-
摘要: 對比了國內外高疲勞壽命軸承鋼主要雜質元素、主要夾雜物特征等冶金性能的差異,并對比了不同冶金質量下,軸承鋼的疲勞性能及誘發疲勞斷裂的因素,總結了國產軸承鋼潔凈度現狀及與國外優質軸承鋼的差距。在此基礎上,圍繞高疲勞壽命軸承鋼,以進一步提高國產軸承鋼質量為目的,分析梳理了國產軸承鋼冶煉技術及夾雜物控制方法的發展軌跡,探討了國產軸承鋼進一步提高疲勞壽命及質量的發展方向。Abstract: Bearing steel is a significant material for producing basic components in many industrial sectors, such as automotive, high-speed trains, and aerospace. In most cases, the bearings belong to the safety-relevant parts of these structures, so that extensive quality control measures are applied to ensure the entire assembly’s reliability and safety. In the last century, the precise instruments’ bearings were almost dependent on imports, which cost a large fortune. In recent years, the production technique and the production quality of domestic bearing steels keep improving, and the cleanliness keeps increasing. The qualities of some superior domestic bearing steels have become close to foreign bearing steels with high quality. However, the stability still needs to be improved, especially in the aspects of calcium aluminate inclusions and the titanium content in steels. To understand the gaps between domestic and foreign bearing steels, the differences in metallurgical properties of high-fatigue-life bearing steels, such as the main impurity elements and the characteristics of main inclusions, were compared in this paper. Fatigue properties of bearing steels and factors that cause fatigue fracture under various metallurgical properties were also compared. The cleanliness status of domestic bearing steels and the gap with foreign high-quality bearing steels were summarized. There are two types of controlling strategies of the cleanliness for bearing steels: 1) controlling the total oxygen content strictly to get an extremely low total oxygen content; 2) controlling the size and type of oxide inclusions with a relatively low total oxygen content. On this basis, in order to further improve the efficiency of domestic steel bearings, the development of the smelting technology and the integration control system for domestic steel bearings were analyzed and sorted out. Besides, the development direction of further improving the quality and fatigue life of domestic bearing steel was discussed.
-
Key words:
- bearing steel /
- inclusion /
- fatigue property /
- cleanliness /
- deoxidation method
-
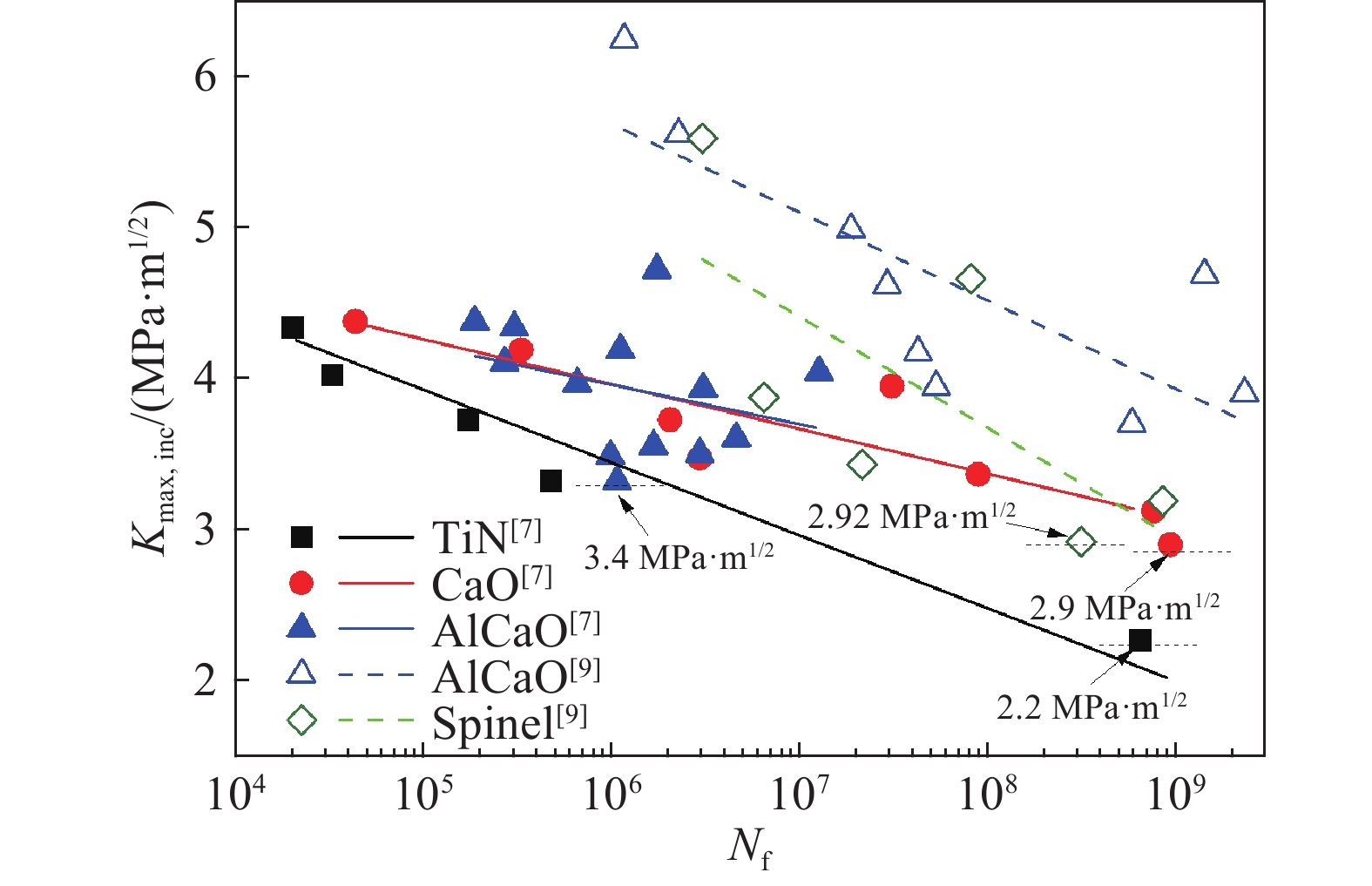
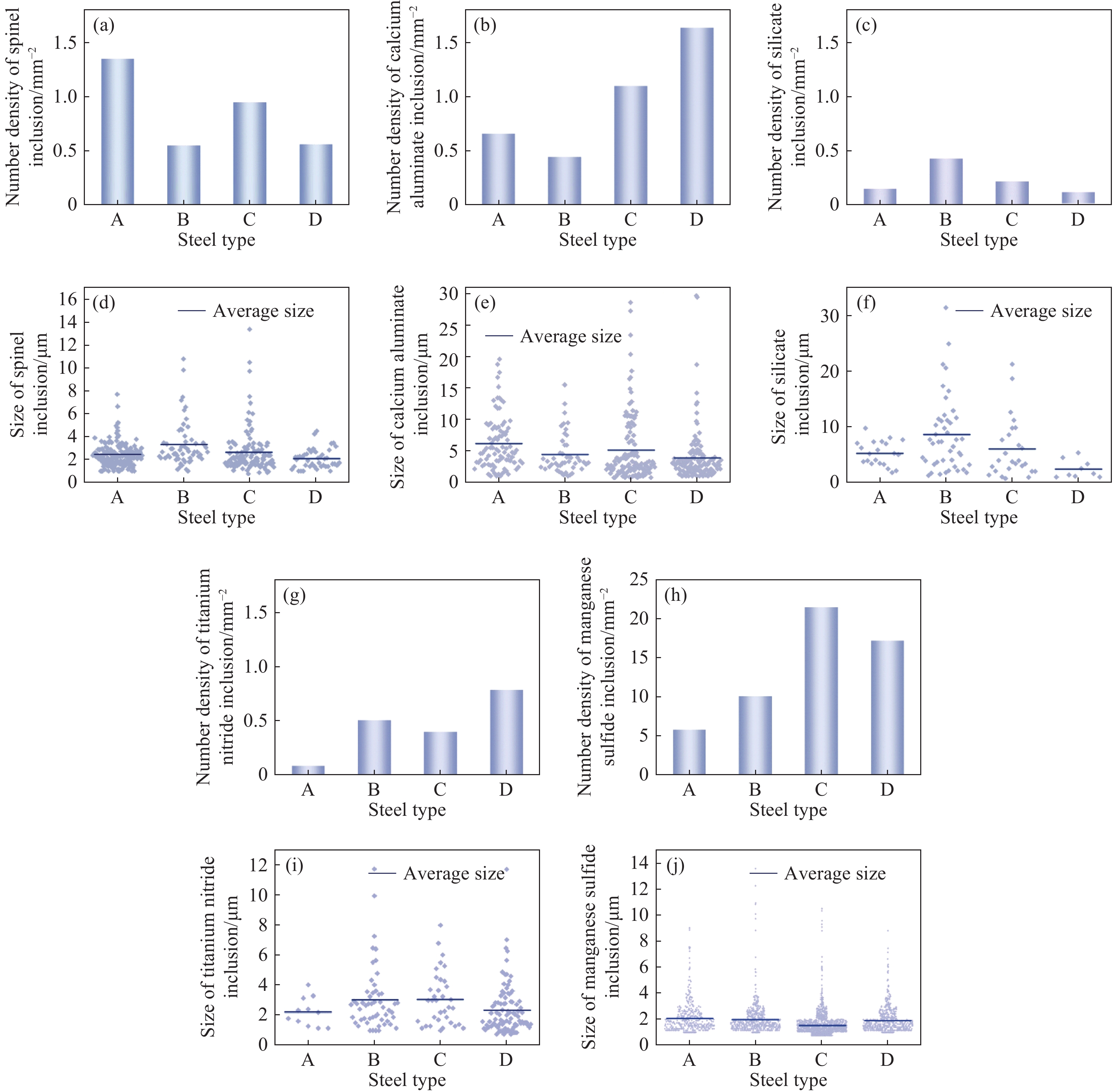
圖 4 國內外軸承鋼主要夾雜物對比。(a)尖晶石類夾雜物個數密度;(b)鈣鋁酸鹽類夾雜物個數密度;(c)硅酸鹽類夾雜物個數密度;(d)尖晶石類夾雜物尺寸分布;(e)鈣鋁酸鹽類夾雜物尺寸分布;(f)硅酸鹽類夾雜物尺寸分布;(g)氮化鈦類夾雜物個數密度;(h)硫化錳類夾雜物個數密度;(i)氮化鈦類夾雜物尺寸分布;(j)硫化錳類夾雜物尺寸分布
Figure 4. Composition of main inclusion in domestic and foreign bearing steels: (a) number density of spinel inclusion; (b) size distribution of spinel inclusion; (c) number density of calcium aluminate inclusion; (d) size distribution of calcium aluminate inclusion; (e) number density of silicate inclusion; (f) size distribution of silicate inclusion; (g) number density of titanium nitride inclusion; (h) size distribution of titanium nitride inclusion; (i) number density of manganese sulfide inclusion; (j) size distribution of manganese sulfide inclusion
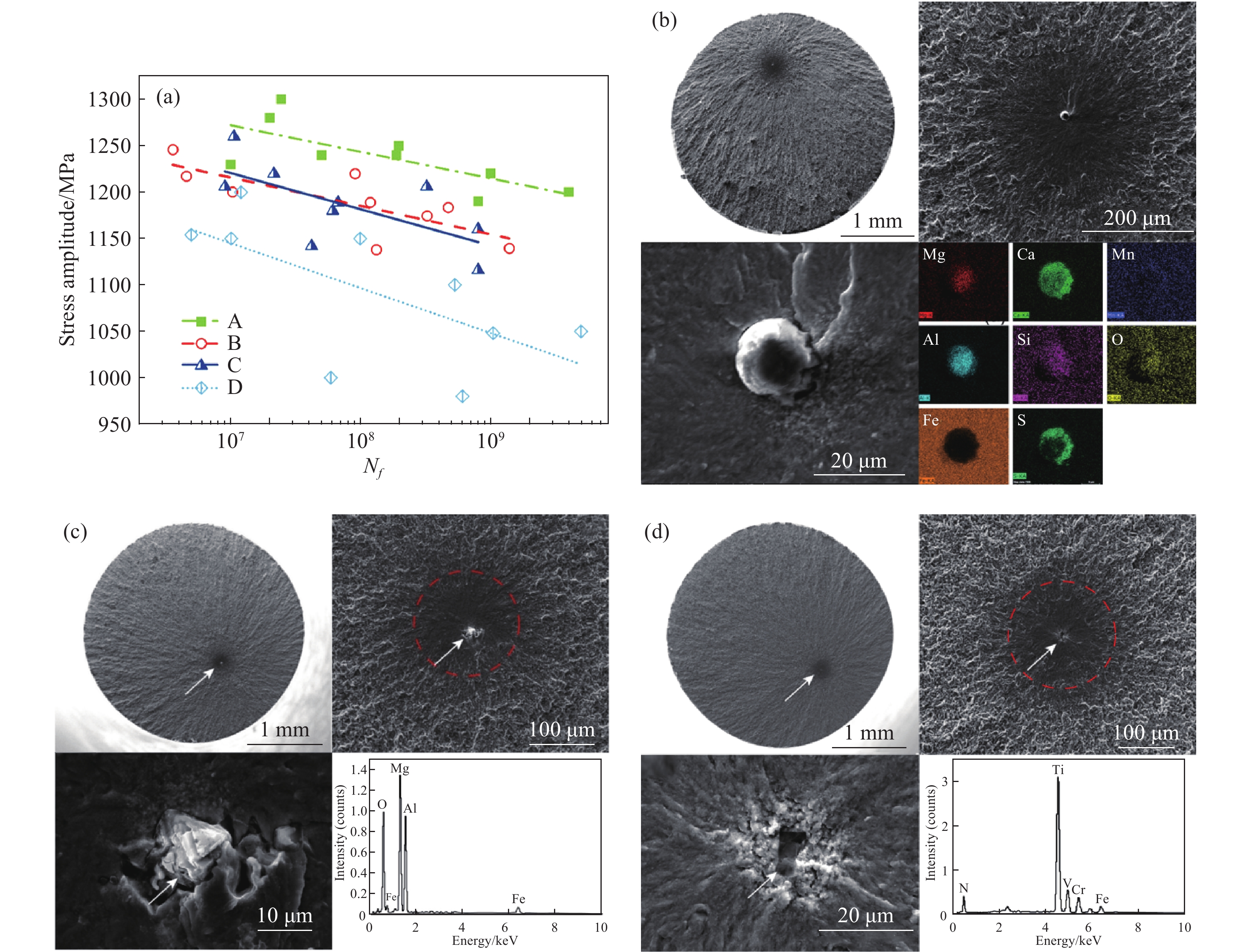
圖 5 國內外軸承鋼典型疲勞特征。(a)疲勞壽命對比[3];(b)鈣鋁酸鹽類夾雜物致疲勞斷口形貌(軸承鋼B)[3];(c)尖晶石類類夾雜物致疲勞斷口形貌(軸承鋼C)[12];(d)氮化鈦類類夾雜物致疲勞斷口形貌(軸承鋼D)[12]
Figure 5. Typical fatigue characterization of domestic and foreign bearing steels: (a) comparison of fatigue life[3]; (b) morphology of fatigue fracture induced by calcium aluminate inclusion (bearing steel B)[3]; (c) morphology of fatigue fracture induced by spinel inclusion (bearing steel C)[12]; (d) morphology of fatigue fracture induced by titanium nitride inclusion (bearing steel D)[12]
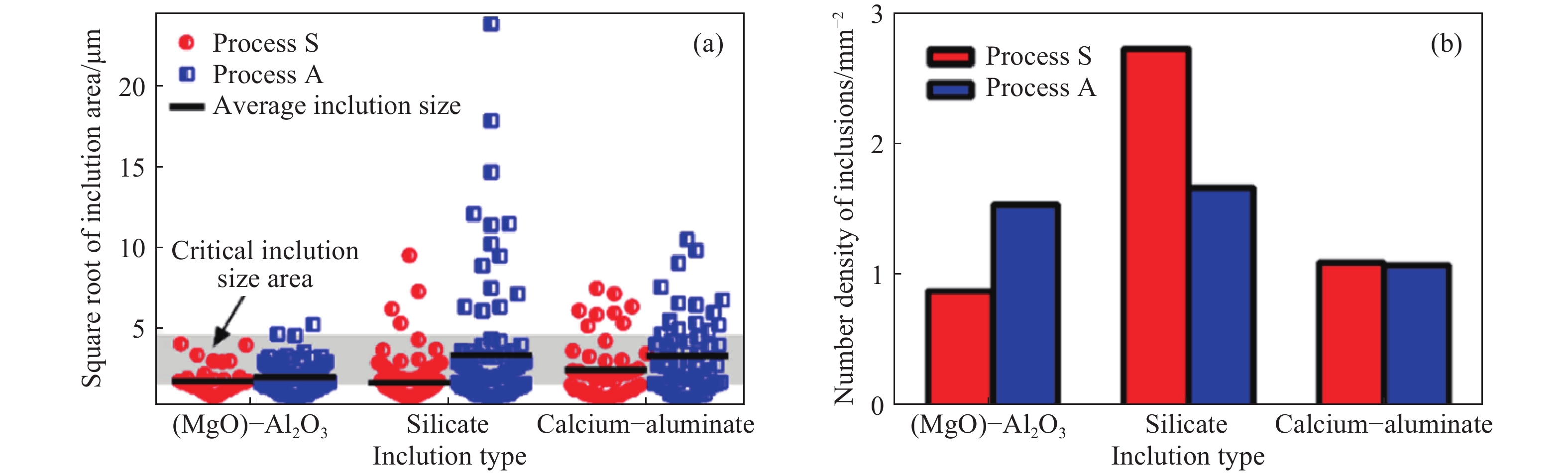
圖 9 非鋁脫氧鋼(S)和鋁脫氧鋼(A)中夾雜物對比[46].(a)尺寸;(b)密度
Figure 9. Comparison of inclusions in non-Al deoxidation steel (S) and Al deoxidation steel (L): (a) size; (b) number density
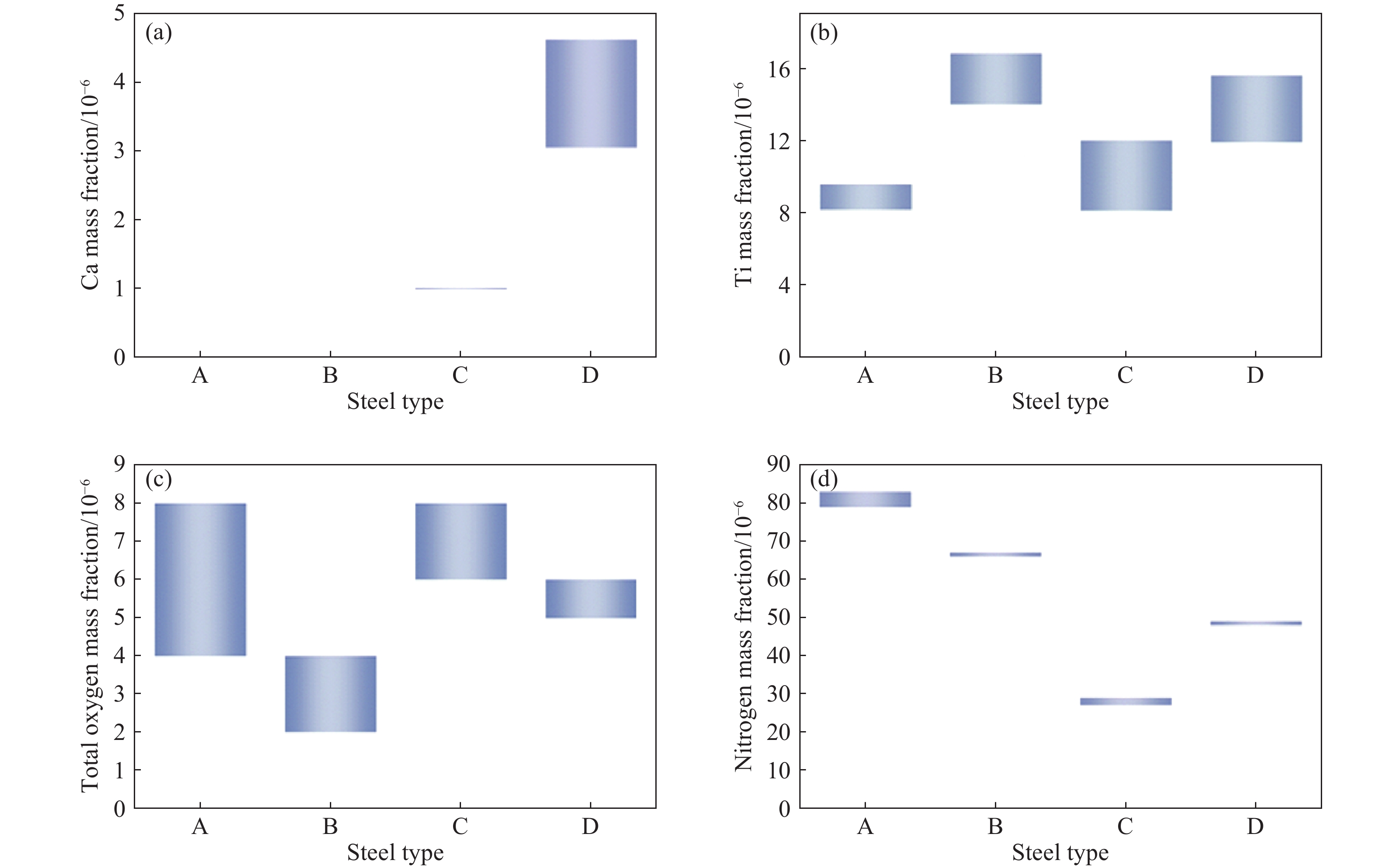
表 1 GB/T 18254—2016高碳鉻軸承鋼中殘余元素含量要求(質量分數)
Table 1. Requirements of residual elements in high carbon chromium bearing steel in GB/T 18254—2016
% Metallurgical quality Ni Cu P S Ca Oa Tib Al As As+Sn+Sb Pb High-quality steel ≤0.25 ≤0.25 ≤0.025 ≤0.020 ― ≤0.0012 ≤0.0050 ≤0.050 ≤0.04 ≤0.075 ≤0.002 Advanced high-quality steel ≤0.25 ≤0.25 ≤0.020 ≤0.020 ≤0.0010 ≤0.0009 ≤0.0030 ≤0.050 ≤0.04 ≤0.075 ≤0.002 Super high-quality steel ≤0.25 ≤0.25 ≤0.015 ≤0.015 ≤0.0010 ≤0.0006 ≤0.0015 ≤0.050 ≤0.04 ≤0.075 ≤0.002 Note: a The oxygen content is tested in billets or rolled steels; b The composition in steel grade GCr15SiMn, GCr15SiMo, and GCr18Mo is allowed 0.0005% addition. 表 2 Al?O平衡常數計算值和實驗值對比
Table 2. Comparison of calculation results and experimental data of Al?O equilibrium constant
Thermodynamic calculation Experiments without oxygen Experiments with oxygen Researchers -lg Kd Researchers -lg Kd Researchers -lg Kd Chipman 14 Chipman 14 Hessenbruch 9 Kubaschewski 15 Gller 13 Herty 9 Richardson 13 Kuznetchov 12 Wentrup 10 Sawamura 14 Eutrement 13 Hilty 9 Elliott 14 Fruehan 14 Repetylo 9 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Li Z K, Lei J Z, Xu H F, et al. Current status and development trend of bearing steel in China and abroad. J Iron Steel Res, 2016, 28(3): 1李昭昆, 雷建中, 徐海峰, 等. 國內外軸承鋼的現狀與發展趨勢. 鋼鐵研究學報, 2016, 28(3):1 [2] Ren X. Current situation and development direction of special steel in China. World Metal Guide, 2016-10-18: B14任秀平: 我國特殊鋼現狀及發展方向. 世界金屬導報, 2016-10-18: B14 [3] Gu C, Bao Y P, Gan P, et al. Effect of main inclusions on crack initiation in bearing steel in the very high cycle fatigue regime. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2018, 25(6): 623 doi: 10.1007/s12613-018-1609-4 [4] Qian G A, Hong Y S, Zhou C G. Investigation of high cycle and very-high-cycle fatigue behaviors for a structural steel with smooth and notched specimens. Eng Fail Anal, 2010, 17(7-8): 1517 doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2010.06.002 [5] Gao G H, Zhang B X, Cheng C, et al. Very high cycle fatigue behaviors of bainite/martensite multiphase steel treated by quenching-partitioning tempering process. Int J Fatigue, 2016, 92: 203 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2016.06.025 [6] Li S X, Weng Y Q, Hui W J, et al. Very High Cycle Fatigue Properties of High Strength Steels-Effects of Nonmetallic Inclusions. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2010李守新, 翁宇慶, 惠衛軍, 等. 高強度鋼超高周疲勞性能: 非金屬夾雜物的影響. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2010 [7] Spriestersbach D, Grad P, Kerscher E. Influence of different non-metallic inclusion types on the crack initiation in high-strength steels in the VHCF regime. Int J Fatigue, 2014, 64: 114 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2014.03.003 [8] Karr U, Schuller R, Fitzka M, et al. Influence of inclusion type on the very high cycle fatigue properties of 18Ni maraging steel. J Mater Sci, 2017, 52(10): 5954 doi: 10.1007/s10853-017-0831-1 [9] Gu C, Wang M, Bao Y P, et al. Quantitative analysis of inclusion engineering on the fatigue property improvement of bearing steel. Metals, 2019, 9(4): 476 doi: 10.3390/met9040476 [10] Murakami Y, Kodama S, Konuma S. Quantitative evaluation of effects of nonmetallic inclusions on fatigue strength of high strength steels. I: Basic fatigue mechanism and evaluation of correlation between the fatigue fracture and the size and location of non-metallic inclusions. Int J Fatigue, 1989, 11(5): 291 [11] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 18254—2016 High Carbon Chromium Bearing Steel. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2016中華人民共和國國家質量監督檢驗檢疫總局, 中國國家標準化管理委員會. GB/T 18254—2016 高碳鉻軸承鋼. 北京: 中國標準出版社, 2016 [12] Gu C. Microstructure Fatigue Life Prediction Model Based on the Effect of Inclusions in Bearing Steel [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019顧超. 高品質軸承鋼疲勞壽命預測模型及夾雜物影響規律研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2019 [13] Xu L M, Wang C S, Wang D H. Deoxidation of steel making and application of complex ferroalloy. Ferro-Alloys, 2004, 35(5): 12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1943.2004.05.003徐鹿鳴, 王春生, 王德華. 煉鋼的脫氧和復合合金的應用. 鐵合金, 2004, 35(5):12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1943.2004.05.003 [14] Shirokov N I, Petukhov B G. Deoxidation of rail steel by a reduced quantity of aluminum. Metallurgist, 1958, 2(1): 22 doi: 10.1007/BF00734438 [15] Yu Z S. Noduling and blockage at nozzle of continuous casting tundish and ladle. Angang Technol, 1980(5): 8余宗森. 連鑄中間包及盛鋼桶水口結瘤堵塞問題. 鞍鋼技術, 1980(5):8 [16] Ofengenden A M, Nesterovich R P. Reducing the amount of aluminum for the deoxidation of steel. Metallurgist, 1958, 2(6): 286 doi: 10.1007/BF00736270 [17] Lu S Y. Elimination of nozzle clogging by substitution Si for Al as deoxidant. Steelmaking, 2004, 20(6): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2004.06.011盧盛意. 用硅代替鋁脫氧來消除連鑄水口堵塞. 煉鋼, 2004, 20(6):32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2004.06.011 [18] Cai X F, Bao Y P, Lin L, et al. Effect of Al content on the evolution of non-metallic inclusions in Si–Mn deoxidized steel. Steel Res Int, 2016, 87(9): 1168 doi: 10.1002/srin.201500305 [19] Lyu S, Ma X D, Huang Z Z, et al. Understanding the formation and evolution of oxide inclusions in Si-deoxidized spring steel. Metall Mater Trans B, 2019, 50(4): 1862 doi: 10.1007/s11663-019-01613-0 [20] Li J Y, Cheng G G, Li L Y, et al. Formation mechanism of non-metallic inclusions in 202 stainless steel. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(12): 1567李璟宇, 成國光, 李六一, 等. 202不銹鋼中非金屬夾雜物的形成機理. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(12):1567 [21] Li Y, Chen C Y, Qin G Q, et al. Influence of crucible material on inclusions in 95Cr saw-wire steel deoxidized by Si–Mn. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2020, 27(8): 1083 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1957-8 [22] Xu J C, Palmer A R. Studies on morphology and compositions of oxide inclusions formed in liquid steel after deoxidation with aluminum. J Lanzhou Univ Technol, 1987, 13(1): 55徐金城, A. R. 帕莫. 鋁脫氧鋼液中氧化物夾雜的形態和成分. 甘肅工業大學學報, 1987, 13(1):55 [23] Shi Z Y, Wang S L. Analysis of aluminum deoxidation and silicon-aluminum-iron deoxidation. Steelmaking, 1991(1): 22史宗耀, 王樹林. 鋁脫氧和硅鋁鐵脫氧分析. 煉鋼, 1991(1):22 [24] Zhang W L. "A Blank" in aluminum deoxidization for steel. Sci Technol Baotou Steel, 1980(1): 58張文祿. 鋼用鋁脫氧的“一段空白”. 包鋼科技, 1980(1):58 [25] Li H L, Zhang Z P, Wang F H. Brief talk on aluminum deoxidation and nitrogen determination function in liquid steel. Tianjin Metall, 2008(05): 51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-110X.2008.05.013李會玲, 張哲平, 汪鳳華. Al在鋼中脫氧定氮作用淺析. 天津冶金, 2008(05):51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-110X.2008.05.013 [26] Zhang F X. Effect of aluminum on performance of non-alloy soft steel. Res Iron Steel, 1974(4): 44張復祥. 鋁對非合金軟鋼性能的影響. 鋼鐵研究情報, 1974(4):44 [27] Cui H, Bao Y P, Wang M, et al. Clogging behavior of submerged entry nozzles for Ti-bearing IF steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2010, 17(2): 154 doi: 10.1007/s12613-010-0206-y [28] Hua C J, Wang M, Zhang M Y, et al., Effect of submerged entry nozzle wall surface morphologies on boundary layer structure and alumina inclusions transport. Chin J Eng, https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.05.05.001華承健, 王敏, 張孟昀, 等. 浸入式水口內壁特征對邊界層流場結構和氧化鋁夾雜物運動行為的影響. 工程科學學報, https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.05.05.001 [29] Wang X H, Wang L F. Control of the non-metallic inclusions in hard wire steels. Steel Wire Products, 2005, 31(5): 9王新華, 王立峰. 硬線鋼中非金屬夾雜物控制. 金屬制品, 2005, 31(5):9 [30] Gladman T. Developments in inclusions control and their effects on steel properties. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1992, 19(6): 457 [31] Zhu L H, Zhao Q X, Gu H C, et al. A new understanding of deoxidation by aluminum in steels. J Iron Steel Res, 1999, 11(4): 65 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.1999.04.016朱麗慧, 趙欽新, 顧海澄, 等. 關于鋼用鋁脫氧的再認識. 鋼鐵研究學報, 1999, 11(4):65 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.1999.04.016 [32] Gu C, Lian J H, Bao Y P, et al. Microstructure-based fatigue modelling with residual stresses: Prediction of the microcrack initiation around inclusions. Mater Sci Eng A, 2019, 751: 133 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.02.058 [33] Gu C, Lian J H, Bao Y P, et al. Microstructure-based fatigue modelling with residual stresses: Prediction of the fatigue life for various inclusion sizes. Int J Fatigue, 2019, 129: 105158 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.06.018 [34] Bao S, Chen B, Jiang M, et al. Experimental research of simultaneous reducing [Al]s and [O] of ultra low oxygen steel. Iron Steel, 2007, 42(6): 30 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2007.06.007包薩日娜, 陳斌, 姜敏, 等. 超低氧鋼中同時降低[Al]s、[O]實驗研究. 鋼鐵, 2007, 42(6):30 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2007.06.007 [35] Li H B, Lin W, Wang X H, et al. Formation and transformation of spinel inclusion in aluminium killed steel. Special Steel, 2007, 28(4): 30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2007.04.011李海波, 林偉, 王新華, 等. 鋁脫氧鋼中尖晶石夾雜物的生成與轉變. 特殊鋼, 2007, 28(4):30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2007.04.011 [36] Hu W H, Bao Y P, Jin Y H. Study and control practice of Als in GCr15 bearing steel strip. Steelmaking, 2009, 25(2): 22胡文豪, 包燕平, 金耀輝. GCr15板帶軸承鋼中的Als研究與實踐. 煉鋼, 2009, 25(2):22 [37] Wang X H. Technologies of deoxidation, refining and non-metallic inclusion control for special steels // Proceedings of 2010 National Steelmaking Continuous Casting Technology Conference. Qian’an, 2010王新華. 超低氧含量特殊鋼的脫氧、精煉與非金屬夾雜物控制 // 2010年全國煉鋼—連鑄生產技術會議. 遷安, 2010 [38] Zhao D W, Li H B, Gao P, et al. Inclusion formation and deformation in Al-killed wheel steel without calcium treatment. Iron Steel, 2016, 51(1): 25趙東偉, 李海波, 高攀, 等. 非鈣處理鋁脫氧車輪鋼夾雜物形成及變形行為. 鋼鐵, 2016, 51(1):25 [39] Chen B, Bao S, Jiang M, et al. Cleanliness of molten steel improved by Mg. J Iron Steel Res, 2008, 20(6): 14陳斌, 包薩日娜, 姜敏, 等. 鎂提高鋼水純凈度的研究. 鋼鐵研究學報, 2008, 20(6):14 [40] Deng Z Y, Zhu M Y. Evolution mechanism of non-metallic inclusions in Al-killed alloyed steel during secondary refining process. ISIJ Int, 2013, 53(3): 450 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.53.450 [41] Deng Z Y, Zhu M Y. Deoxidation mechanism of Al-killed steel during industrial refining process. ISIJ Int, 2014, 54(7): 1498 [42] Zhai X L, He Z M, Liu Y H, et al. Thermodynamic analysis on the non-metallic inclusion formation in deoxidation of austenitic Mn-steels with Ca-Al. Iron Steel, 1986(6): 42翟學來, 何鎮明, 劉耀輝, 等. 鈣鋁脫氧對奧氏體錳鋼非金屬夾雜物形成的熱力學分析. 鋼鐵, 1986(6):42 [43] Qiao M R, Guo S Q, Zheng H Y, et al. Study on the modification of inclusions by Mg treatment in GCr18Mo bearing steel. Shanghai Met, 2019, 41(2): 86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2019.02.016喬夢然, 郭曙強, 鄭紅妍, 等. GCr18Mo軸承鋼的鎂處理改質效果研究. 上海金屬, 2019, 41(2):86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2019.02.016 [44] Yang C Y, Liu P, Luan L K, et al. Study on transverse-longitudinal fatigue properties and their effective inclusion-size mechanism of hot rolled bearing steel with rare earth addition. Int J Fatigue, 2019, 128: 105193 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105193 [45] Chang L Z, Gao G, Zheng F Z, et al. Effect of rare earth and magnesium complex treatment on inclusions in GCr15 bearing steel. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(6): 763常立忠, 高崗, 鄭福舟, 等. 稀土?鎂復合處理對GCr15軸承鋼中夾雜物的影響. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(6):763 [46] Gu C, Bao Y P, Gan P, et al. An experimental study on the impact of deoxidation methods on the fatigue properties of bearing steels. Steel Res Int, 2018, 89(9): 1800129 doi: 10.1002/srin.201800129 [47] Ladutkin D, Korte E, Bleymehl M, et al. Advantages of Si deoxidation of bearing steels for steel cleanness and for composition and morphology of nonmetallic inclusions in rolled product // Bearing Steel Technologies: 11th Volume, Progress in Steel Technologies and Bearing Steel Quality Assurance. West Conshohocken, 2017: 48 [48] Shimamoto M, Sugimura T, Kimura S, et al. Improvement of the rolling contact fatigue resistance in bearing steels by adjusting the composition of oxide inclusions // Bearing Steel Technologies: 10th Volume, Advances in Steel Technologies for Rolling Bearings. West Conshohocken, 2015: 173 [49] Owaki A, Shimamoto M, Sugimura T, et al. The study of the evaluation of the fracture initiation and propagation on the rolling contact fatigue in bearing steels // Bearing Steel Technologies: 11th Volume, Progress in Steel Technologies and Bearing Steel Quality Assurance. West Conshohocken, 2017: 487 [50] Xue Z L, Li Z B, Zhang J W. Deoxidization and oxide inclusion control of steel. Special Steel, 2001, 22(6): 24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2001.06.008薛正良, 李正邦, 張家雯. 鋼的脫氧與氧化物夾雜控制. 特殊鋼, 2001, 22(6):24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2001.06.008 [51] Wu W, Liu L, Li J. Deoxidization process with low aluminum addition for heavy rail steel. Iron Steel, 2007, 42(3): 33 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2007.03.009吳偉, 劉瀏, 李峻. 重軌鋼無鋁脫氧工藝的研究. 鋼鐵, 2007, 42(3):33 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2007.03.009 [52] Li Y, Jiang Z H, Yuan W X, et al. Effect of refining slag on inclusions in non-aluminum deoxidation steel. China Metall, 2006, 16(6): 28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9356.2006.06.008李陽, 姜周華, 袁偉霞, 等. 精煉渣對非鋁脫氧鋼中夾雜物影響的實驗研究. 中國冶金, 2006, 16(6):28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9356.2006.06.008 -




 下載:
下載: