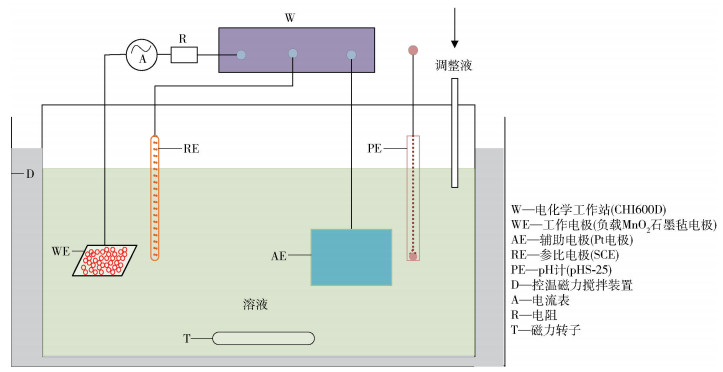
-
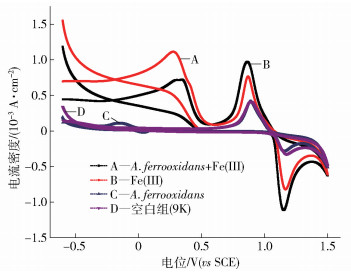
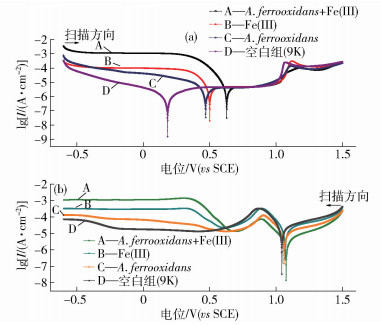
摘要: 利用循環伏安、交流阻抗譜和極化曲線研究了Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans對軟錳礦在模擬浸出溶液(9K基礎培養基, A.ferrooxidans, Fe (Ⅲ), A.ferrooxidans+Fe (Ⅲ))中電化學腐蝕行為的影響; 利用模擬有菌/無菌浸出溶液中鈍化膜的Mott-Schottky理論比較了有無細菌存在情況下形成的鈍化膜的優劣性.結果表明, A.ferrooxidans促進MnO2/Mn2+氧化還原轉化, 催化MnO2/Mn (OH)2電極反應; 加速軟錳礦/溶液界面電子交換, 無鐵存在時A.ferrooxidans使電荷轉移內阻降低34%, 比含Fe (Ⅲ)無菌體系低11%;引起軟錳礦電極極化, 增強其氧化活性; 加速MnO2向MnO·OH轉化及其產物擴散.A.ferrooxidans與軟錳礦作用更傾向于間接作用機理.在選取的各模擬電解液(pH值為2.0)中, 0.2~0.4 V區間內軟錳礦形成耗盡層, 在模擬浸出溶液中形成的鈍化膜都表現出p-n-p-n型半導體性能.在選取的0.2 V極化電位下, 無鐵時引入A.ferrooxidans使膜中的施主/受主密度減少, 細菌含有多種基團參與半導體/溶液界面電子轉移反應, 接受界面間自由電子或填充空穴, 促使軟錳礦與溶液界面物質交換變頻繁; 含鐵溶液中加入A.ferrooxidans使得鈍化膜受主/施主密度增大, A.ferrooxidans降低了膜的耐腐蝕性, 因而促進軟錳礦浸出.Abstract: Biohydrometallurgy is an increasingly popular ore extraction technology and is especially applicable for low-grade ores. In particular, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (A. ferrooxidans) is by far the most widely used bioleaching microorganism for leaching ores, including for sulfide ores and manganese dioxide ores. At present, many works are focused on the vital facilitating role of A. ferrooxidans in the cycles of sulfur and iron for sulfide ores bioleaching. However, research on the effect of A. ferrooxidans on manganese dioxide ores leaching is limited. The effects of A. ferrooxidans on the electrochemistry behavior of pyrolusite in simulated solutions (9K basic medium, A. ferrooxidans, Fe(Ⅲ), A. ferrooxidans+Fe(Ⅲ)) were investigated using cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and potentiodynamic polarization. Mott-Schottky curves were utilized to determine the passive film formed on the surface of pyrolusite ore in the presence or absence of bacteria bath solutions. The results show that A. ferrooxidans promotes the redox of MnO2/Mn2+ and triggers the reaction of MnO2/Mn(OH)2. A. ferrooxidans accelerates electron exchange between pyrolusite and solution; in the A. ferrooxidans-simulated solution, the charge-transfer reaction resistance of manganese dioxide is 34% lower than that of the control (9K) and 11% lower than that of the Fe(Ⅲ) solution. Germs cause polarization of pyrolusite, leading to an increase in oxidative activity of manganese dioxide. Bacteria facilitate the transformation of MnO2 to MnO·OH and is beneficial to its diffusion. The indirect action mechanism is adopted to explain the interaction between A. ferrooxidans and pyrolusite. The passive films formed in simulated solutions exhibit p-n-p-n type semiconductor properties at the polarization potential of 0.2 V when pH is 2.0, and the depletion layer of pyrolusite appears between 0.2 and 0.4 V. Introducing A.ferrooxidans to the Fe(Ⅲ)-free solution decreases the donor density and the acceptor density because bacteria contain a variety of groups involved in electron transfer, which accept free electrons or fill holes, prompting the exchange of species between manganese oxide and solution. Admixing A. ferrooxidans to Fe(Ⅲ)-containing solution increases carrier density, reducing the corrosion resistance of membrane. The corrosion rate of pyrolusite increases with the addition of A. ferrooxidans.
-
Key words:
- pyrolusite /
- Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans /
- electrochemical corrosion /
- charge transfer /
- semiconductor /
-
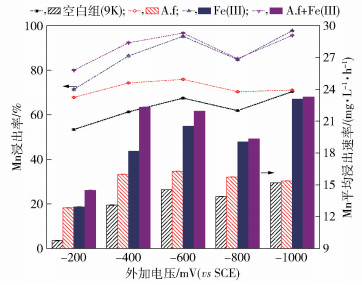
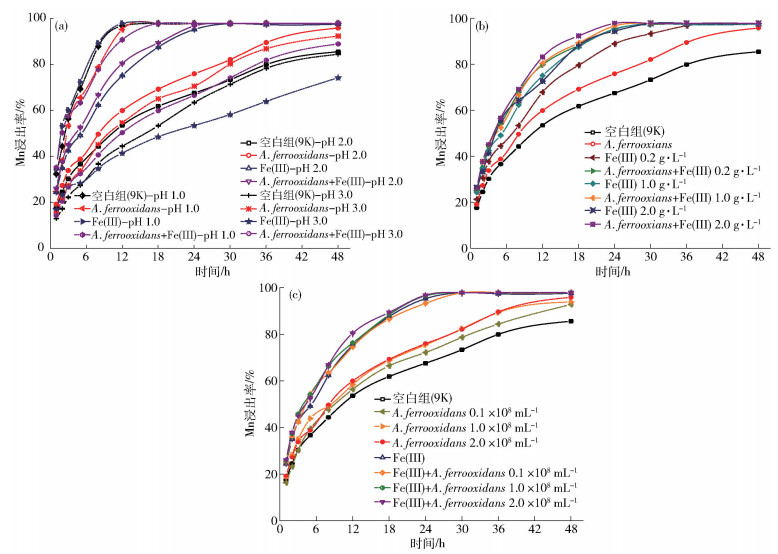
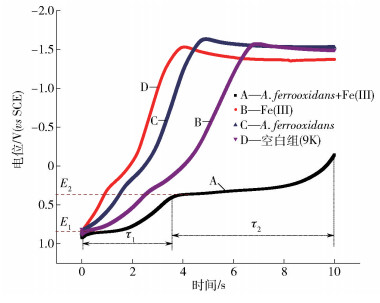
圖 4 不同因素對軟錳礦浸出的影響(25 ℃, 輸入電壓為-400 mV). (a) pH (A. ferrooxidnas數量1.0×108 mL-1,Fe(Ⅲ)質量濃度1.0 g·L-1); (b) Fe(Ⅲ)質量濃度(pH 2.0,A. ferrooxidnas數量1.0×108 mL-1); (c) A. ferrooxidnas數量(pH 2.0,Fe(Ⅲ)質量濃度1.0 g·L-1)
Figure 4. Effects of different factors on dissolution of pyrolusite (25 ℃, input voltage -400 mV(vs SCE)): (a) pH(A. ferrooxidnas concentration 1.0×108 mL-1, Fe(Ⅲ) concentration 1.0 g·L-1); (b) Fe(Ⅲ) concentration (pH 2.0, A. ferrooxidnas concentration 1.0×108 mL-1); (c) A. ferrooxidnas concentration (pH 2.0, Fe(Ⅲ) concentration 1.0 g·L-1)
表 1 軟錳礦的主要化學成分(質量分數)
Table 1. Chemical compositions of pyrolusite ?
% Mn Fe SiO2 CaO Zn Pb Ba Na2O K2O Al2O3 S TiO2 59.46 0.11 3.51 0.11 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.11 表 2 阻抗譜測試后等效電路中各元器件擬合參數
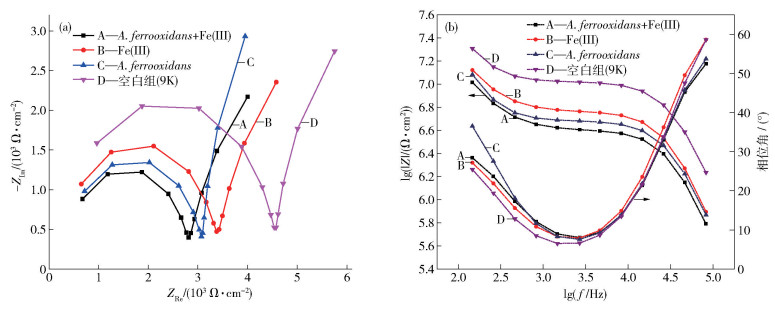
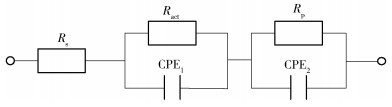
Table 2. Fitted values of the parameters used in Fig. 8
電解液 Rs/(Ω·cm2) CPE1的Y0/(10-6 Ω-1·cm-2·sη1) CPE1的η1 Ract/(Ω·cm2) CPE2的Y0 /(10-6 Ω-1·cm-2·sη2) CPE2的η2 Rp/(Ω·cm2) A.ferrooxians+Fe(Ⅲ) 311.7 1.94 0.998 2479 793.3 0.895 718 Fe(Ⅲ) 216.7 1.78 0.990 3154 678.7 0.911 785.3 A. ferrooxidans 285.2 2.14 0.981 2806 368.6 0.989 1137 空白組(9K) 195.8 1.39 0.974 4274 360.1 0.989 772.4 表 3 不同體系中軟錳礦鈍化膜的載流子濃度及平帶電位
Table 3. Carrier densities and flatband potential of the passive films on pyrolusite in various solutions
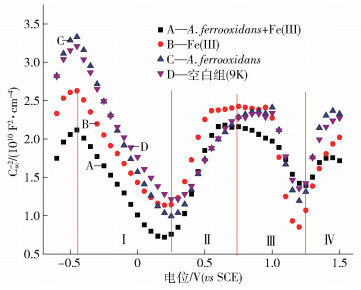
區域 A.ferrooxidans+Fe(Ⅲ) Fe(Ⅲ) A.ferrooxidans 空白組(9K) Nd/(1017 cm3) Efb/V Na/(1017 cm3) Efb/V Nd/(1017 cm3) Efb/V Na/(1017 cm3) Efb/V Ⅰ 1.15 -0.22 1.09 -0.05 0.74 1.49 0.90 -0.49 Ⅱ 0.54 -0.36 0.59 0.16 0.76 1.05 0.91 -0.85 Ⅲ 0.97 -0.21 0.31 0.16 0.38 1.13 0.48 -0.83 Ⅳ 1.11 -0.36 0.56 0.25 0.42 1.20 0.58 -0.76 259luxu-164<th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <th id="5nh9l"></th> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><span id="5nh9l"></span> <strike id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><strike id="5nh9l"></strike> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> <span id="5nh9l"></span> <span id="5nh9l"><video id="5nh9l"></video></span> <th id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"><th id="5nh9l"></th> <progress id="5nh9l"><noframes id="5nh9l"> -
參考文獻
[1] Li C Q, Tian Z P, Cao J, et al. An application of manganese ore in non-metallurgy. China's Manganese Ind, 2016, 34(6): 91 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201606030.htm李超群, 田宗平, 曹健, 等. 錳礦石在非冶金工業領域中的應用. 中國錳業, 2016, 34(6): 91 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201606030.htm [2] Fu Y, Xu Z G, Pei H X, et al. Study on metallogenic regularity of manganese ore deposits in China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(12): 2192 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412004.htm付勇, 徐志剛, 裴浩翔, 等. 中國錳礦成礦規律初探. 地質學報, 2014, 88(12): 2192 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412004.htm [3] He F, Chen H F, Chen G, et al. A new technology of low grade pyrolusite ore in reduction process. China's Manganese Ind, 2017, 35(6): 94 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201706026.htm和飛, 陳滬飛, 陳菓, 等. 低品位軟錳礦還原新技術和研究進展. 中國錳業, 2017, 35(6): 94 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201706026.htm [4] Li Z G, Chen W L, Zhang J J, et al. Reductive leaching technology of pyrolusite optimized by response surface methodology. Chem Eng China, 2018, 46(2): 72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2018.02.015李照剛, 陳為亮, 張建軍, 等. 響應曲面法優化軟錳礦還原浸出的工藝. 化學工程, 2018, 46(2): 72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2018.02.015 [5] Hu K J. Study on Breeding of Alkalophilic Bacteria for Bioleaching of Complex Oxidized Copper Ore and Leaching Mechanism[Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017胡凱建. 復雜氧化銅礦堿性浸礦菌種的選育及浸出規律研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2017 [6] Huang M Q. Rules of Air Flow and Enhanced Leaching Mechanism by Forced Aeration in Heap Bioleaching of Copper Sulfides [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015黃明清. 硫化銅礦生物堆浸氣體滲流規律及通風強化浸出機制[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2015 [7] Qi F J, Feng Y L, Li H R, et al. Leaching characteristics and recovery method of nickel from low-grade nickel pyrrhotite. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2011, 33(9): 1065 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201109005.htm齊鳳杰, 馮雅麗, 李浩然, 等. 低品位鎳磁黃鐵礦鎳浸出特性及回收方法. 北京科技大學學報, 2011, 33(9): 1065 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201109005.htm [8] Peng Z J, Yu R L, Qiu G Z, et al. Really active form of fluorine toxicity affecting Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans activity in bioleaching uranium. Trans Nonf errous Met Soc China, 2013, 23(3): 812 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62533-9 [9] Choi N C, Cho K H, Kim B J, et al. Enhancement of Au--Ag--Te contents in tellurium-bearing ore minerals via bioleaching. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2018, 25(3): 262 doi: 10.1007/s12613-018-1569-8 [10] Nú?ez-Ramírez D M, Solís-Soto A, López-Miranda J, et al. Zinc bioleaching from an iron concentrate using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain from Hercules Mine of Coahuila, Mexico. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2011, 18(5): 523 doi: 10.1007/s12613-011-0472-3 [11] Cheng F F, Guan J F, Zhang F, et al. A research status of manganese ore chemical processing. China's Manganese Ind, 2015, 33(4): 4 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201504037.htm程飛飛, 管俊芳, 張帆, 等. 錳礦化學選礦的研究現狀. 中國錳業, 2015, 33(4): 4 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201504037.htm [12] Zhong H F, Cai W L, Li Y Q. Bacterial leaching of manganese ores and semi-industrial scale practice. Acta Microbiol Sinica, 1990, 30(3): 228 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB199003010.htm鐘慧芳, 蔡文六, 李雅芹. 細菌浸錳及其半工業性試驗. 微生物學報, 1990, 30(3): 228 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB199003010.htm [13] Guo Y, Zhang D Q, Cao L H, et al. Pyrolusite leaching with different stage of leachate from bio-leaching of different grade pyrites. Min Metall Eng, 2016, 36(5): 76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2016.05.020郭盈, 張德強, 曹麗華, 等. 不同品質黃鐵礦-生物浸出液制劑浸出軟錳礦研究. 礦冶工程, 2016, 36(5): 76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2016.05.020 [14] Liu X R, Jiang S C, Liu Y J, et al. Biodesulfurization of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite concentrates and pH control of bioleaching solution. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2013, 20(10): 925 doi: 10.1007/s12613-013-0816-2 [15] Fu K B, Lin H, Mo X L, et al. Study on bioleaching of different types of chalcopyrite. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2011, 33(7): 806 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201107006.htm傅開彬, 林海, 莫曉蘭, 等. 不同類型黃銅礦的生物浸出研究. 北京科技大學學報, 2011, 33(7): 806 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201107006.htm [16] Qu B, Deng L, Deng B, et al. Oxidation kinetics of dithionate compound in the leaching process of manganese dioxide with manganese dithionate. React Kinet Mech Catal, 2018, 123(2): 743 doi: 10.1007/s11144-017-1284-x [17] Nazari B, Jorjani E, Hani H, et al. Formation of jarosite and its effect on important ions for Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans bacteria. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2014, 24(4): 1152 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63174-5 [18] Chabre Y, Pannetier J. Structural and electrochemical properties of the proton/γ-MnO2 system. Prog Solid State Chem, 1995, 23(1): 1 doi: 10.1016/0079-6786(94)00005-2 [19] Senanayake G. Acid leaching of metals from deep-sea manganese nodules——a critical review of fundamentals and applications. Miner Eng, 2011, 24(13): 1379 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2011.06.003 [20] Walanda D K, Lawrance G A, Donne S W. Hydrothermal MnO2: synthesis, structure, morphology and discharge performance. J Power Sour, 2005, 139(1-2): 325 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.06.062 [21] Li C T, Cheng X Q, Dong C F, et al. Influence of Cl- on the corrosion electrochemical behavior of Alloy 690. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2011, 33(4): 444 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201104009.htm李成濤, 程學群, 董超芳, 等. Cl-對690合金腐蝕電化學行為的影響. 北京科技大學學報, 2011, 33(4): 444 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201104009.htm [22] Luo J, Wang Y, Jiang J B, et al. Electrochemistry behavior of rebars with different grain size and Mott-Schottky research of passive films. Acta Chim Sinica, 2012, 70(10): 1213 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB201210013.htm羅檢, 王毅, 蔣繼波, 等. 不同晶粒度螺紋鋼的電化學行為及其鈍化膜的Mott-Schottky研究. 化學學報, 2012, 70(10): 1213 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB201210013.htm [23] Zhang J Q. Electrochemical Measurement Technology. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2010張鑒清. 電化學測試技術. 北京: 化學工業出版社, 2010 -




 下載:
下載: