Electrical and magnetic properties of (In, Co) co-doped ZnO films deposited using radio frequency magnetron sputtering
-
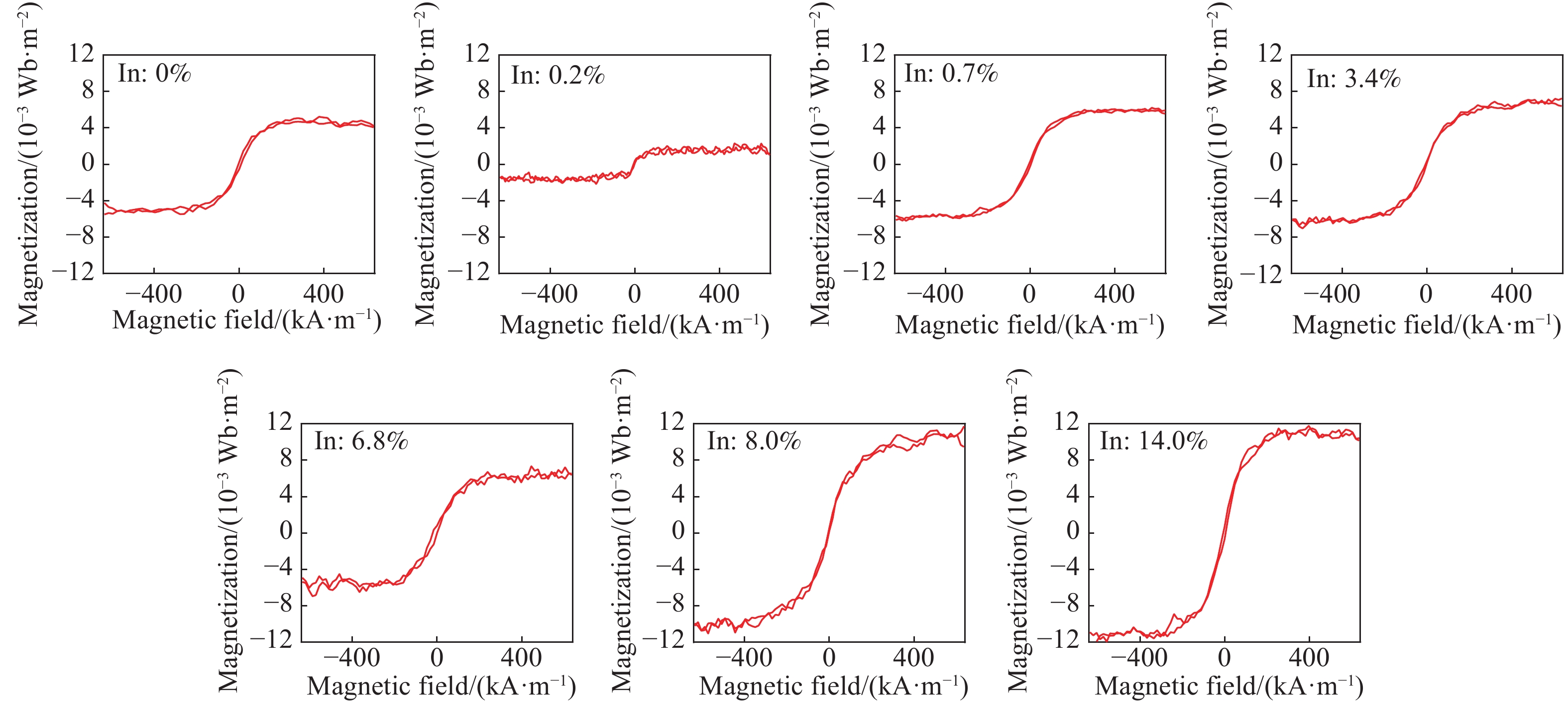
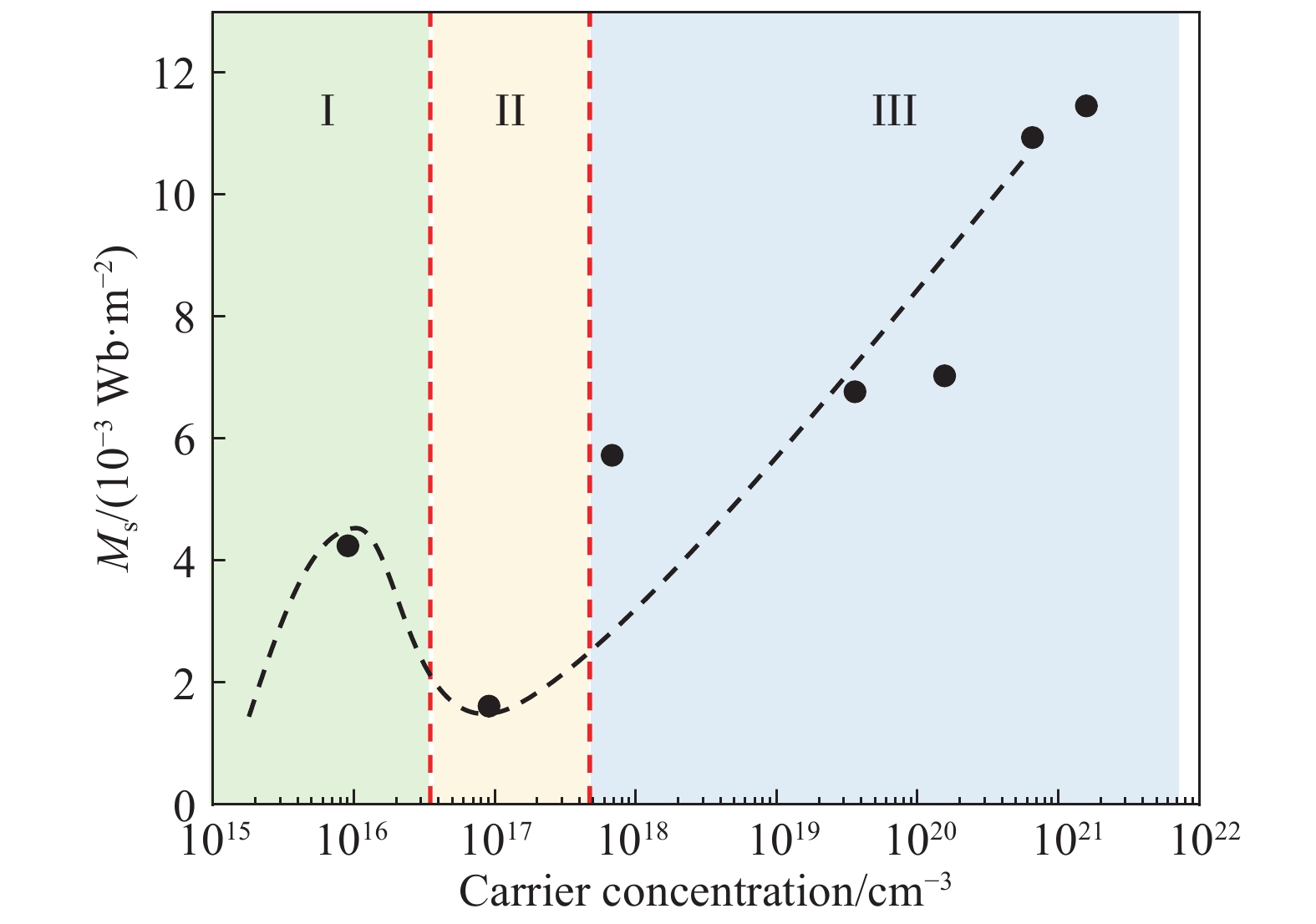
摘要: (In, Co)共摻的ZnO薄膜(ICZO薄膜)在100 ℃下通過射頻(RF)濺射沉積至玻璃基板上。沉積過程采用In、Co、Zn三靶共濺射。通過調節靶功率,獲得了不同In含量的ICZO薄膜。研究了不同In含量下薄膜電學性質和磁學性質的變化。分別使用掃描電子顯微鏡(SEM)、高分辨透射電子顯微鏡(HR-TEM)、原子力顯微鏡(AFM)、電子探針掃描(EPMA)、X射線衍射儀(XRD)、霍爾測試(Hall measurement)和振動樣品磁強計(VSM)對薄膜的成分、形貌、結構、電學特性和磁學特性進行了表征和分析。詳細分析了薄膜中載流子濃度對磁學性質的影響。實驗結果表明,隨著薄膜中In含量的提高,薄膜中載流子濃度顯著提高,薄膜的導電性得到優化。所有的薄膜均表現出室溫下的鐵磁特性。與此同時,束縛磁極化子(BMP)模型與交換耦合效應兩種不同的機制作用于ICZO半導體材料,致使薄膜的飽和磁化強度隨載流子濃度發生改變,并呈現在三個不同的區域。Abstract: Diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMSs) have attracted much attention in recent years due to their dual control of charge and spin degrees of freedom in carriers. Potential applications of DMSs include spin light-emitting diodes, spin field-effect transistors, magnetoresistance random access memory, and ultrafast optical switches. However, the Curie temperature (Tc) of most DMSs below ambient temperature limits the efficiency of these devices. Thus, the biggest challenge for developing DMS materials has been producing host materials that exhibit ferromagnetic behavior above ambient temperature. A series of theoretical simulations and experiments show that the Tc value of ZnO-based DMSs could satisfy this requirement. Incorporation of selective transition metal elements (e.g., Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Mn2+) has been confirmed as an effective way to enhance the magnetic properties of ZnO. In the present research, (In, Co) co-doped ZnO (ICZO) films were deposited by radio frequency sputtering at 100 ℃ on a glass substrate. The sputtering process was performed through In, Co, and ZnO co-sputtering. The presence of ICZO films has been adjusted by changing the target sputtering power. The variation of electric and magnetic properties of the film was studied with different In content. The composition, morphology, structure, electric and magnetic properties of films were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, electron probe microanalyzer, X-ray diffractometer, Hall effect analysis, and vibrating sample magnetometer. The effect of carrier concentration on the magnetic properties of the film was analyzed extensively. These results show that, in the presence of In, the carrier concentration increases, thereby optimizing films’ conductivity. All the films present ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature. Besides, with an influence of bound magnetic polaron model and carrier-mediated exchange mechanisms on the film’s saturation magnetization, carrier-concentration dependent behavior can be expressed in three different regions.
-
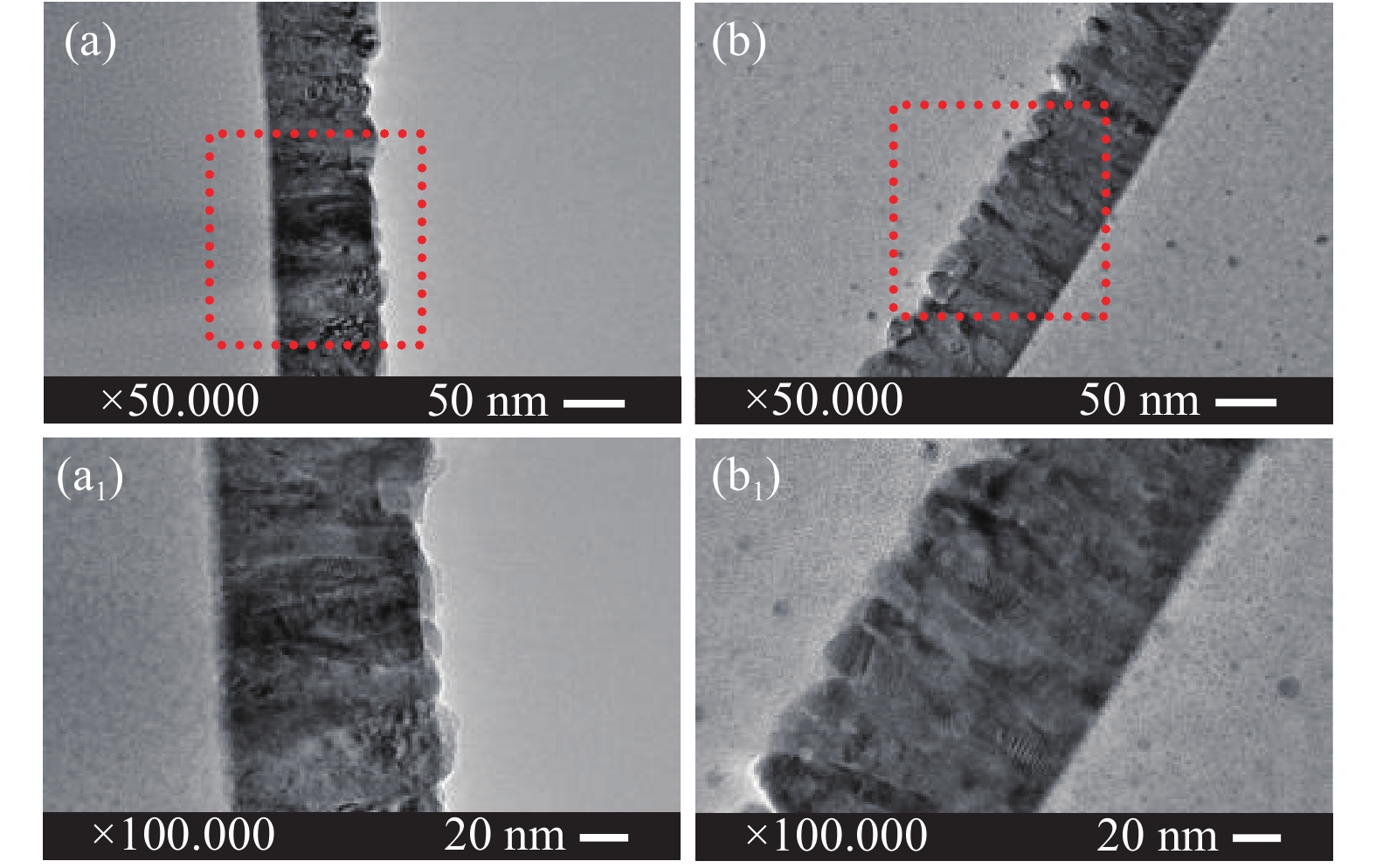
圖 4 薄膜的橫截面透射電鏡圖像。(a)純ZnO;(b)(In, Co)?ZnO(In原子數分數3.4%);(a1)圖(a)紅色區域放大圖;(b1)圖(b)紅色區域放大圖
Figure 4. Cross-sectional TEM images: (a) pure ZnO; (b) (In Co)?ZnO (atomic ratio of In is 3.4%); (a1) the magnified images from the portions marked with red dotted squares of Fig.4(a); (b1) the magnified images from the portions marked with red dotted squares of Fig.4(b)
表 1 Co?ZnO和(In, Co)?ZnO薄膜的沉積參數
Table 1. Sputtering parameters maintained during the deposition of Co-ZnO and (In, Co)-ZnO thin films
Background
pressure/PaWorking
pressure/PaWorking
gasHot
substrate/KFilm
thickness/nmSubstrate Draw
distance/cmSputtering
power/WZnO Co In2O3 < 6.7 × 10?4 1.67 Ar 373 100 Glass 10 80 15→10 0→25 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Wolf S A, Awschalom D D, Buhrman R A, et al. Spintronic: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science, 2001, 294(5546): 1488 doi: 10.1126/science.1065389 [2] Jindal S, Sharma P. Optical and magnetic properties of Dy3+ doped CdS dilute magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2020, 108: 104884 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104884 [3] Li Y, Li J M, Yu Z R, et al. Study on the high magnetic field processed ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductors. Ceram Int, 2019, 45(16): 19583 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.011 [4] Ohno H. Marking nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science, 1998, 281(5379): 951 doi: 10.1126/science.281.5379.951 [5] Jeon H C, Li M K, Lee S J, et al. The distinct behavior of specific heat of diluted magnetic semiconductor (Ga, Mn)As quantum wells. Curr Appl Phys, 2015, 15(Suppl 2): S26 [6] Li H B, Qiao Y F, Li J, et al. A sensitive and label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor using Co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron, 2016, 77: 378 doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.066 [7] Chen W B, Liu X C, Zhuo S Y, et al. Influence of proton irradiation on defect and magnetism of Yb-doped ZnO dluted magnetic semiconductor thin films. J Inorg Mater, 2018, 33(8): 903 doi: 10.15541/jim20170420陳衛賓, 劉學超, 卓世異, 等. 質子輻照對Yb摻雜ZnO稀磁半導體薄膜缺陷與磁性的影響. 無機材料學報, 2018, 33(8):903 doi: 10.15541/jim20170420 [8] Al-Zahrani J H, El-Hagary M, El-Taher A. Gamma irradiation induced effects on optical properties and single oscillator parameters of Fe-doped CdS diluted magnetic semiconductors thin films. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2015, 39: 74 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2015.04.042 [9] Zutic I, Fabian J, Das Sarma S. Spintronics: fundamentals and applications. Rev Mod Phys, 2004, 76: 323 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.76.323 [10] Robkhob P, Tang I M, Thongmee S. Magnetic properties of the dilute magnetic semiconductor Zn1?xCoxO nanoparticles. J Supercond Novel Magn, 2019, 32: 3637 doi: 10.1007/s10948-019-5135-z [11] Obeid M M, Jappor H R, Al-Marzoki K, et al. Unraveling the effect of Gd doping on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductor nanorods. RSC Adv, 2019, 9(57): 33207 doi: 10.1039/C9RA04750F [12] Zhong M, Wang S W, Li Y, et al. Room temperature ferromagnetic Cr-Ni codoped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors synthesized by hydrothermal method under high pulsed magnetic field. Ceram Int, 2015, 41(1): 451 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.08.091 [13] Wang X T, Zhu L P, Ye Z G, et al. Influence of N dopant on the electric and magnetic properties of Co doped ZnO thin films. J Inorg Mater, 2010, 25(7): 711 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2010.00711王雪濤, 朱麗萍, 葉志高, 等. N摻雜對Co?ZnO薄膜電學和磁學性能的影響. 無機材料學報, 2010, 25(7):711 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2010.00711 [14] Liu Z H, Wang X L, Ji J Z, et al. Influence of photoelectric parameters for AZO transparent conductive films on electromagnetic scattering characteristics. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(10): 1259劉戰合, 王曉璐, 姬金祖, 等. AZO透明導電膜電磁散射光電參數影響試驗. 工程科學學報, 2018, 40(10):1259 [15] Zang Z G. Efficiency enhancement of ZnO/Cu2O solar cells with well oriented and micrometer grain sized Cu2O films. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112(4): 042106 doi: 10.1063/1.5017002 [16] Li C L, Zang Z G, Han C, et al. Highly compact CsPbBr3 perovskite thin films decorated by ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced random lasing. Nano Energy, 2017, 40: 195 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.08.013 [17] Sluiter M H F, Kawazoe Y, Sharma P, et al. First principles based design and experimental evidence for a ZnO-based ferromagnet at room temperature. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94(18): 187204 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.187204 [18] Zong Y, Sun Y, Meng S Y, et al. Doping effect and oxygen defects boost room temperature ferromagnetism of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: experimental and theoretical studies. RSC Adv, 2019, 9(40): 23012 doi: 10.1039/C9RA03620B [19] Dinia A, Schmerber G, Meny C, et al. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1?xCoxO magnetic semiconductors prepared by sputtering. J Appl Phys, 2005, 97(12): 123908 doi: 10.1063/1.1937478 [20] Shatnawi M, Alsmadi A M, Bsoul I, et al. Magnetic and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline particles. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 655: 244 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.166 [21] Siddheswaran R, Mangalaraja R V, Gomez M E, et al. Room temperature ferromagnetism in combustion synthesized nanocrystalline Co, Al co-doped ZnO. J Alloys Compd, 2013, 581: 146 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.06.117 [22] Kumar S, Tripathi D M, Vaibhav P, et al. Effect of Al and Fe doping in ZnO on magnetic and magneto-transport properties. J Magn Magn Mater, 2016, 419: 68 doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.06.007 [23] Paul S, Dalal B, Das M, et al. Enhanced magnetic properties of In-Mn-codoped plasmonic ZnO nanoflowers: evidence of delocalized charge carrier-mediated ferromagnetic coupling. Chem Mater, 2019, 31(19): 8191 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b03059 [24] Wang X T, Zhu L P, Zhang L Q, et al. Properties of Ni doped and Ni-Ga co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509(7): 3282 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.049 [25] Liu Q Y, Yang P. First-principles study on ZnO-based diluted magnetic semiconductors in different doping configurations. Electron Sci Technol, 2018, 31(2): 44劉喬亞, 楊平. 不同構型下ZnO基稀磁半導體的第一性原理研究. 電子科技, 2018, 31(2):44 [26] Luthra A V. Tweaking electrical and magnetic properties of Al-Ni co-doped ZnO nanopowders. Ceram Int, 2014, 40(9): 14927 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.06.089 [27] Henni A, Merrouche A, Telli L, et al. Studies on the structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO nanorods prepared by electrochemical deposition. J Electroanal Chem, 2016, 763: 149 doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.12.037 [28] Yoo R, Cho S, Song M J, et al. Highly sensitive gas sensor based on Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles for detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate as a chemical warfare agent simulant. Sens Actuators B, 2015, 221: 217 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.076 [29] Sun H, Chen S C, Wang C H, et al. Electrical and magnetic properties of (Al, Co) co-doped ZnO films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Surf Coat Technol, 2019, 359: 390 doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.10.105 [30] Shannon R D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst, 1976, 32: 751 doi: 10.1107/S0567739476001551 [31] Lu Z L, Hsu H S, Tzeng Y H, et al. Tunable magnetic and transport properties of single crystalline (Co, Ga)-codoped ZnO films. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95(6): 062509 doi: 10.1063/1.3204016 [32] Chen S C, Wang C H, Sun H, et al. Microstructure, electrical and magnetic properties of (Ga, Co)?ZnO films by radio frequency magnetron co-sputtering. Surf Coat Technol, 2016, 303: 203 doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.03.064 [33] Coey J M D, Venkatesan M, Fitzgerald C B. Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat Mater, 2005, 4: 173 doi: 10.1038/nmat1310 [34] Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F, et at. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science, 2000, 287(5455): 1019 doi: 10.1126/science.287.5455.1019 [35] Griffin K A, Pakhomov A B, Wang C M, et al. Intrinsic ferromagnetism in insulating cobalt doped anatase TiO2. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94(15): 157204 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.157204 [36] Behan A J, Mokhtari A, Blythe H J, et al. Two magnetic regimes in doped ZnO corresponding to a dilute magnetic semiconductor and a dilute magnetic insulator. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 100(4): 047206 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.047206 -




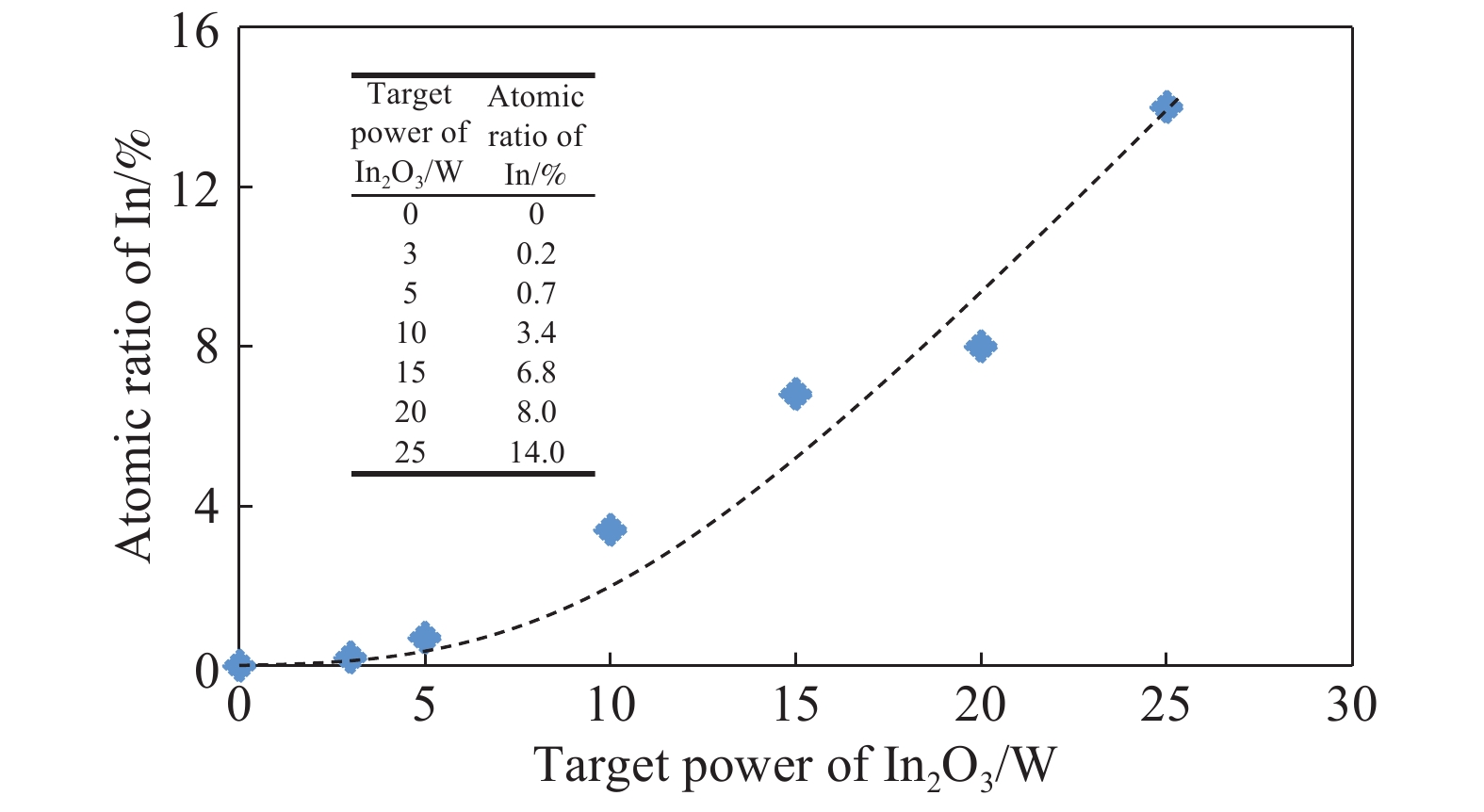
 下載:
下載: