-
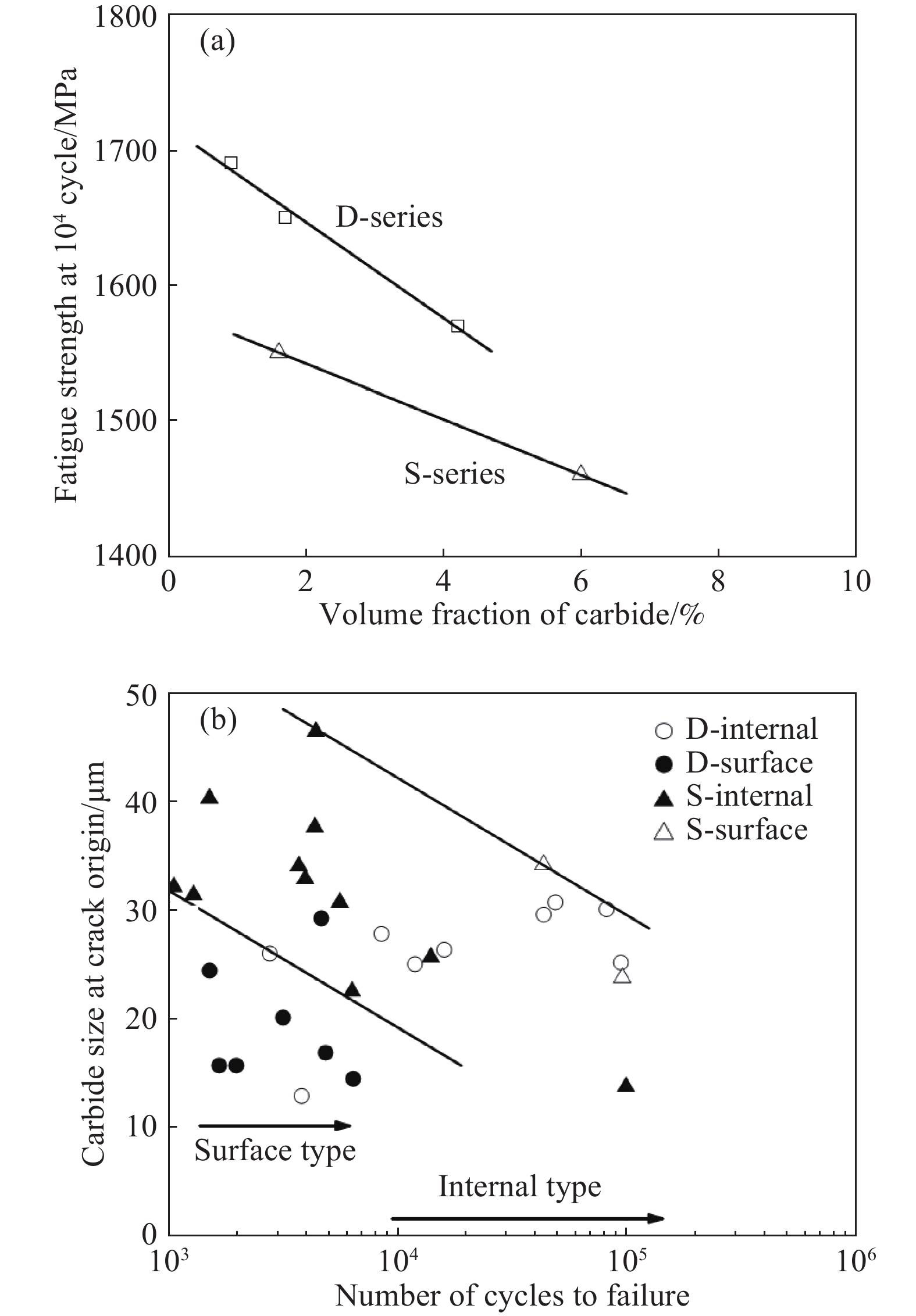
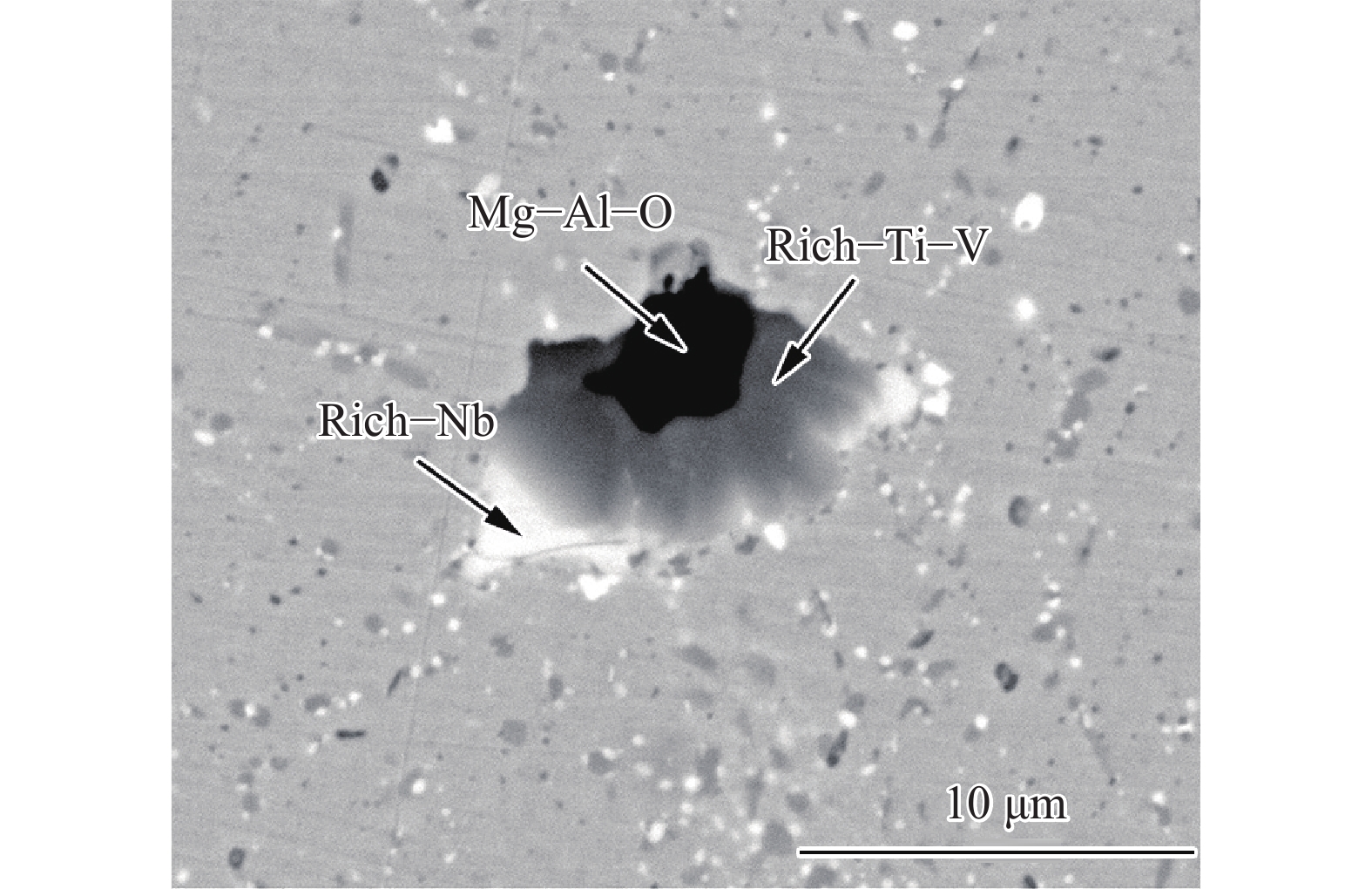
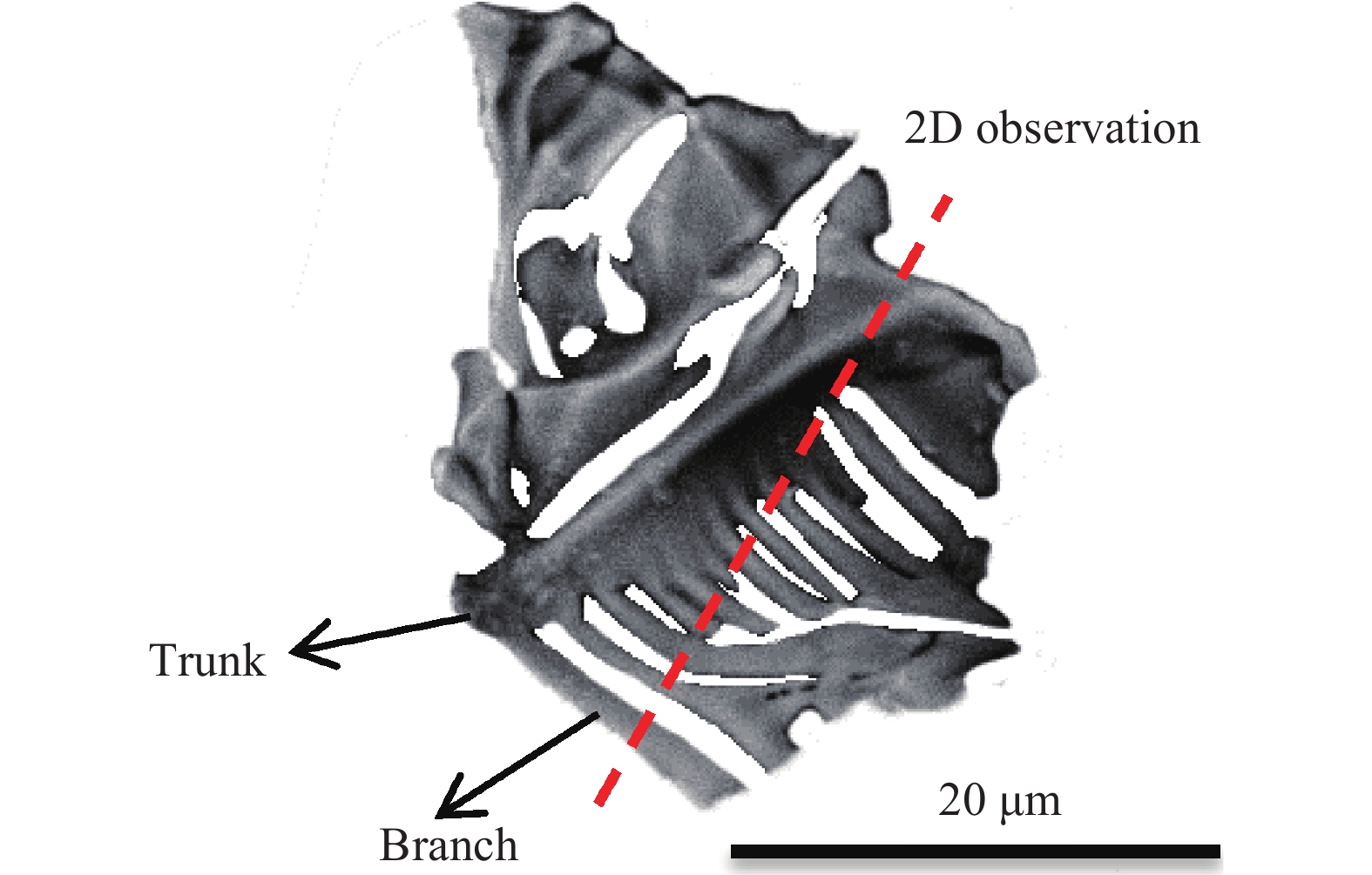
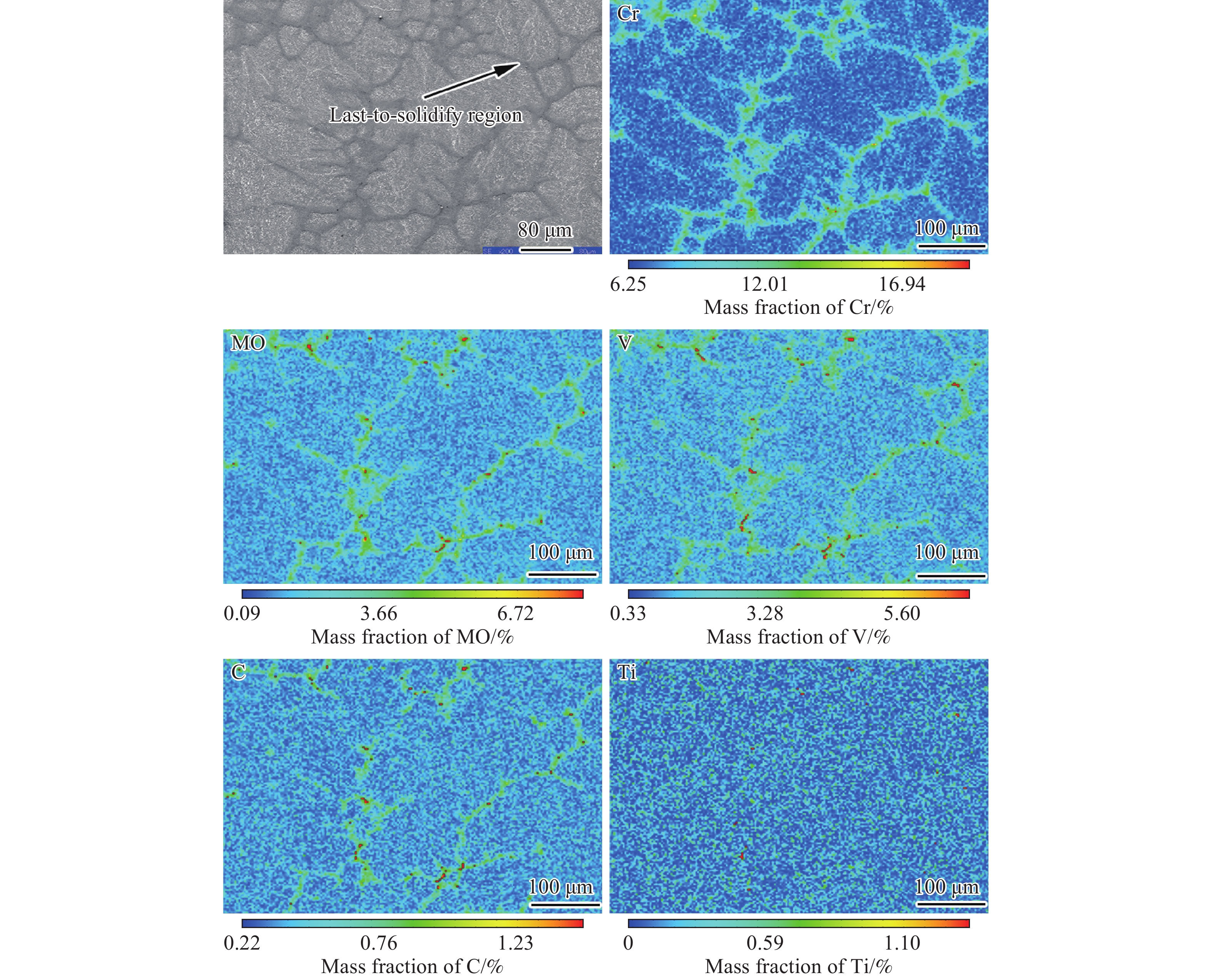
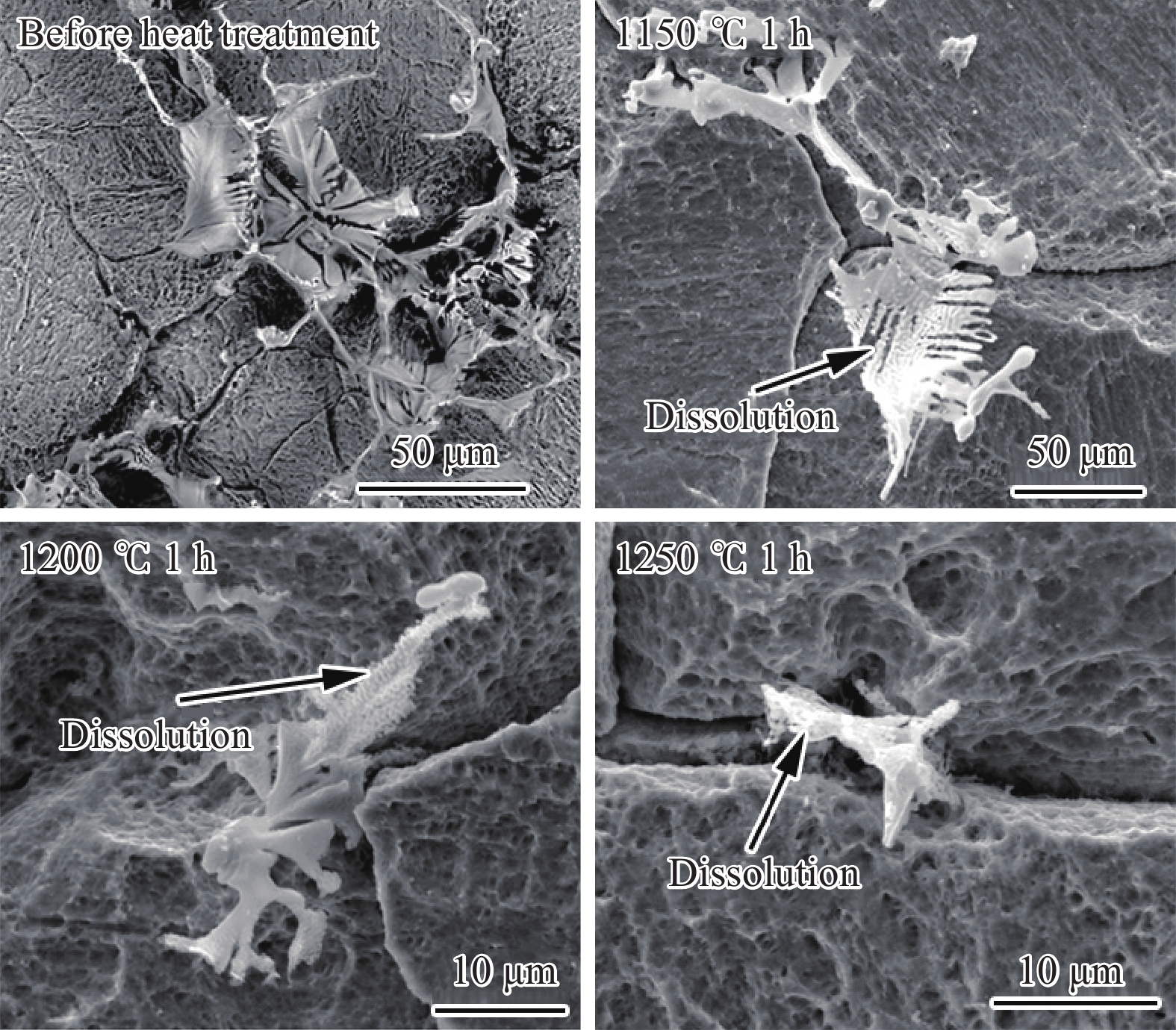
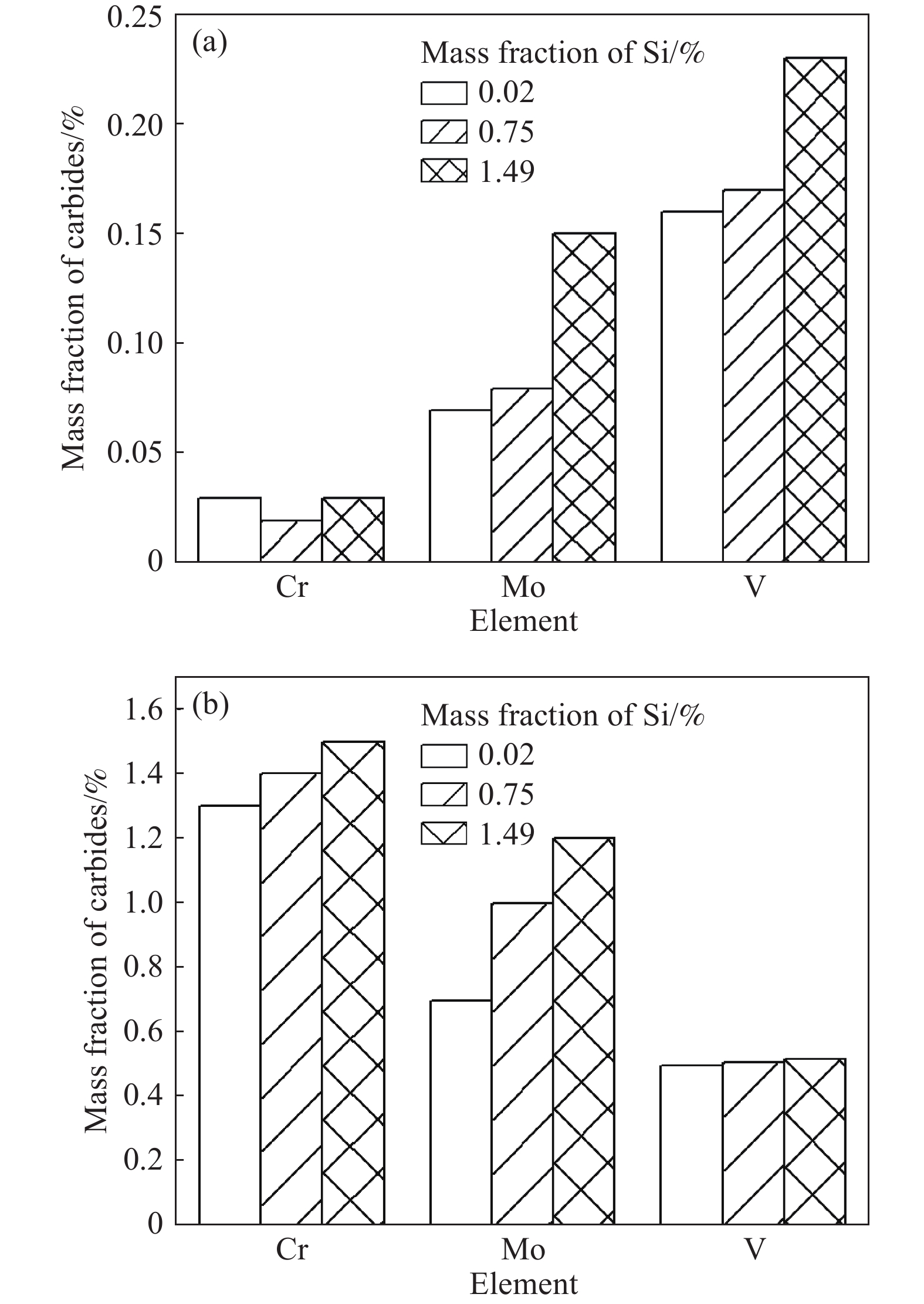
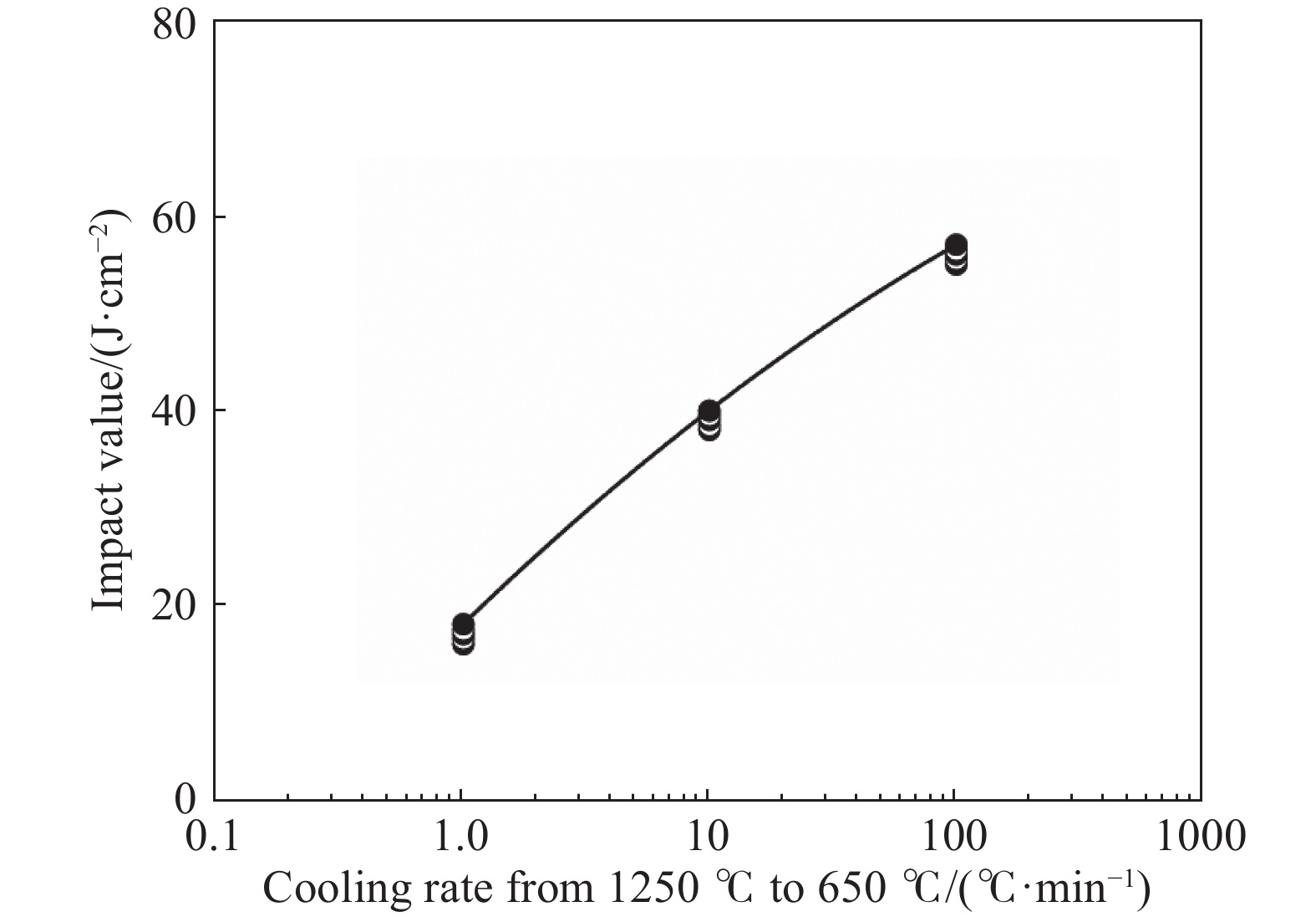
摘要: 首先結合H13鋼的成分特點肯定了H13鋼優異的材料性能,隨后總結了一次碳化物與H13鋼使用壽命之間的關系。進一步系統地論述和研究了H13鋼中一次碳化物的特征,包括二維和三維形貌、熱穩定性、析出機理等。最后對比了4種H13鋼中一次碳化物的控制手段,包括成分優化、冷速控制、Mg處理和稀土處理。相關論述和研究工作能夠對鋼中一次碳化物的合理優化起到一定的啟發作用。Abstract: The H13 steel is widely used in hot rolling, hot extrusion, and hot forging because of its remarkable fatigue resistance performance, hot strength, and impact toughness. To further extend the service life of the steel, the production of high-purity die steel is vital. Carbide-forming elements with a mass fraction of about 8%, including Cr, Mo, and V, are contained in H13 steel to prevent the coarsening of austenite or strengthen the steel through secondary hardening. However, owing to the presence of these elements, primary carbides are easily to be found in H13 steel because of the segregation of carbide-forming elements during solidification. The presence of large primary carbides is one of the main causes of the fatigue crack of H13 steel. Therefore, it is of great significance to systematically study the behavior of primary carbides in H13 steel. The excellent material properties of H13 steel were firstly affirmed in combination with the composition characteristics, and then the relationship between the primary carbides and the service life of H13 steel were summarized. The service life of H13 steel reduces with an increase in the primary carbide size. The hazard of primary carbide on the H13 surface steel is much greater than that inside the steel. The characteristics of primary carbides in H13 steel were further systematically discussed, including two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) morphologies, thermal stability and precipitation mechanism. A great difference exits between the 2D and 3D characteristics of primary carbides. In the 2D analyses, the density of the primary carbides appears high, while their size is small. The actual characteristics of primary carbides can be obtained only by 3D observation. Four primary carbide control methods in H13 steel are compared, including composition optimization, cooling rate control, Mg treatment and rare earth treatment. Composition optimization and cooling rate control have been successfully applied in the actual production process. Rare earth treatment may be an effective control method with Chinese characteristics. The relevant discussion and research work in this article can play a certain enlightening role in the rational control of the primary carbides in H13 steel.
-
Key words:
- H13 steel /
- primary carbide /
- morphology /
- characteristic /
- control
-
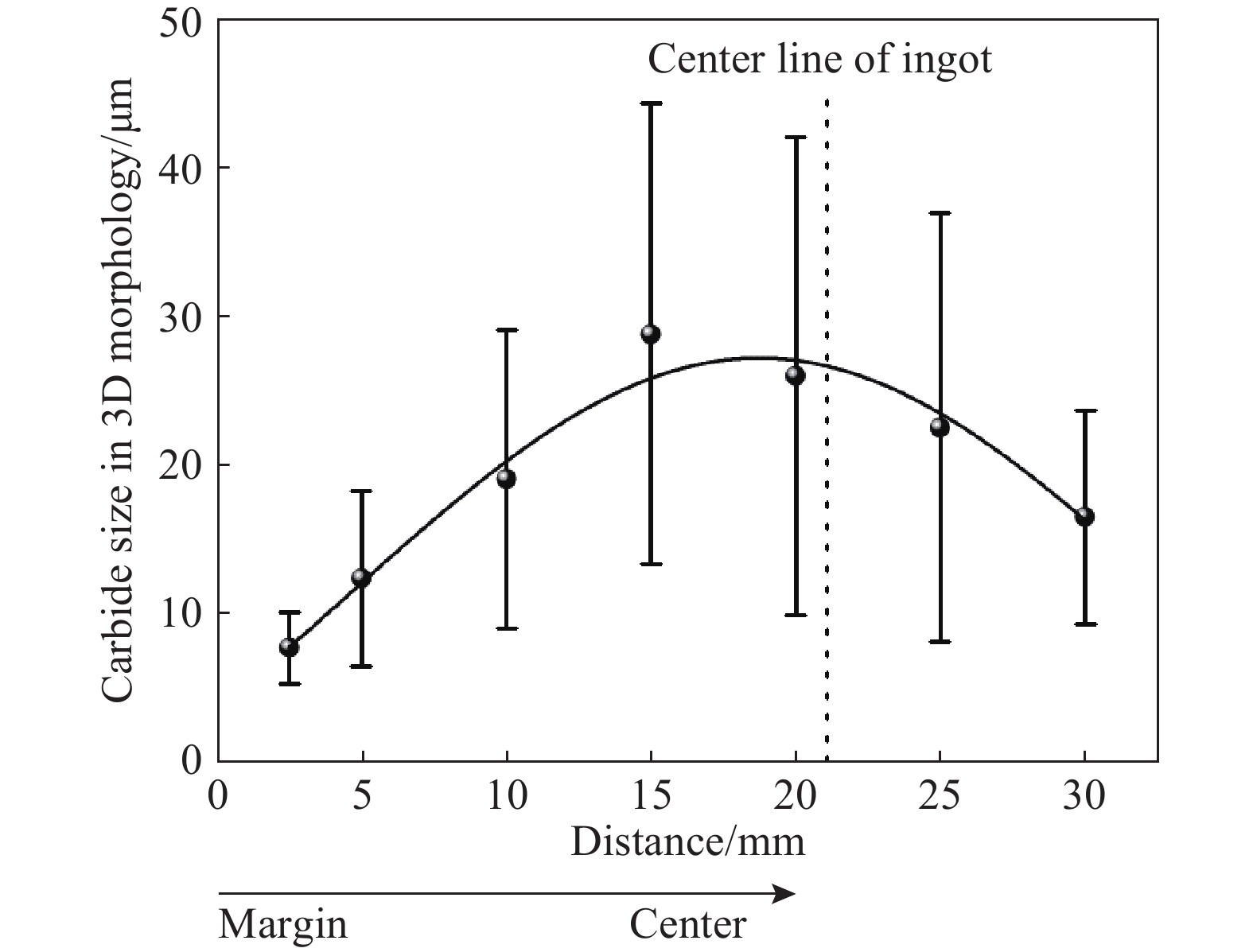
表 1 Mg元素的質量分數對一次碳化物特征的影響[32]
Table 1. Effect of Mg content on the characteristics of the primary carbide
Mg content/10?6 Number Area/μm2 Maximal size/μm 3 89 1986.48 10.05 14 72 1474.73 9.27 18 56 887.42 8.56 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Starling C M D, Branco J R T. Thermal fatigue of hot work tool steel with hard coatings. Thin Solid Films, 1997, 308-309: 436 doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(97)00600-7 [2] Li G B, Ling C, Li X Z. Study on thermal fatigue of 4Cr5MoSiV1 and 3Cr2W8V steels. Iron Steel, 1997, 32(4): 51李國彬, 凌超, 李香芝. 4Cr5MoSiV1鋼和3Cr2W8V鋼熱疲勞壽命的研究. 鋼鐵, 1997, 32(4):51 [3] Yoshida J, Katsumata M, Yamazaki Y. Effect of primary carbide on fatigue life in die steel for cold working. Tetsu-To-Hagane, 1998, 84(1): 79 doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.84.1_79吉田潤二, 勝亦正昭, 山崎善夫. 冷間金型用鋼の疲労壽命に及ぼす-次炭化物の影響. 鉄と鋼, 1998, 84(1):79 doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.84.1_79 [4] Ozaki K. Effect of the distribution of primary carbide on fatigue strength of cold work die steels. Denki-Seiko, 2005, 76(4): 249 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.76.249尾崎公造. 冷間金型用鋼の疲労壽命に及ぼす-次炭化物分布の影響. 電気製鋼, 2005, 76(4):249 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.76.249 [5] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Chen L, et al. Mechanism of generation of large (Ti, Nb, V)(C, N)-type precipitates in H13+Nb tool steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2016, 23(11): 1264 doi: 10.1007/s12613-016-1348-3 [6] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Chen L, et al. The degeneration of the heterogeneous nucleation for the large precipitates (Ti, Nb, V)(C, N) in ESR H13+Nb tool steel with low-MgO slag. Metall Res Technol, 2016, 113(2): 206 doi: 10.1051/metal/2016002 [7] Liu J H, Yang Y, Zhuang C L, et al. Inclusion distribution in H13 ingots. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2011, 33(Suppl1): 179劉建華, 陽燕, 莊昌凌, 等. H13模鑄鋼錠中夾雜物的分布解剖. 北京科技大學學報, 2011, 33(增刊1): 179 [8] Li J, Li J, Wang L L, et al. Study on carbide in forged and annealed H13 hot work die steel. High Temp Mater Processes, 2015, 34(6): 593 [9] Qi Y F, Li J, Shi C B, et al. Effect of directional solidification of electroslag remelting on the microstructure and primary carbides in an austenitic hot-work die steel. J Mater Process Technol, 2017, 249: 32 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.05.034 [10] Huang Y, Cheng G G, Li S J, et al. Precipitation behavior of large primary carbides in cast H13 steel. Steel Res Int, 2019, 90(7): 1900035 doi: 10.1002/srin.201900035 [11] Mao M T, Guo H J, Wang F, et al. Chemical composition and structural identification of primary carbides in as-cast H13 steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2019, 26(7): 839 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1796-7 [12] Mao M T, Wang F, Sun X L, et al. In situ research of partial melt in as-cast H13 steel at elevated temperature. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2020, 47(2): 159 doi: 10.1080/03019233.2018.1498760 [13] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Chen L, et al. Characteristics and generating mechanism of large precipitates in Nb–Ti–microalloyed H13 tool steel. ISIJ Int, 2016, 56(6): 995 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-569 [14] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Meng X L, et al. Precipitation behavior of primary precipitates in Ti–microalloyed H13 tool steel. ISIJ Int, 2016, 56(11): 1996 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-199 [15] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Chen L, et al. Generating mechanism of large heterogeneous carbonitrides with multiple layers in H13+Nb bar. Steel Res Int, 2017, 88(1): 1600119 doi: 10.1002/srin.201600119 [16] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Chen L, et al. The characteristics and generating mechanism of large precipitates in Ti-containing H13 tool steel. High Temp Mater Processes, 2017, 36(2): 189 doi: 10.1515/htmp-2015-0177 [17] Huang Y, Cheng G G, Li S J, et al. Distribution characteristics and thermal stability of primary carbide in cast Ce–H13 steel. ISIJ Int, 2020, 60(2): 267 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-364 [18] Pei Y K, Ma D S, Liu B S, et al. Effect of forging ratio on microstructure and mechanical property of H13 steel. Iron Steel, 2012, 47(2): 81裴悅凱, 馬黨參, 劉寶石, 等. 鍛造比對H13鋼組織和力學性能的影響. 鋼鐵, 2012, 47(2):81 [19] Xie Y, Cheng G G, Meng X L, et al. Thermal stability of primary elongated V-rich carbonitrides in H13 tool steel. Metall Res Technol, 2017, 114(2): 206 doi: 10.1051/metal/2016072 [20] Mesquita R A, Barbosa C A, Morales E V, et al. Effect of silicon on carbide precipitation after tempering of H11 hot work steels. Metall Mater Trans A, 2011, 42(2): 461 doi: 10.1007/s11661-010-0430-0 [21] Mesquita R A, Kestenbach H J. On the effect of silicon on toughness in recent high quality hot work steels. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(13-14): 4856 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.065 [22] Delagnes D, Lamesle P, Mathon M H, et al. Influence of silicon content on the precipitation of secondary carbides and fatigue properties of a 5% Cr tempered martensitic steel. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 394(1-2): 435 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.11.050 [23] Sudoh K I. Influence of C, Si, Mn, Cr, Mo and V on the characteristics of 5% chromium hot-work die steel. Denki-Seiko, 1989, 60(4): 367 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.60.367須藤興一. 5%Cr系熱間ダイス鋼の特性に及ぼすC, Si, Mn, Cr, Mo, Vの影響. 電気製鋼, 1989, 60(4):367 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.60.367 [24] Umino M, Sera T, Kondo K, et al. Effect of silicon content on tempered hardness, high temperature strength and toughness of hot working tool steels. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2003, 89(6): 673 doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.89.6_673海野正英, 瀬羅知暁, 近藤邦夫, 等. 熱間工具鋼の焼戻し硬さ, 高溫強度と靭性に及ぼすシリコン量の影響. 鉄と鋼, 2003, 89(6):673 doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.89.6_673 [25] Fujii T, Matsuda Y. Effect of Si content on the machinability of hot working die steels. Denki-Seiko, 2000, 71(2): 119 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.71.119藤井利光, 松田幸紀. 熱間工具鋼の被削性におよぼすSi量の影響. 電気製鋼, 2000, 71(2):119 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.71.119 [26] Fujii T, Matsuda Y. Effect of Si content and hardness on the machinability of hot working die steels. Denki-Seiko, 2003, 74(2): 83 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.74.83藤井利光, 松田幸紀. 熱間工具鋼の被削性におよぼす Si および硬さの影響. 電気製鋼, 2003, 74(2):83 doi: 10.4262/denkiseiko.74.83 [27] Mao M T, Guo H J, Wang F, et al. Effect of cooling rate on the solidification microstructure and characteristics of primary carbides in H13 steel. ISIJ Int, 2019, 59(5): 848 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-524 [28] History of carbide at grain boundary and its influence on impact property of SKD61. Denki-Seiko, 2018, 89(2): 101河野正道. 粒界での炭化物の歴史とそのSKD61の衝撃特性への影響. 電気製鋼, 2018, 89(2): 101 [29] Wu Z, Li J, Shi C B, et al. Effect of magnesium addition on inclusions in H13 die steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2014, 21(11): 1062 doi: 10.1007/s12613-014-1010-x [30] Li J, Li J, Shi C B, et al. Effect of trace magnesium on carbide improvement in H13 steel. Can Metall Q, 2016, 55(3): 321 doi: 10.1179/1879139515Y.0000000030 [31] Takata R, Yang J, Kuwabara M. Characteristics of inclusions generated during Al–Mg complex deoxidation of molten steel. ISIJ Int, 2007, 47(10): 1379 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.47.1379 [32] He B, Li J, Shi C B, et al. Effect of Mg addition on carbides in H13 steel during electroslag remelting process. Metall Res Technol, 2018, 115(5): 501 doi: 10.1051/metal/2018071 [33] Wang L M, Lin Q, Ji J W, et al. New study concerning development of application of rare earth metals in steels. J Alloys Compd, 2006, 408-412: 384 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.04.090 [34] Song C B, Seo I K, Park H G. Effect of rare earth metals addition on the solidification characteristics of 5Cr hot working tool steel. J Korean Inst Met Mater, 1996, 34(8): 1021宋致褔, 徐仁敎, 林炫均. 5Cr? ?????? ????? ??? ????? ?????. ?? ?? ?? ???, 1996, 34(8):1021 [35] Song C B, So J W, Park H G. Effect of rare earth metals addition on the impact toughness and machinability of 5Cr hot working tool steel. J Korean Inst Met Mater, 1995, 33(8): 1010宋致褔, 蘇鎭王, 林炫均. 5Cr? ?????? ???? ??? ??? ????? ??? ??. ?? ?? ?? ???, 1995, 33(8):1010 [36] Lan J, He J J, Ding W J, et al. Effect of rare earth metals on the microstructure and impact toughness of a cast 0.4C–5Cr–1.2Mo–1.0V steel. ISIJ Int, 2000, 40(12): 1275 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.1275 [37] Huang Y, Cheng G G, Li S J, et al. Effect of cerium on the behavior of inclusions in H13 steel. Steel Res Int, 2018, 89(12): 1800371 doi: 10.1002/srin.201800371 [38] Fu H G, Xiao Q, Li Y X. A study of the microstructures and properties of Fe–V–W–Mo alloy modified by rare earth. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 395(1-2): 281 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.12.029 [39] Yang J, Zou D N, Li X M, et al. Effect of rare earth on microstructures and properties of high speed steel with high carbon content. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2007, 14(1): 47 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(07)60011-9 [40] Liu Q X, Lu D P, Lu L, et al. Effect of mischmetal on as-cast microstructure and mechanical properties of M2 high speed steel. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2015, 22(3): 245 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15)60037-1 [41] Wang M J, Li Y M, Wang Z X, et al. Effect of rare earth elements on the thermal cracking resistance of high speed steel rolls. J Rare Earths, 2011, 29(5): 489 doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60485-1 [42] Xu Z M. Influence of Ce and Al on nodularization of eutectic in austenite–bainite steel. Mater Res Bull, 2000, 35(8): 1261 doi: 10.1016/S0025-5408(00)00319-6 [43] Gao J Z, Fu P X, Liu H W, et al. Effects of rare earth on the microstructure and impact toughness of H13 steel. Metals, 2015, 5(1): 383 doi: 10.3390/met5010383 [44] Zeli? K, Burja J, McGuiness P J, et al. Effect of rare earth elements on the morphology of eutectic carbides in AISI D2 tool steels: experimental and modelling approaches. Sci Rep, 2018, 8: 9233 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27658-w -




 下載:
下載: