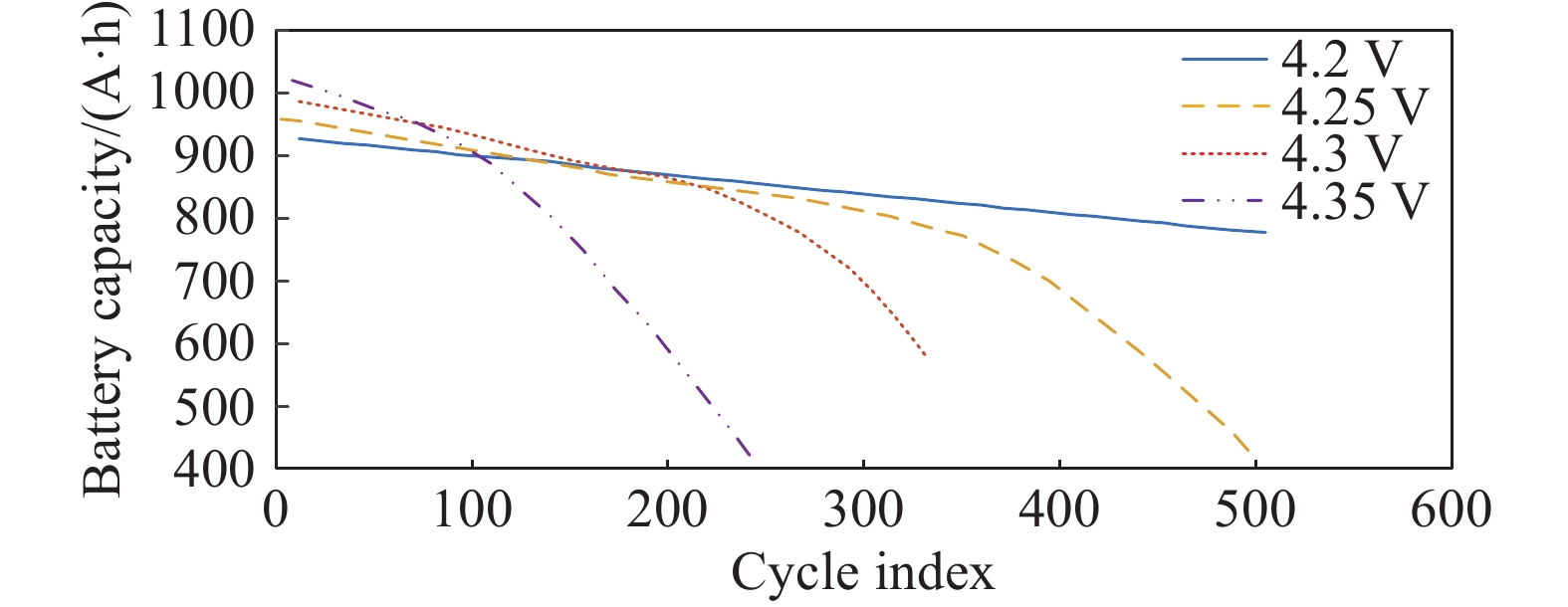
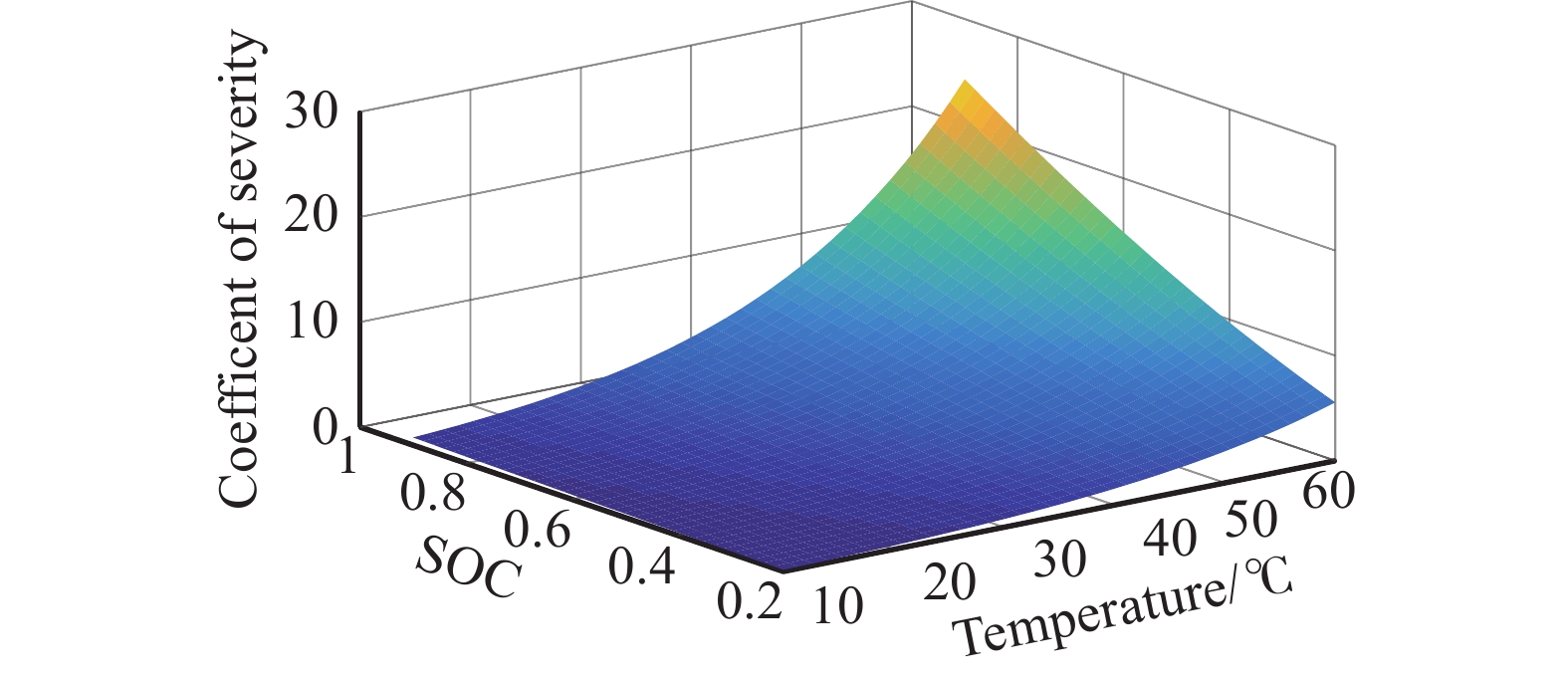
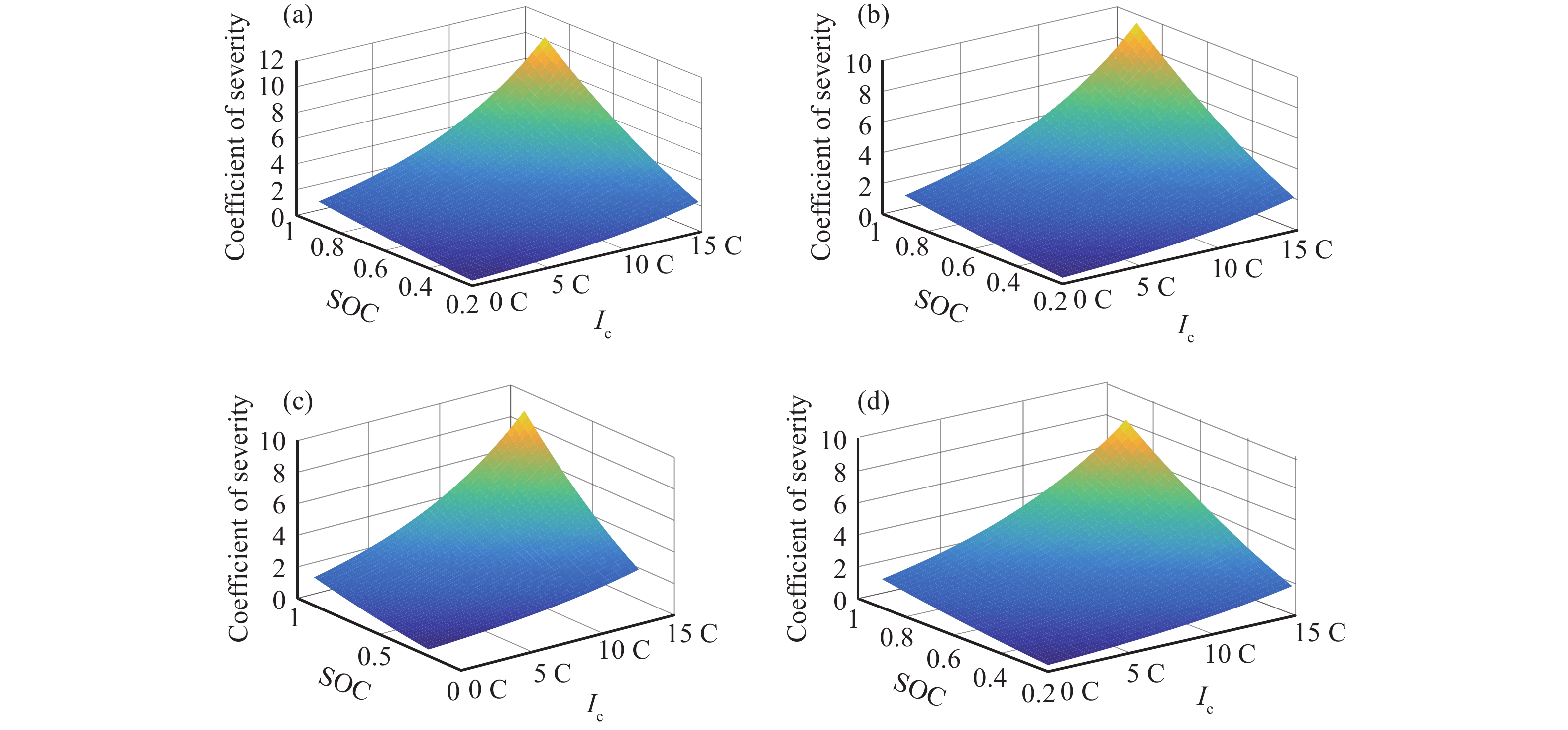
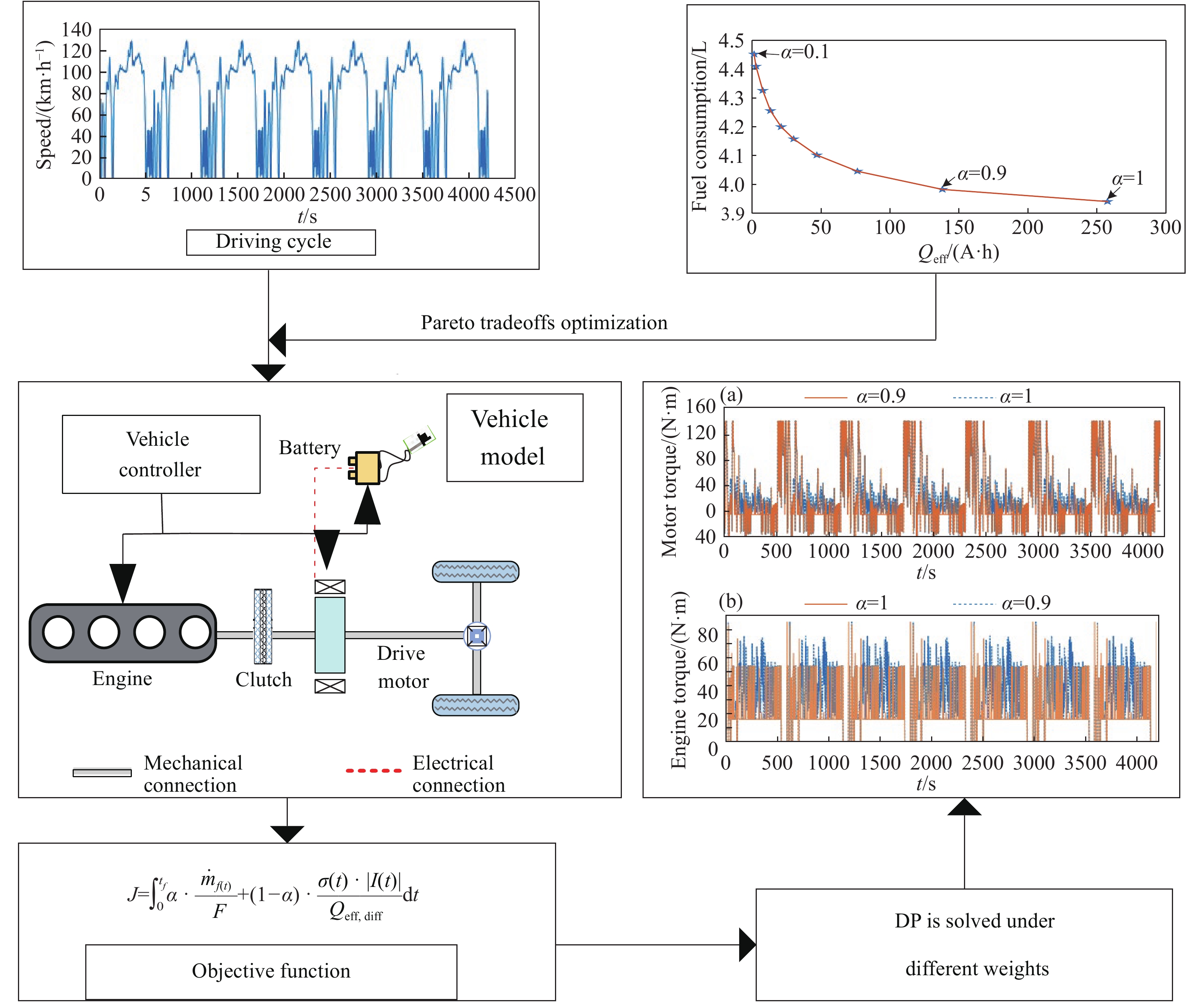
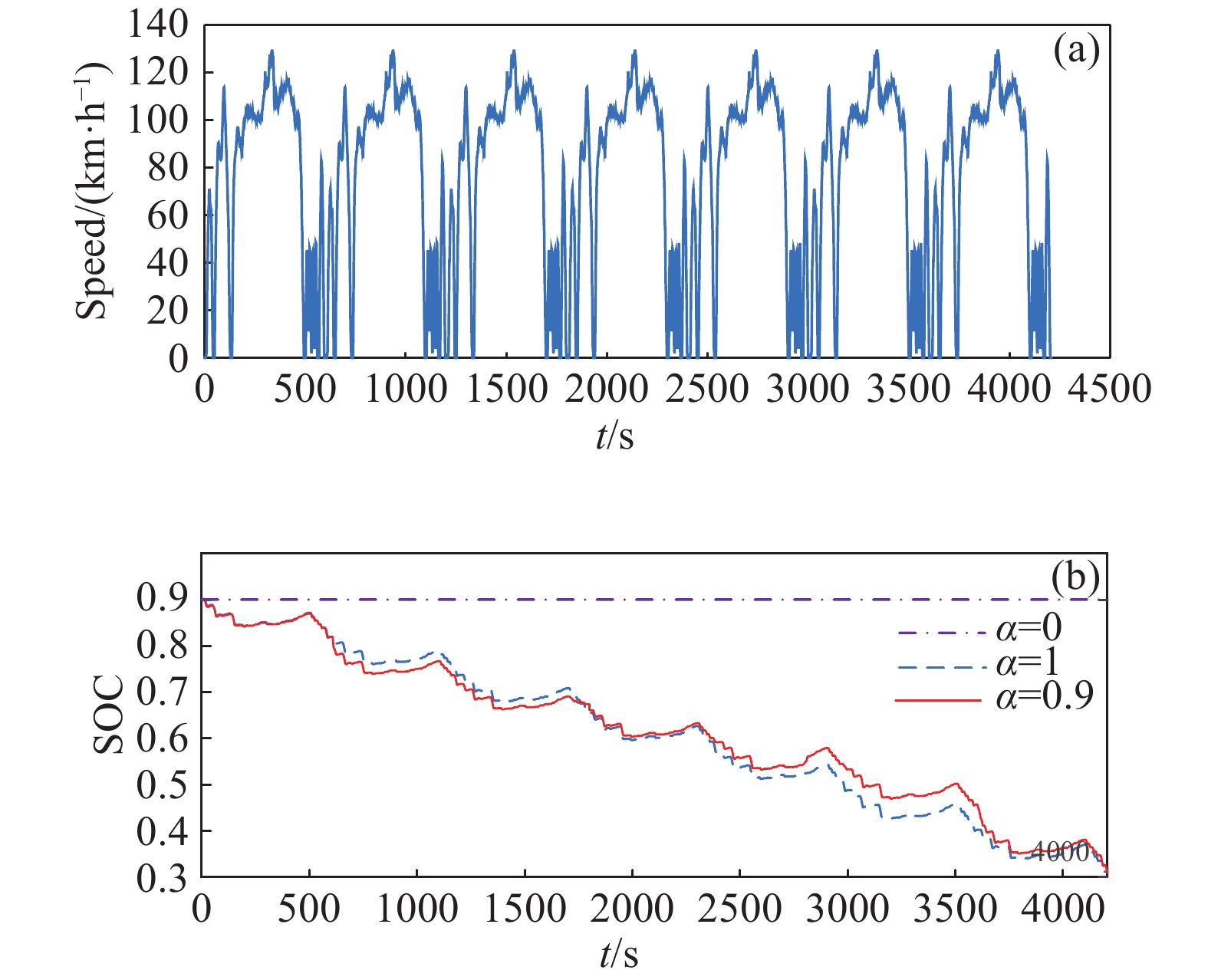
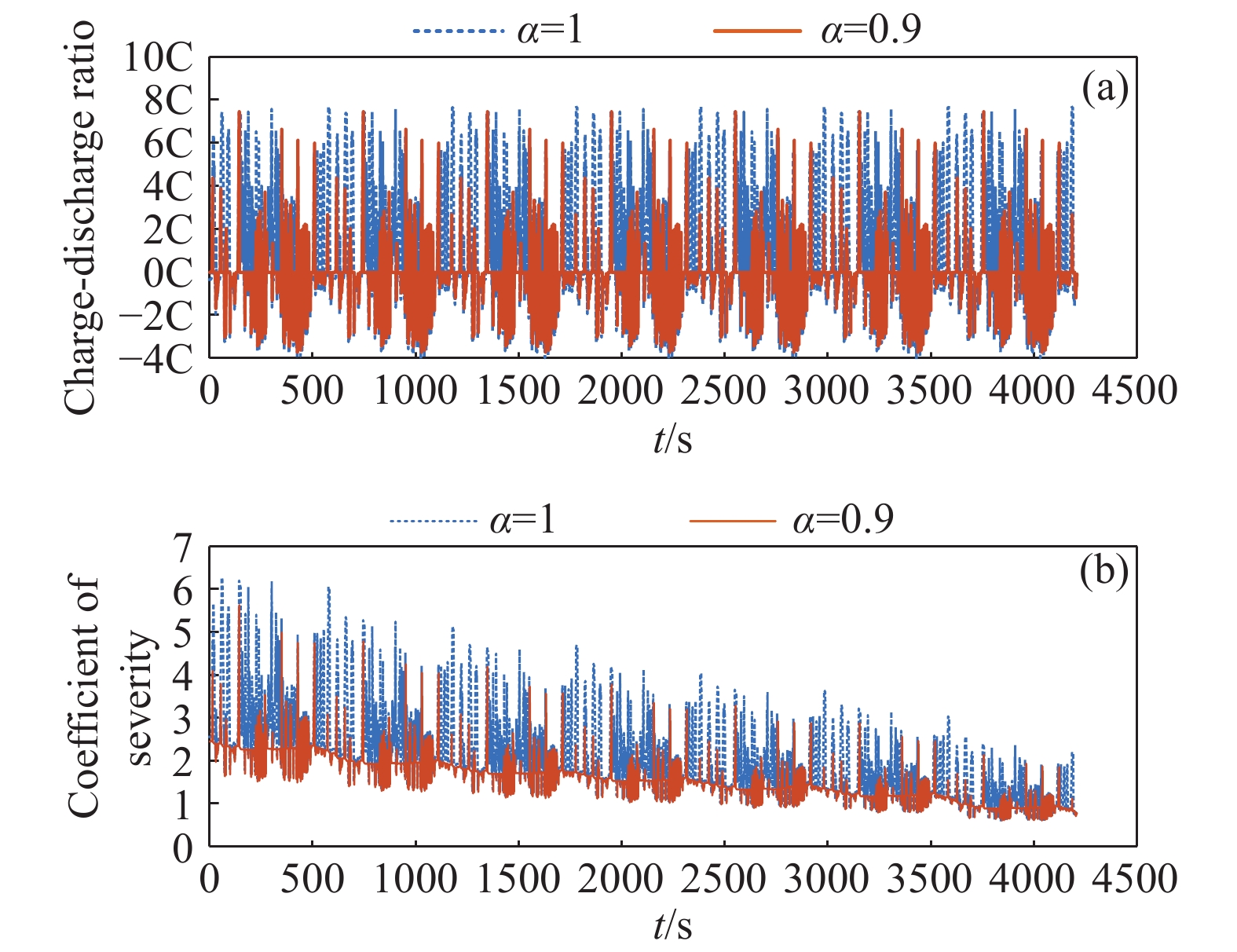
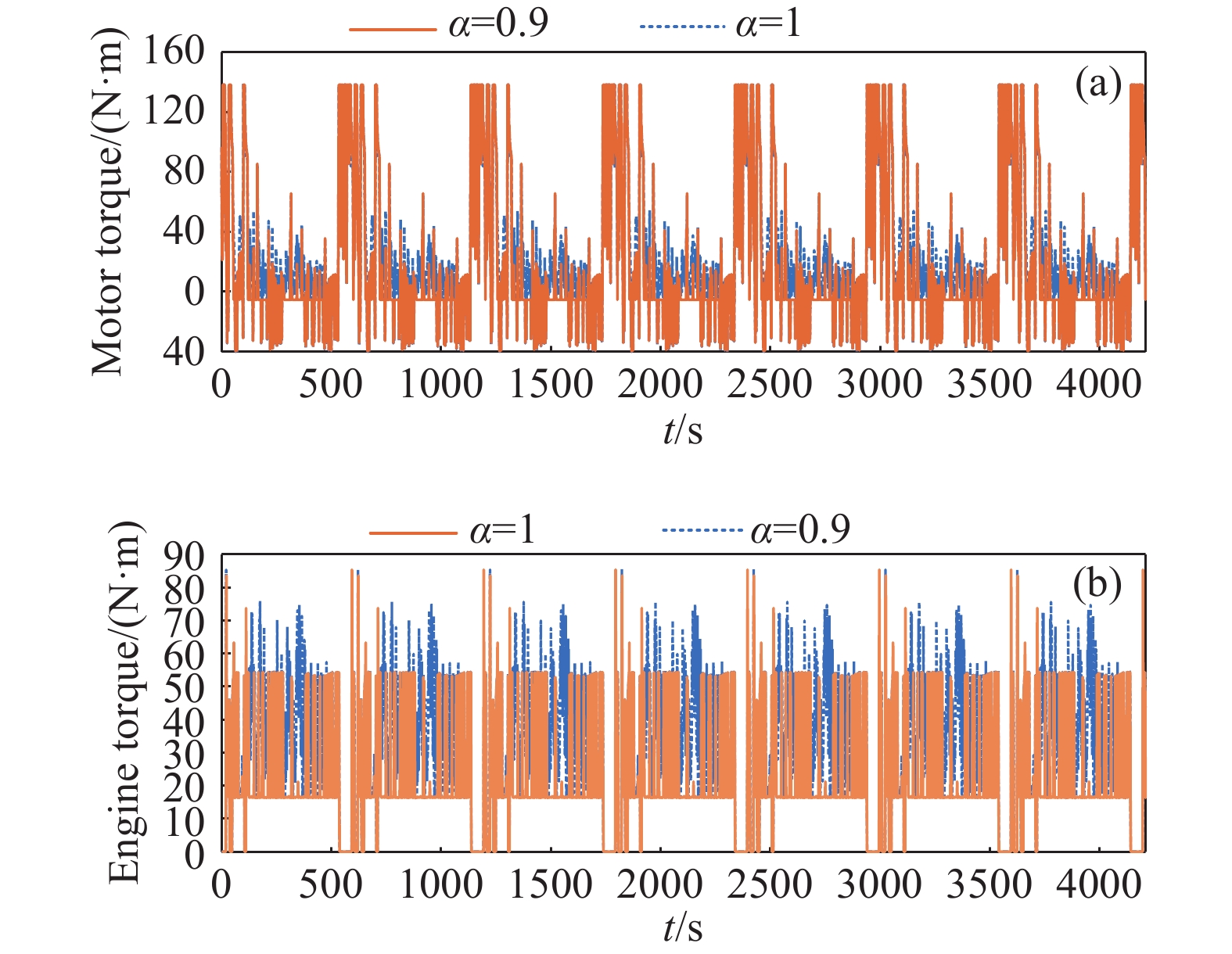
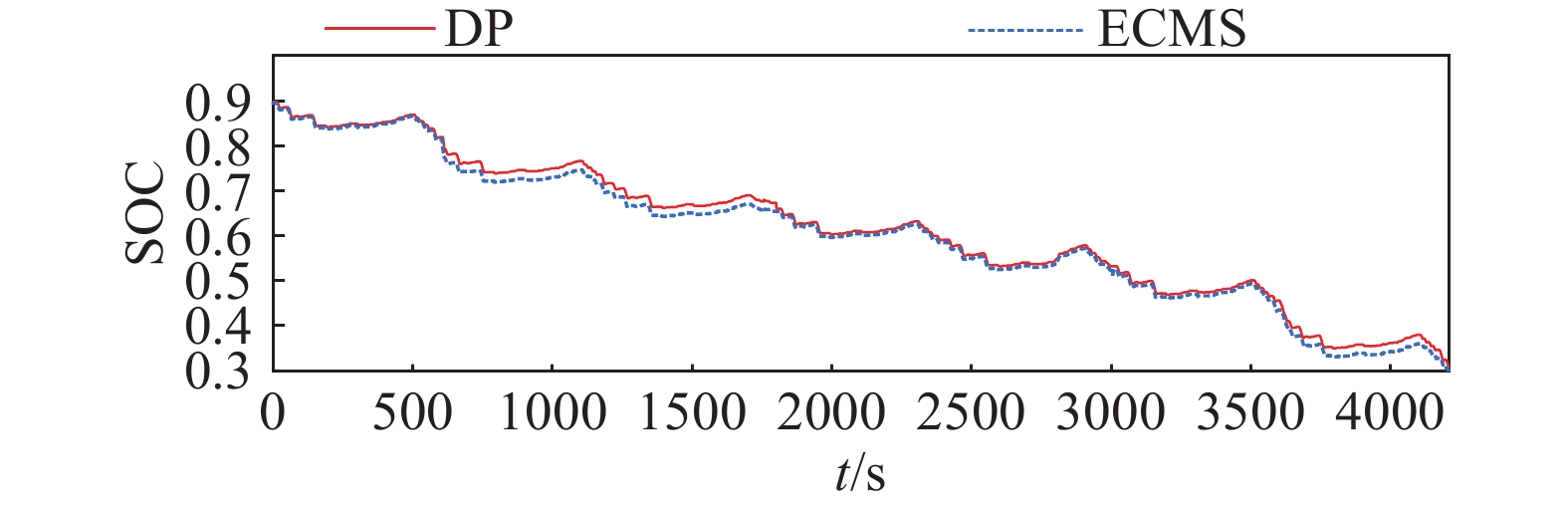
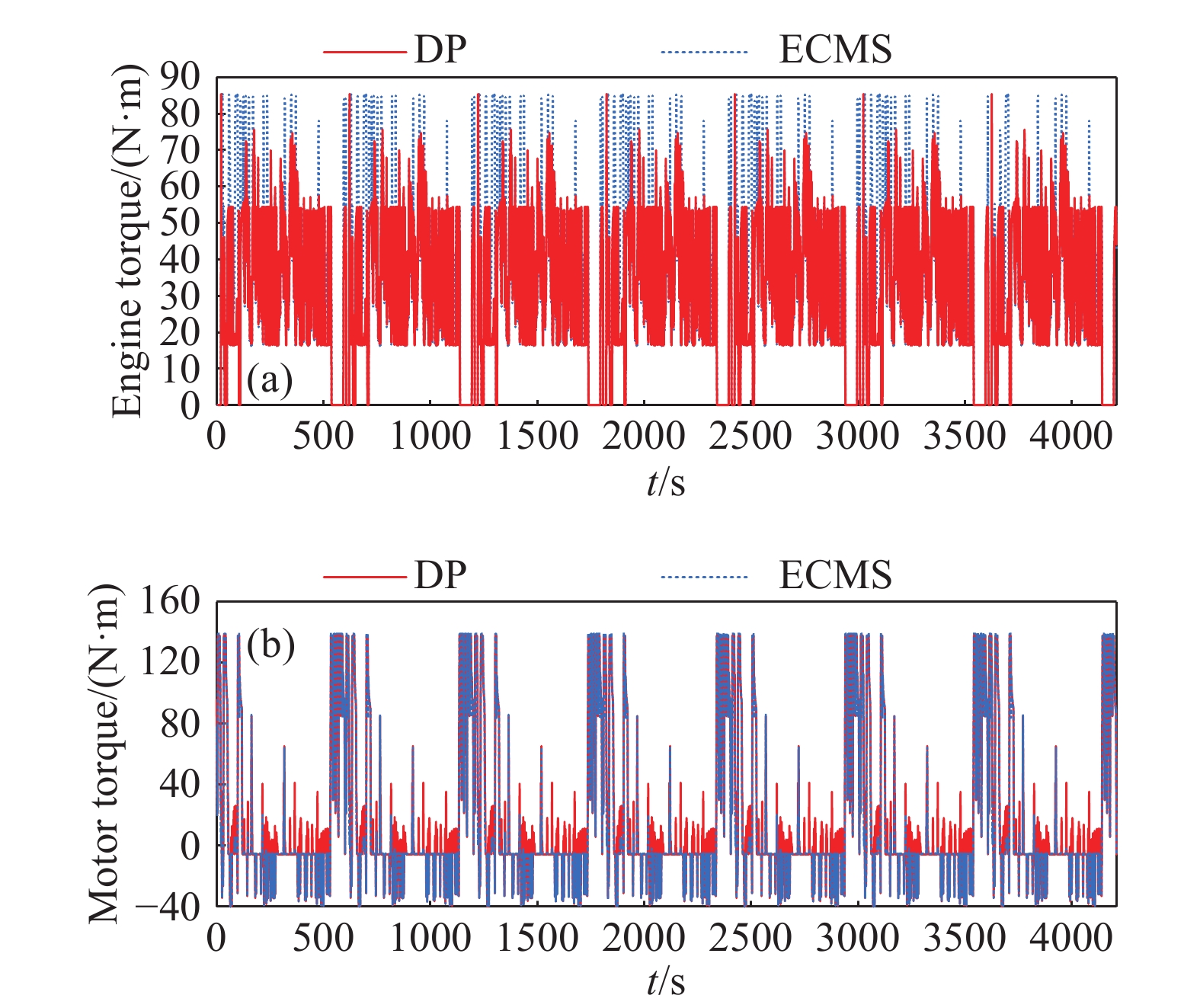
摘要: 由于插電式混合動力汽車電池可以通過電網獲取比較廉價的電量,傳統的控制策略只考慮充分利用電池電量,但忽略了過度使用電池,會加快動力電池容量的衰退。因此,如何權衡充分利用電池電量與抑制電池容量衰退是新的研究重點。基于電池的半經驗衰退模型,引入電池利用程度因子,建立權衡電池容量衰退的能量管理策略。通過Pareto非劣目標域選取合適的權重因子,將多目標優化問題轉化為單目標問題,采用動態規劃算法獲得權重系數全局最優解,通過權衡不同權重下的油耗和電池容量衰退程度選擇最優權重系數。在燃油消耗相當的情況下,當權重系數為0.9時,可有效抑制電池壽命的衰減速度。最后,通過在線等效油耗最小策略仿真與在同一權重下的動態規劃解進行比較來驗證其有效性。Abstract: As environmental problems become increasingly severe, achieving qualitative breakthroughs in the energy consumption and emissions of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles is difficult. In contrast, new energy vehicles are environmentally friendly and have low fuel consumption, which is important for the future development of vehicles. A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is widely regarded as the most promising alternative solution for improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions. The optimization of the energy management strategy (EMS) mainly focuses on reducing fuel consumption and improving the economy. However, the durability of the power battery also needs attention, as the lack of life remains a major obstacle to the large-scale commercialization of PHEVs. Because PHEV batteries can obtain relatively cheap power through the grid, the traditional control strategy only considers the full use of the battery power but ignores its excessive use, which will accelerate the decline of the power battery capacity. Therefore, determining how to make full use of the battery power and control the decline of the battery capacity is a new research focus. Based on the semiempirical decay model of the battery, the energy management strategy of balancing the degradation of the battery capacity was established by introducing the battery utilization degree factor. The multiobjective optimization problem was transformed into a single-objective problem by selecting the appropriate weight factor through the Pareto noninferior target domain. A dynamic programming algorithm was used to obtain the global optimal solution of the weight coefficient. The optimal weight coefficient was selected by weighing the fuel consumption and battery capacity decline degree under different weights. In the case of equivalent fuel consumption, the decay rate of battery life can be effectively inhibited when the weight coefficient is 0.9. Finally, the validity of the proposed solution is verified by comparing the online equivalent consumption minimization strategy (ECMS) simulation with the dynamic programming solution under the same weight.
-
Key words:
- battery aging /
- energy management strategy /
- fuel consumption /
- weight coefficient /
- dynamic programming
-
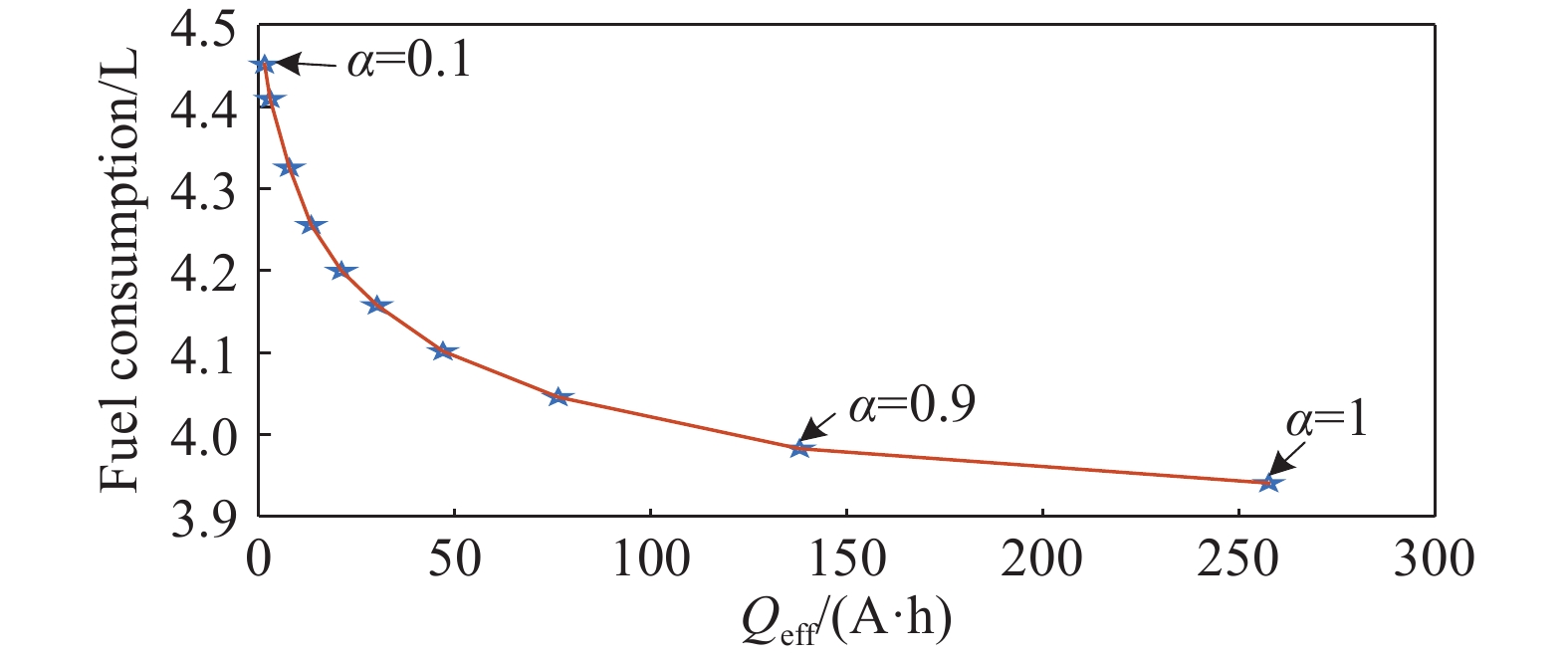
表 1 7個US06工況下的仿真結果
Table 1. Simulation results of 7 US06 operating conditions
$ \alpha $ Fuel consumption/L Effective ampere-hour flux/(A·h) 1 3.941 257.6 0.9 3.983 137.9 0.8 4.046 76.3 0.7 4.102 46.9 0.6 4.158 30.1 0.5 4.200 21 0.4 4.256 13.3 0.3 4.326 7.7 0.2 4.410 2.8 0.1 4.452 1.4 表 2 不同方法下的仿真結果對比
Table 2. Comparison of simulation results under different methods
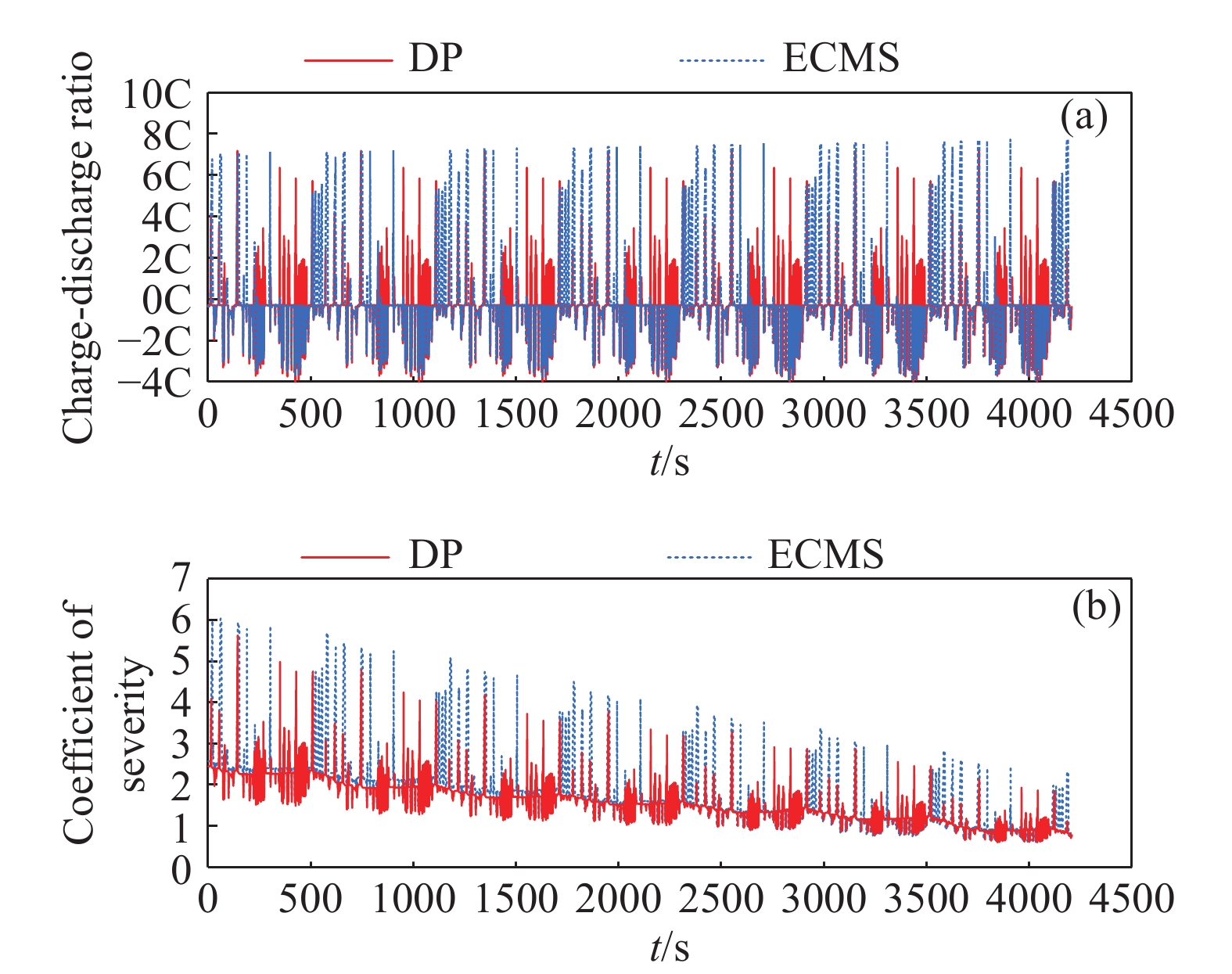
Control strategy Fuel consumption/L Effective ampere-hour flux/(A·h) The final SOC DP 3.983 137.9 0.3032 ECMS 4.016 143.2 0.3010 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Biswas A, Emadi A. Energy management systems for electrified powertrains: State-of-the-art review and future trends. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2019, 68(7): 6453 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2914457 [2] Ding Z T, Deng T, Li Z F, et al. SOC estimation of lithium-ion battery based on ampere hour integral and unscented Kalman filter. China Mech Eng, 2020, 31(15): 1823 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.15.009丁鎮濤, 鄧濤, 李志飛, 等. 基于安時積分和無跡卡爾曼濾波的鋰離子電池SOC估算方法研究. 中國機械工程, 2020, 31(15):1823 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.15.009 [3] Sheng J X, Zhang B J, Zhu B, et al. Parameter optimization and experimental comparison of two-speed pure electric vehicle transmission systems. China Mech Eng, 2019, 30(7): 763 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.07.002盛繼新, 張邦基, 朱波, 等. 兩擋純電動汽車傳動系統參數優化和試驗對比. 中國機械工程, 2019, 30(7):763 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.07.002 [4] Chen S Y, Hung Y H, Wu C H, et al. Optimal energy management of a hybrid electric powertrain system using improved particle swarm optimization. Appl Energy, 2015, 160: 132 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.09.047 [5] Liu Y G, Lu L L, Xie Q B, et al. Energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle based on road slope information. Chin J Eng, 2016, 38(7): 1025劉永剛, 盧立來, 解慶波, 等. 基于道路坡度信息的插電式混合動力汽車能量管理策略. 工程科學學報, 2016, 38(7):1025 [6] Ming L, Ying Y, Liang L J, et al. Energy management strategy of a plug-in parallel hybrid electric vehicle using fuzzy control. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 2660 doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.771 [7] Lin X Y, Li X F, Shen Y, et al. Charge depleting range dynamic strategy with power feedback considering fuel-cell degradation. Appl Math Model, 2020, 80: 345 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.11.019 [8] Tian H, Lu Z W, Wang X, et al. A length ratio based neural network energy management strategy for online control of plug-in hybrid electric city bus. Appl Energy, 2016, 177: 71 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.05.086 [9] Xie S B, Hu X S, Xin Z K, et al. Pontryagin's Minimum Principle based model predictive control of energy management for a plug-in hybrid electric bus. Appl Energy, 2019, 236: 893 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.032 [10] Lin X Y, Li H L. Adaptive control strategy extracted from dynamic programming and combined with driving pattern recognition for SPHEB. Int J Automot Technol, 2019, 20(5): 1009 doi: 10.1007/s12239-019-0095-7 [11] Hua Y, Zhou S D, He R, et al. Review on lithium-ion battery equilibrium technology applied for EVs. J Mech Eng, 2019, 55(20): 73華旸, 周思達, 何瑢, 等. 車用鋰離子動力電池組均衡管理系統研究進展. 機械工程學報, 2019, 55(20):73 [12] Liu H L, Chen G P, Wang J W. Design and energy management of electro-hydraulic parallel hybrid power system for battery bus. Automot Eng, 2020, 42(12): 1621劉桓龍, 陳冠鵬, 王家為. 蓄電池公交車電液并聯混合動力系統設計與能量管理. 汽車工程, 2020, 42(12):1621 [13] Shi Y S, Shi M Z, Ding E S, et al. Life prediction method of lithium ion battery based on CEEMDAN-LSTM combination. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(7): 985史永勝, 施夢琢, 丁恩松, 等. 基于CEEMDAN–LSTM組合的鋰離子電池壽命預測方法. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(7):985 [14] Bai Y F, He H W, Li J W, et al. Battery anti-aging control for a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle with a hierarchical optimization energy management strategy. J Clean Prod, 2019, 237: 117841 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117841 [15] Feng Y B, Dong Z M. Optimal energy management with balanced fuel economy and battery life for large hybrid electric mining truck. J Power Sources, 2020, 454: 227948 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.227948 [16] Zhang X, Gao Y Z, Guo B J, et al. A novel quantitative electrochemical aging model considering side reactions for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 343: 136070 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136070 [17] Moura S J, Stein J L, Fathy H K. Battery-health conscious power management in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles via electrochemical modeling and stochastic control. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol, 2013, 21(3): 679 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2189773 [18] Zhang F T, Yang F Y, Xue D L, et al. Optimization of compound power split configurations in PHEV bus for fuel consumption and battery degradation decreasing. Energy, 2019, 169: 937 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.059 [19] Zhang S, Hu X S, Xie S B, et al. Adaptively coordinated optimization of battery aging and energy management in plug-in hybrid electric buses. Appl Energy, 2019, 256: 113891 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113891 [20] Lin X Y, Li X F, Lin H B. Optimazation feedback control strategy based ECMS for plug-in FCHEV considering fuel cell decay. China J Highw Transp, 2019, 32(5): 153林歆悠, 李雪凡, 林海波. 考慮燃料電池衰退的FCHEV反饋優化控制策略. 中國公路學報, 2019, 32(5):153 [21] Xie S B, Hu X S, Zhang Q K, et al. Aging-aware co-optimization of battery size, depth of discharge, and energy management for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. J Power Sources, 2020, 450: 227638 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227638 [22] Engbroks L, G?rke D, Schmiedler S, et al. Combined energy and thermal management for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles -analyses based on optimal control theory. IFAC PapersOnLine, 2019, 52(5): 610 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.09.097 [23] Wang J, Liu P, Hicks-Garner J, et al. Cycle-life model for graphite-LiFePO4 cells. J Power Sources, 2011, 196(8): 3942 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.11.134 [24] Tang L, Rizzoni G, Onori S. Energy management strategy for HEVs including battery life optimization. IEEE Trans Transp Electrif, 2015, 1(3): 211 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2015.2471180 [25] Suri G, Onori S. A control-oriented cycle-life model for hybrid electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries. Energy, 2016, 96: 644 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2015.11.075 [26] Onori S, Spagnol P, Marano V, et al. A new life estimation method for lithium-ion batteries in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles applications. Int J Power Electron, 2012, 4(3): 302 doi: 10.1504/IJPELEC.2012.046609 -




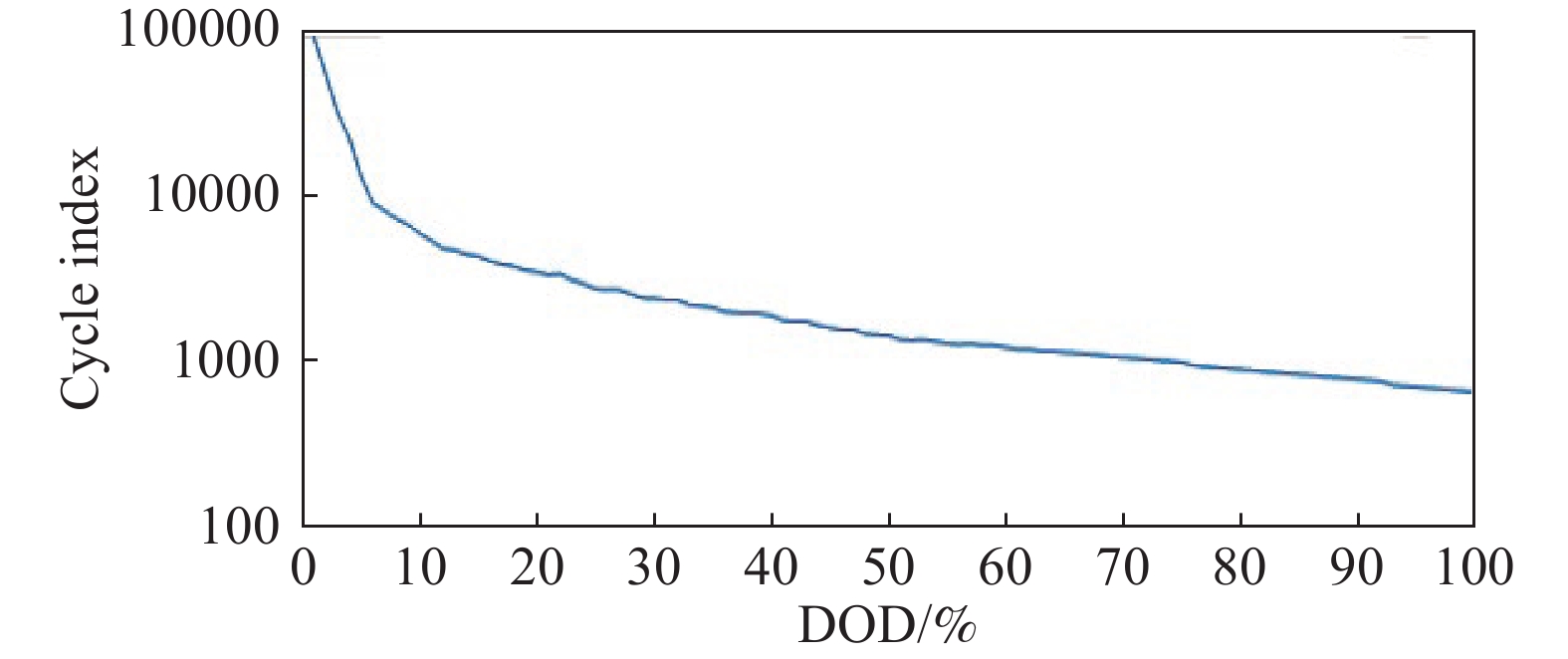
 下載:
下載: