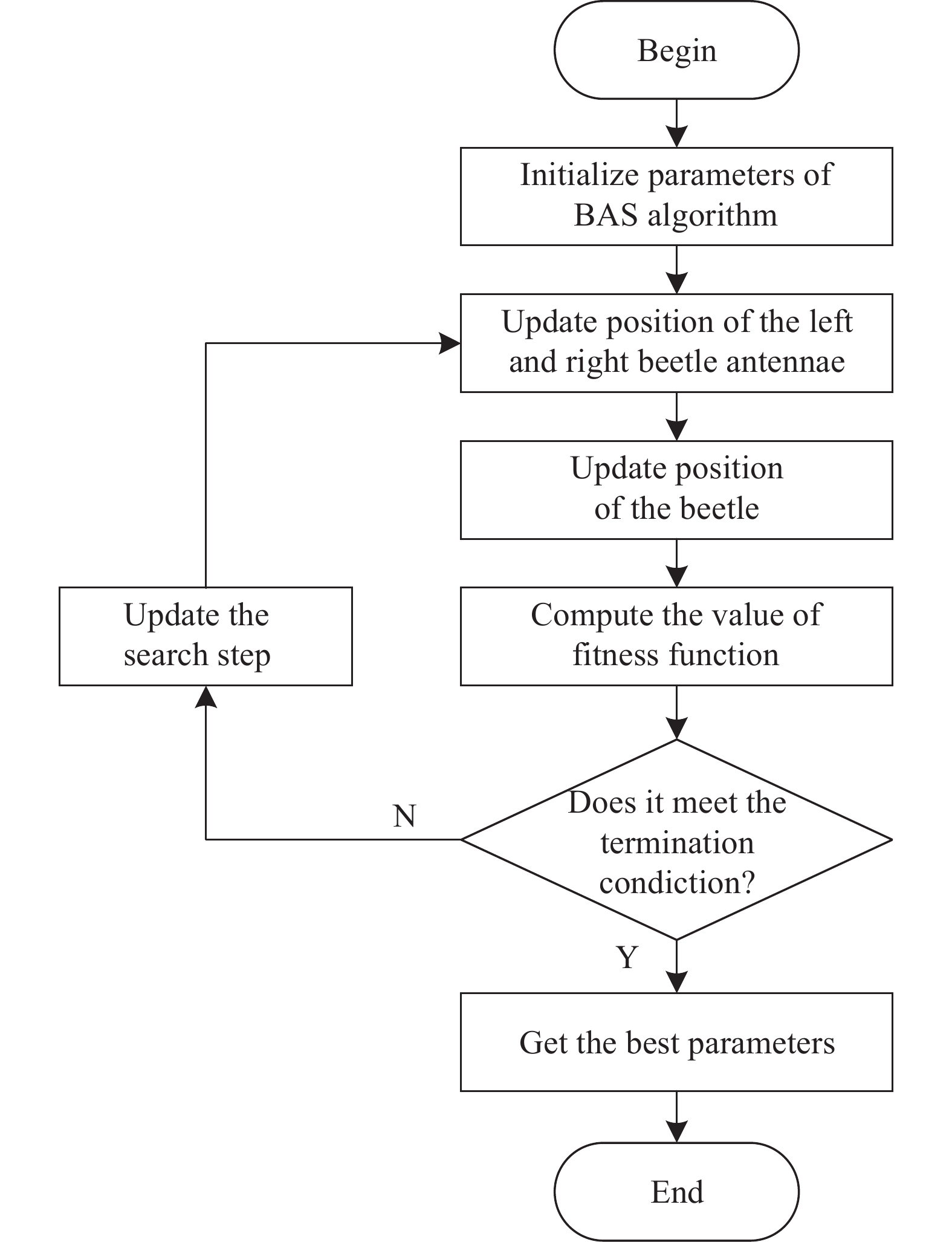
Processing and modeling dual-rate sampled data in seawater corrosion monitoring of low alloy steels
-
摘要: 隨著物聯網技術的發展,前端傳感器的使用使得低合金鋼的海水腐蝕監測成為了現實,從而獲得了大量的腐蝕數據。針對傳統均值法處理雙率腐蝕數據帶來的數據信息損失以及建模精度下降問題,提出了一種基于綜合指標值(CIV)和改進相關向量回歸(IRVR)的雙率腐蝕數據處理和建模算法(CIV-IRVR)。首先,通過構建CIV表征輸入數據的綜合影響并采用天牛須搜索(BAS)算法對其參數進行尋優;然后,建立最優CIV序列與輸出數據間的線性回歸模型將雙率數據轉化為建模用的單率數據,能夠更多地保留原始數據信息;最后,給出了一種BAS算法優化的具有組合核函數的改進相關向量回歸建模方法(IRVR),并建立了針對低合金鋼海水腐蝕雙率數據的CIV-IRVR預測模型。結果表明:相比于均值方法處理雙率腐蝕數據,所提方法將建模樣本數量由196提升到了1834;相比于海水腐蝕建模領域常用的人工神經網絡(ANN)和支持向量回歸(SVR)建模方法,所提模型的平均絕對誤差(MAE)、均方根誤差(RMSE)和決定系數(CD)分別為1.1914 mV、1.5729 mV以及0.9963,在各項指標上均優于對比算法,說明所提模型不僅減少了信息損失還提高了建模精度,對于雙率海水腐蝕數據建模具有一定現實意義。Abstract: With the rapid development of Internet of Things technology, the use of front-end sensors realizes the corrosion potential online detection of low alloy steels in a marine environment, thereby obtaining multitudes of corrosion data. Concerning the problems of data information loss and modeling accuracy reduction caused by the use of the traditional mean value method when processing dual-rate corrosion data, a new dual-rate data processing and modeling algorithm combining the comprehensive index value (CIV) and improved relevance vector regression (IRVR) was proposed. First, the CIV was constructed to characterize the comprehensive influence of the input data, and the beetle antennae search (BAS) algorithm was applied to optimize its parameters. Then, linear regression models between the best CIV sequence and the output data were established to convert the dual-rate corrosion data into single-rate data for modeling, which retained more information of the original corrosion data. Finally, the IRVR method based on BAS optimization of compounding kernels was given to establish the prediction model for dual-rate seawater corrosion data of low alloy steels. The results show that the proposed model CIV-IRVR increases the number of modeling samples from 196 for the mean value method to 1834. Moreover, the mean absolute error, root mean square error, and coefficient of determination of the CIV-IRVR model are 1.1914 mV, 1.5729 mV, and 0.9963, respectively, which outperforms commonly used comparison algorithms, such as the artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector regression (SVR). Moreover, the CIV-IRVR model can help obtain the prediction results with error bars, and it has the absolute error distribution closest to 0, which highlights its excellent predictive performance on the seawater corrosion potential of low alloy steels. Thus, the proposed model not only reduces the information loss and improves the modeling accuracy but also has practical significance for modeling dual-rate seawater corrosion data.
-
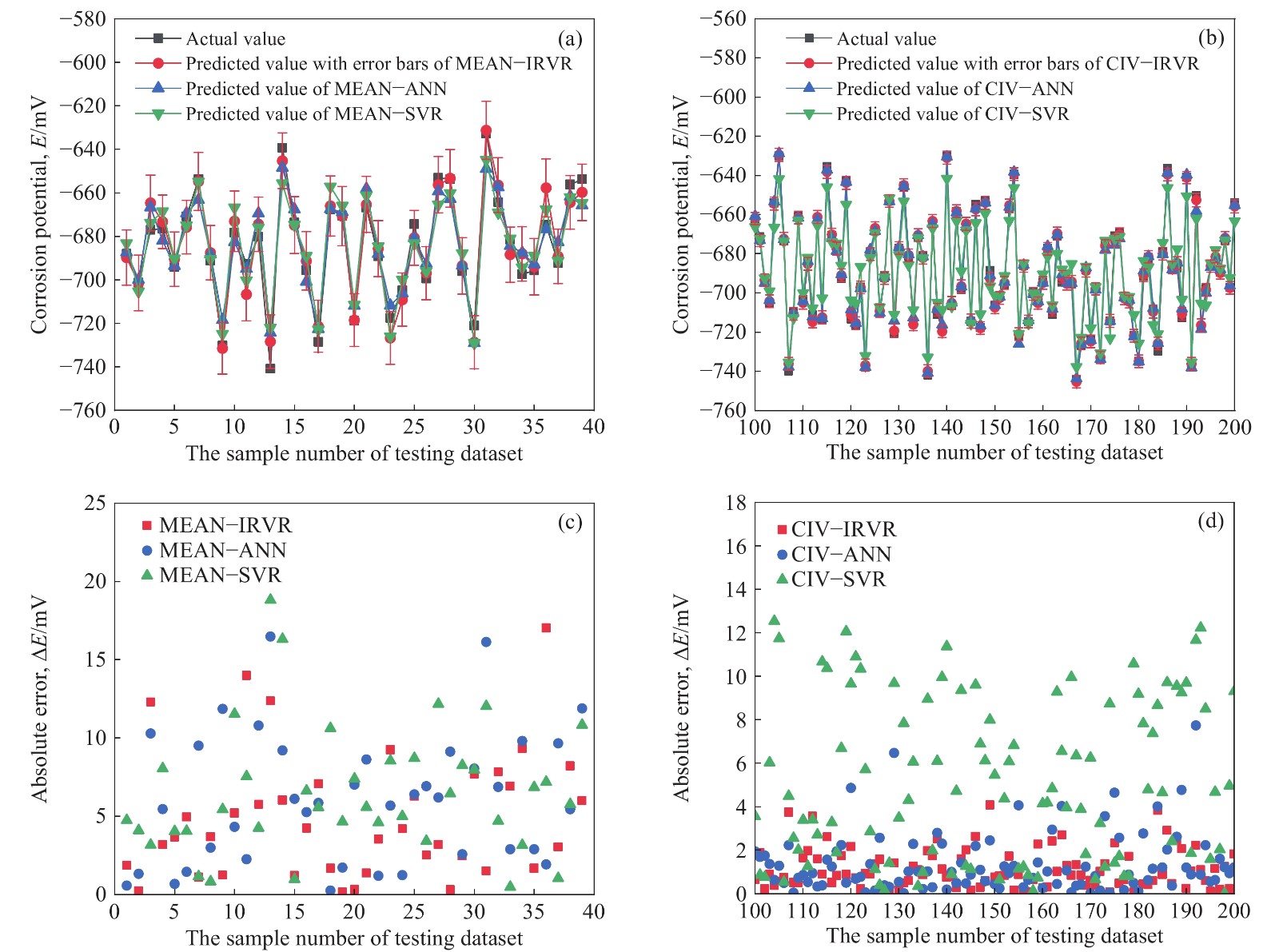
圖 4 不同模型在測試集上的預測結果及絕對誤差。(a)基于MEAN的三種模型;(b)基于CIV的三種模型;(c)基于MEAN的三種模型的絕對誤差值;(d)基于CIV的三種模型的絕對誤差值
Figure 4. Prediction results and absolute errors of different models: (a) three models based on the MEAN method; (b) three models based on the CIV method; (c) absolute errors of the three models based on the MEAN method; (d) absolute errors of the three models based on the CIV method
表 1 14種低合金鋼的化學元素成分(質量分數)
Table 1. Elemental compositions of 14 low alloy steels
LAS Elemental compositions/ % C Si Mn P S Ni Cr Mo Cu Others 1 0.1554 0.0959 0.3193 0.0241 0.0086 0.0145 0.0415 0 0.0496 Al: 0.0205 2 0.1 0.28 1.42 0.01 0.002 0 0 0 0 0 3 0.072 0.1388 1.2186 0.0124 0.0034 0 0 0 0 Al: 0.0394; Ti: 0.0178; Nb: 0.015 4 0.17 0.22 0.88 0.018 0.005 0 0 0 0 Al:0.023 5 0.12 0.33 0.37 0.08 0.04 2.72 1.05 0.24 0 V:0.08 6 0.0697 0.3257 1.0426 0.0167 0.0079 0.1299 0.6239 0 0.2636 Al: 0.0288; Ti: 0.017; Nb: 0.0264 7 0.0672 0.181 1.5407 0.0131 0.0027 0 0.2075 0.0575 0 Al: 0.0382; Ti: 0.0176; Nb: 0.063 8 0.04 0.3 1.79 0.013 0.001 0 0.025 0 0 0 9 0.11 0.29 1.12 0.013 0.003 0.41 0.46 0.41 0.27 Al: 0.036; Ti: 0.019; V: 0.03; B: 0.015 10 0.06 0.17 1.5 0.014 0.002 0.4 0.25 0.2 0.26 Al: 0.026; Ti: 0.012; Nb: 0.02 11 0.042 0.18 0.35 0.008 0.003 0 0 0 0 Al: 0.029 12 0.097 0.26 1.64 0.01 0.006 0 0 0 0.2 Ti: 0.017; Nb: 0.048; V: 0.067; B: 0.004 13 0.091 0.21 0.4 0.013 0.016 0 0 0 0.04 N: 0.028 14 0.064 0.22 1.18 0.008 0.005 0 0 0 0.32 Ti: 0.014; Nb: 0.035; V: 0.049; N: 0.033 表 2 經CIV方法處理得到的海水腐蝕數據集
Table 2. Seawater corrosion dataset obtained via the CIV method
k 16 Inputs 1 Output CIVavg(kT2) C/% Si/% Mn/% P/% S/% Ni/% V/% N/% B/% E/mV 1 28.1078 0.1554 0.0959 0.3193 0.0241 0.0086 0.0145 … 0 0 0 ?710.578 2 27.0536 0.1554 0.0959 0.3193 0.0241 0.0086 0.0145 … 0 0 0 ?714.553 3 27.2814 0.1554 0.0959 0.3193 0.0241 0.0086 0.0145 … 0 0 0 ?719.096 4 27.2969 0.1554 0.0959 0.3193 0.0241 0.0086 0.0145 … 0 0 0 ?720.240 5 28.0726 0.1554 0.0959 0.3193 0.0241 0.0086 0.0145 … 0 0 0 ?721.835 $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ 1832 7.72111 0.0640 0.2200 1.1800 0.0080 0.0050 0 … 0.0490 0.0330 0 ?658.022 1833 7.50411 0.0640 0.2200 1.1800 0.0080 0.0050 0 … 0.0490 0.0330 0 ?656.644 1834 7.29048 0.0640 0.2200 1.1800 0.0080 0.0050 0 … 0.0490 0.0330 0 ?656.657 表 3 不同模型的樣本數量和預測誤差表
Table 3. Sample size and prediction errors of different models
Models N N3 MAE/mV RMSE/mV CD MEAN?ANN 196 39 6.0757 7.3530 0.9247 MEAN?SVR 196 39 6.4792 7.6111 0.9113 MEAN?IRVR 196 39 4.9367 6.3617 0.9373 CIV?ANN 1834 367 1.3627 1.8324 0.9950 CIV?SVR 1834 367 5.3905 6.4542 0.9553 CIV?IRVR 1834 367 1.1914 1.5729 0.9963 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Li X G, Zhang D W, Liu Z Y, et al. Materials science: Share corrosion data. Nature, 2015, 527(7579): 441 doi: 10.1038/527441a [2] Li Z L, Fu D M, Li Y, et al. Application of an electrical resistance sensor-based automated corrosion monitor in the study of atmospheric corrosion. Materials, 2019, 12(7): 1065 doi: 10.3390/ma12071065 [3] Chen M D, Zhang H J, Chen L, et al. An electrochemical method based on OCP fluctuations for anti-corrosion alloy composition optimization. Anti-Corros Methods Mater, 2018, 65(3): 325 doi: 10.1108/ACMM-03-2018-1913 [4] Pei Z B, Cheng X Q, Yang X J, et al. Understanding environmental impacts on initial atmospheric corrosion based on corrosion monitoring sensors. J Mater Sci Technol, 2021, 64: 214 doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.01.023 [5] Ni B Y, Xiao D Y. A survey on identification of multirate sampled systems. Control Theory Appl, 2009, 26(1): 62倪博溢, 蕭德云. 多采樣率系統的辨識問題綜述. 控制理論與應用, 2009, 26(1):62 [6] Kranc G. Input-output analysis of multirate feedback systems. IRE Trans Autom Control, 1957, 3(1): 21 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1957.1104783 [7] Friedland B. Sampled-data control systems containing periodically varying members. IFAC Proc Vol, 1960, 1(1): 371 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)70078-X [8] Khargonekar P, Poolla K, Tannenbaum A. Robust control of linear time-invariant plants using periodic compensation. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 1985, 30(11): 1088 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1985.1103841 [9] Ni B Y, Xiao D Y. A recursive identification method for non-uniformly sampled systems. Acta Autom Sin, 2009, 35(12): 1520倪博溢, 蕭德云. 非均勻采樣系統的一種遞推辨識方法. 自動化學報, 2009, 35(12):1520 [10] Li D G, Shah S L, Chen T W. Analysis of dual-rate inferential control systems. Automatica, 2002, 38(6): 1053 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(01)00295-3 [11] Ding F, Chen T W. Modeling and identification for multirate systems. Acta Autom Sin, 2005, 31(1): 105 [12] Zhi Y J, Fu D M, Zhang D W, et al. Prediction and knowledge mining of outdoor atmospheric corrosion rates of low alloy steels based on the random forests approach. Metals, 2019, 9(3): 383 doi: 10.3390/met9030383 [13] Shi Y N, Fu D M, Zhi Y J, et al. Improved ANFIS-based imputation method for missing data on atmospheric corrosion environment. Equip Environ Eng, 2016, 13(6): 78石雅楠, 付冬梅, 支元杰, 等. 基于 ANFIS 改進的大氣腐蝕環境缺失數據填補方法. 裝備環境工程, 2016, 13(6):78 [14] Wei X, Fu D M, Chen M D, et al. Data mining to effect of key alloying elements on corrosion resistance of low alloy steels in Sanya seawater environment. J Mater Sci Technol, 2021, 64: 222 doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.01.040 [15] Liu X Q, Tang X, Wang J. Correlation between seawater environmental factors and marine corrosion rate using artificial neural network analysis. J Chin Soc Corros Prot, 2005, 25(1): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4537.2005.01.003劉學慶, 唐曉, 王佳. 金屬腐蝕速度與海水環境參數相關模型的人工神經網絡分析. 中國腐蝕與防護學報, 2005, 25(1):11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4537.2005.01.003 [16] Shirazi A Z, Mohammadi Z. A hybrid intelligent model combining ANN and imperialist competitive algorithm for prediction of corrosion rate in 3C steel under seawater environment. Neural Comput Appl, 2017, 28(11): 3455 doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2251-6 [17] Wen Y F, Cai C Z, Liu X H, et al. Corrosion rate prediction of 3C steel under different seawater environment by using support vector regression. Corros Sci, 2009, 51(2): 349 doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.10.038 [18] Bi A R, Luo Z S, Qiao W, et al. Prediction of pipeline inner-corrosion based on principal component analysis and particle swarm optimization-support vector machine. Surf Technol, 2018, 47(9): 133畢傲睿, 駱正山, 喬偉, 等. 基于主成分和粒子群優化支持向量機的管道內腐蝕預測. 表面技術, 2018, 47(9):133 [19] Li M X, Zhang H C, Qiu P Y, et al. Predicting future locations with deep fuzzy-LSTM network. Acta Geodaet Cartograph Sin, 2018, 47(12): 1660 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170268李明曉, 張恒才, 仇培元, 等. 一種基于模糊長短期神經網絡的移動對象軌跡預測算法. 測繪學報, 2018, 47(12):1660 doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170268 [20] Chen M D, Zhang F, Liu Z Y, et al. Galvanic series of metals and effect of alloy compositions on corrosion resistance in Sanya seawater. Acta Metall Sin, 2018, 54(9): 1311 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00521陳閩東, 張帆, 劉智勇, 等. 金屬材料在三亞海水中的腐蝕電位序及合金成分對耐蝕性的影響. 金屬學報, 2018, 54(9):1311 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00521 [21] Jiang X Y, Li S. BAS: beetle antennae search algorithm for optimization problems. Int J Rob Control, 2018, 1(1): 1 doi: 10.5430/ijrc.v1n1p1 [22] Zhao Y Q, Qian Q, Zhou T J, et al. Hybrid optimization algorithm based on beetle antennae search and genetic evolution. J Chin Comput Syst, 2020, 41(7): 1438 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2020.07.016趙玉強, 錢謙, 周田江, 等. 天牛須搜索與遺傳的混合算法. 小型微型計算機系統, 2020, 41(7):1438 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2020.07.016 [23] Tipping M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J Mach Learn Res, 2001, 1: 211 [24] Wu X T. Prediction Model of Solar Irradiance Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Relevance Vector Machine [Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018吳小濤. 基于變分模態分解和相關向量機的太陽輻照度預測模型研究[學位論文]. 武漢: 華中科技大學, 2018 [25] Duan Q, Zhao J G, Ma Y. Relevance vector machine based on particle swarm optimization of compounding kernels in elextricity load forecasting. Electr Mach Control, 2010, 14(6): 33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-449X.2010.06.006段青, 趙建國, 馬艷. 優化組合核函數相關向量機電力負荷預測模型. 電機與控制學報, 2010, 14(6):33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-449X.2010.06.006 [26] Wu J, Cheng H C, Liu Y Q, et al. Learning soft sensors using time difference-based multi-kernel relevance vector machine with applications for quality-relevant monitoring in wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2020, 27(23): 28986 doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09192-3 -




 下載:
下載: